Abstract
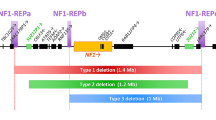
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is caused, in 4.7–11% of cases, by large deletions encompassing the NF1 gene and its flanking regions within 17q11.2. Different types of large NF1 deletion occur which are distinguishable by their breakpoint location and underlying mutational mechanism. Most common are the type-1 NF1 deletions of 1.4 Mb which exhibit recurrent breakpoints caused by nonallelic homologous recombination (NAHR), also termed unequal crossover. Here, we analyzed 37 unrelated families of patients with de novo type-1 NF1 deletions by means of short tandem repeat (STR) profiling to determine the parental origin of the deletions. We observed that 33 of the 37 type-1 deletions were of maternal origin (89.2% of cases; p < 0.0001). Analysis of the patients’ siblings indicated that, in 14 informative cases, ten (71.4%) deletions resulted from interchromosomal unequal crossover during meiosis I. Our findings indicate a strong maternal parent-of-origin bias for type-1 NF1 deletions. A similarly pronounced maternal transmission bias has been reported for recurrent copy number variants (CNVs) within 16p11.2 associated with autism, but not so far for any other NAHR-mediated pathogenic CNVs. Region-specific genomic features are likely to be responsible for the maternal bias in the origin of both the 16p11.2 CNVs and type-1 NF1 deletions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho A, Kouznetsova A, Hernández-Hernández A, Bernhem K, Blom H, Brismar H, Höög C (2018) Sexual dimorphism in the width of the mouse synaptonemal complex. J Cell Sci. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.212548
Baumer A, Dutly F, Balmer D, Riegel M, Tükel T, Krajewska-Walasek M, Schinzel AA (1998) High level of unequal meiotic crossovers at the origin of the 22q11.2 and 7q11.23 deletions. Hum Mol Genet 7:887–894
Bayés M, Magano LF, Rivera N, Flores R, Pérez Jurado LA (2003) Mutational mechanisms of Williams–Beuren syndrome deletions. Am J Hum Genet 73:131–151
Bengesser K, Cooper DN, Steinmann K, Kluwe L, Chuzhanova NA, Wimmer K, Tatagiba M, Tinschert S, Mautner VF, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2010) A novel third type of recurrent NF1 microdeletion mediated by nonallelic homologous recombination between LRRC37B-containing low-copy repeats in 17q11.2. Hum Mutat 31:742–751
Bengesser K, Vogt J, Mussotter T, Mautner VF, Messiaen L, Cooper DN, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2014) Analysis of crossover breakpoints yields new insights into the nature of the gene conversion events associated with large NF1 deletions mediated by nonallelic homologous recombination. Hum Mutat 35:215–226
Carvalho CM, Lupski JR (2016) Mechanisms underlying structural variant formation in genomic disorders. Nat Rev Genet 17:224–238
Cnossen MH, van der Est MN, Breuning MH, van Asperen CJ, Breslau-Siderius EJ, van der Ploeg AT, de Goede-Bolder A, van den Ouweland AM, Halley DJ, Niermeijer MF (1997) Deletions spanning the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: implications for genotype–phenotype correlations in neurofibromatosis type 1? Hum Mutat 9:458–464
De Raedt T, Stephens M, Heyns I, Brems H, Thijs D, Messiaen L, Stephens K, Lazaro C, Wimmer K, Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Vidaud D, Kluwe L, Marynen P, Legius E (2006) Conservation of hotspots for recombination in low-copy repeats associated with the NF1 microdeletion. Nat Genet 38:1419–1423
Delio M, Guo T, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai E, Herman S, Kaminetzky M, Higgins AM, Coleman K, Chow C, Jalbrzikowski M, Bearden CE, Bailey A, Vangkilde A, Olsen L, Olesen C, Skovby F, Werge TM, Templin L, Busa T, Philip N, Swillen A, Vermeesch JR, Devriendt K, Schneider M, Dahoun S, Eliez S, Schoch K, Hooper SR, Shashi V, Samanich J, Marion R, van Amelsvoort T, Boot E, Klaassen P, Duijff SN, Vorstman J, Yuen T, Silversides C, Chow E, Bassett A, Frisch A, Weizman A, Gothelf D, Niarchou M, van den Bree M, Owen MJ, Suñer DH, Andreo JR, Armando M, Vicari S, Digilio MC, Auton A, Kates WR, Wang T, Shprintzen RJ, Emanuel BS, Morrow BE (2013) Enhanced maternal origin of the 22q11.2 deletion in velocardiofacial and DiGeorge syndromes. Am J Hum Genet 92:439–447
Dorschner MO, Sybert VP, Weaver M, Pletcher BA, Stephens K (2000) NF1 microdeletion breakpoints are clustered at flanking repetitive sequences. Hum Mol Genet 9:35–46
Drost JB, Lee WR (1995) Biological basis of germline mutation: comparisons of spontaneous germline mutation rates among drosophila, mouse, and human. Environ Mol Mutagen 26:48–64
Dutly F, Schinzel A (1996) Unequal interchromosomal rearrangements may result in elastin gene deletions causing the Williams–Beuren syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 5:1893–1898
Dutra RL, Pieri Pde C, Teixeira AC, Honjo RS, Bertola DR, Kim CA (2011) Detection of deletions at 7q11.23 in Williams–Beuren syndrome by polymorphic markers. Clinics 66:959–964
Duyzend MH, Nuttle X, Coe BP, Baker C, Nickerson DA, Bernier R, Eichler EE (2016) Maternal modifiers and parent-of-origin bias of the autism-associated 16p11.2 CNV. Am J Hum Genet 98:45–57
El Yakoubi W, Wassmann K (2017) Meiotic divisions: no place for gender equality. Adv Exp Med Biol 1002:1–17
Forbes SH, Dorschner MO, Le R, Stephens K (2004) Genomic context of paralogous recombination hotspots mediating recurrent NF1 region microdeletion. Genes Chromosom Cancer 41:12–25
Gilbert-Dussardier B, Bonneau D, Gigarel N, Le Merrer M, Bonnet D, Philip N, Serville F, Verloes A, Rossi A, Aymé S, Weissenbach J, Mattei MG, Lyonnet S, Munnich A (1995) A novel microsatellite DNA marker at locus D7S1870 detects hemizygosity in 75% of patients with Williams syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 56:542–544
Greenberg F, Guzzetta V, Montes de Oca-Luna R, Magenis RE, Smith AC, Richter SF, Kondo I, Dobyns WB, Patel PI, Lupski JR (1991) Molecular analysis of the Smith–Magenis syndrome: a possible contiguous-gene syndrome associated with del(17)(p11.2). Am J Hum Genet 49:1207–1218
Griswold MD (2016) Spermatogenesis: the commitment to meiosis. Physiol Rev 96:1–17
Guo X, Delio M, Haque N, Castellanos R, Hestand MS, Vermeesch JR, Morrow BE, Zheng D (2016) Variant discovery and breakpoint region prediction for studying the human 22q11.2 deletion using BAC clone and whole genome sequencing analysis. Hum Mol Genet 25:3754–3767
Hehir-Kwa JY, Rodríguez-Santiago B, Vissers LE, de Leeuw N, Pfundt R, Buitelaar JK, Pérez-Jurado LA, Veltman JA (2011) De novo copy number variants associated with intellectual disability have a paternal origin and age bias. J Med Genet 48:776–778
Hillmer M, Wagner D, Summerer A, Daiber M, Mautner VF, Messiaen L, Cooper DN, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2016) Fine mapping of meiotic NAHR-associated crossovers causing large NF1 deletions. Hum Mol Genet 25:484–496
Hillmer M, Summerer A, Mautner VF, Högel J, Cooper DN, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2017) Consideration of the haplotype diversity at nonallelic homologous recombination hotspots improves the precision of rearrangement breakpoint identification. Hum Mutat 38:1711–1722
Hobart HH, Morris CA, Mervis CB, Pani AM, Kistler DJ, Rios CM, Kimberley KW, Gregg RG, Bray-Ward P (2010) Inversion of the Williams syndrome region is a common polymorphism found more frequently in parents of children with Williams syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 154C:220–228
Itsara A, Wu H, Smith JD, Nickerson DA, Romieu I, London SJ, Eichler EE (2010) De novo rates and selection of large copy number variation. Genome Res 20:1469–1481
Jenne DE, Tinschert S, Reimann H, Lasinger W, Thiel G, Hameister H, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2001) Molecular characterization and gene content of breakpoint boundaries in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 with 17q11.2 microdeletions. Am J Hum Genet 69:516–527
Juyal RC, Figuera LE, Hauge X, Elsea SH, Lupski JR, Greenberg F, Baldini A, Patel PI (1996) Molecular analyses of 17p11.2 deletions in 62 Smith–Magenis syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet 58:998–1007
Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Kluwe L, Sandig C, Kohn M, Wimmer K, Krammer U, Peyrl A, Jenne DE, Hansmann I, Mautner VF (2004) High frequency of mosaicism among patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) with microdeletions caused by somatic recombination of the JJAZ1 gene. Am J Hum Genet 75:410–423
Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Mautner VF, Cooper DN (2017) Emerging genotype–phenotype relationships in patients with large NF1 deletions. Hum Genet 136:349–376
Kluwe L, Siebert R, Gesk S, Friedrich RE, Tinschert S, Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Mautner VF (2004) Screening 500 unselected neurofibromatosis 1 patients for deletions of the NF1 gene. Hum Mutat 23:111–116
Kong A, Thorleifsson G, Gudbjartsson DF, Masson G, Sigurdsson A, Jonasdottir A, Walters GB, Jonasdottir A, Gylfason A, Kristinsson KT, Gudjonsson SA, Frigge ML, Helgason A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2010) Fine-scale recombination rate differences between sexes, populations and individuals. Nature 467:1099–1103
Kong A, Frigge ML, Masson G, Besenbacher S, Sulem P, Magnusson G, Gudjonsson SA, Sigurdsson A, Jonasdottir A, Jonasdottir A, Wong WS, Sigurdsson G, Walters GB, Steinberg S, Helgason H, Thorleifsson G, Gudbjartsson DF, Helgason A, Magnusson OT, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2012) Rate of de novo mutations and the importance of father's age to disease risk. Nature 488:471–475. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11396
Koolen DA, Sharp AJ, Hurst JA, Firth HV, Knight SJ, Goldenberg A, Saugier-Veber P, Pfundt R, Vissers LE, Destrée A, Grisart B, Rooms L, Van der Aa N, Field M, Hackett A, Bell K, Nowaczyk MJ, Mancini GM, Poddighe PJ, Schwartz CE, Rossi E, De Gregori M, Antonacci-Fulton LL, McLellan MD 2nd, Garrett JM, Wiechert MA, Miner TL, Crosby S, Ciccone R, Willatt L, Rauch A, Zenker M, Aradhya S, Manning MA, Strom TM, Wagenstaller J, Krepischi-Santos AC, Vianna-Morgante AM, Rosenberg C, Price SM, Stewart H, Shaw-Smith C, Brunner HG, Wilkie AO, Veltman JA, Zuffardi O, Eichler EE, de Vries BB (2008) Clinical and molecular delineation of the 17q21.31 microdeletion syndrome. J Med Genet 45:710–720
Kota SK, Feil R (2010) Epigenetic transitions in germ cell development and meiosis. Dev Cell 19:675–686
Lázaro C, Gaona A, Ainsworth P, Tenconi R, Vidaud D, Kruyer H, Ars E, Volpini V, Estivill X (1996) Sex differences in mutational rate and mutational mechanism in the NF1 gene in neurofibromatosis type 1 patients. Hum Genet 98:696–699
Lindsay SJ, Khajavi M, Lupski JR, Hurles ME (2006) A chromosomal rearrangement hotspot can be identified from population genetic variation and is coincident with a hotspot for allelic recombination. Am J Hum Genet 79:890–902
Lopes J, Vandenberghe A, Tardieu S, Ionasescu V, Lévy N, Wood N, Tachi N, Bouche P, Latour P, Brice A, LeGuern E (1997) Sex-dependent rearrangements resulting in CMT1A and HNPP. Nat Genet 17:136–137
Lopes J, Ravisé N, Vandenberghe A, Palau F, Ionasescu V, Mayer M, Lévy N, Wood N, Tachi N, Bouche P, Latour P, Ruberg M, Brice A, LeGuern E (1998) Fine mapping of de novo CMT1A and HNPP rearrangements within CMT1A-REPs evidences two distinct sex-dependent mechanisms and candidate sequences involved in recombination. Hum Mol Genet 7:141–148
López-Correa C, Brems H, Lázaro C, Marynen P, Legius E (2000) Unequal meiotic crossover: a frequent cause of NF1 microdeletions. Am J Hum Genet 66:1969–1974
López-Correa C, Dorschner M, Brems H, Lázaro C, Clementi M, Upadhyaya M, Dooijes D, Moog U, Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Rutkowski JL, Fryns JP, Marynen P, Stephens K, Legius E (2001) Recombination hotspot in NF1 microdeletion patients. Hum Mol Genet 10:1387–1392
Ma R, Deng L, Xia Y, Wei X, Cao Y, Guo R, Zhang R, Guo J, Liang D, Wu L (2017) A clear bias in parental origin of de novo pathogenic CNVs related to intellectual disability, developmental delay and multiple congenital anomalies. Sci Rep 7:44446
Maezawa S, Yukawa M, Alavattam KG, Barski A, Namekawa SH (2018) Dynamic reorganization of open chromatin underlies diverse transcriptomes during spermatogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 46:593–608
Messiaen L, Vogt J, Bengesser K, Fu C, Mikhail F, Serra E, Garcia-Linares C, Cooper DN, Lazaro C, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2011) Mosaic type-1 NF1 microdeletions as a cause of both generalized and segmental neurofibromatosis type-1 (NF1). Hum Mutat 32:213–219
Miyake N, Kurotaki N, Sugawara H, Shimokawa O, Harada N, Kondoh T, Tsukahara M, Ishikiriyama S, Sonoda T, Miyoshi Y, Sakazume S, Fukushima Y, Ohashi H, Nagai T, Kawame H, Kurosawa K, Touyama M, Shiihara T, Okamoto N, Nishimoto J, Yoshiura K, Ohta T, Kishino T, Niikawa N, Matsumoto N (2003) Preferential paternal origin of microdeletions caused by prezygotic chromosome or chromatid rearrangements in Sotos syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 72:1331–1337
Pasmant E, Sabbagh A, Spurlock G, Laurendeau I, Grillo E, Hamel MJ, Martin L, Barbarot S, Leheup B, Rodriguez D, Lacombe D, Dollfus H, Pasquier L, Isidor B, Ferkal S, Soulier J, Sanson M, Dieux-Coeslier A, Bièche I, Parfait B, Vidaud M, Wolkenstein P, Upadhyaya M, Vidaud D, Members of the NF France Network (2010) NF1 microdeletions in neurofibromatosis type 1: from genotype to phenotype. Hum Mutat 31:E1506-1518
Pavlicek A, House R, Gentles AJ, Jurka J, Morrow BE (2005) Traffic of genetic information between segmental duplications flanking the typical 22q11.2 deletion in velo-cardio-facial syndrome/DiGeorge syndrome. Genome Res 15:1487–1495
Perez-Jurado LA, Peoples R, Kaplan P, Hamel BCJ, Francke U (1996) Molecular definition of the chromosome 7 deletion in Williams syndrome and parent-of-origin effects on growth. Am J Hum Genet 59:781–792
Rahbari R, Wuster A, Lindsay SJ, Hardwick RJ, Alexandrov LB, Turki SA, Dominiczak A, Morris A, Porteous D, Smith B, Stratton MR, UK10K Consortium, Hurles ME (2016) Timing, rates and spectra of human germline mutation. Nat Genet 48:126–133
Rasmussen SA, Colman SD, Ho VT, Abernathy CR, Arn PH, Weiss L, Schwartz C, Saul RA, Wallace MR (1998) Constitutional and mosaic large NF1 gene deletions in neurofibromatosis type 1. J Med Genet 35:468–471
Robinson WP, Waslynka J, Bernasconi F, Wang M, Clark S, Kotzot D, Schinzel A (1996) Delineation of 7q11.2 deletions associated with Williams–Beuren syndrome and mapping of a repetitive sequence to within and to either side of the common deletion. Genomics 34:17–23
Roehl AC, Vogt J, Mussotter T, Zickler AN, Spöti H, Högel J, Chuzhanova NA, Wimmer K, Kluwe L, Mautner VF, Cooper DN, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2010) Intrachromosomal mitotic nonallelic homologous recombination is the major molecular mechanism underlying type-2 NF1 deletions. Hum Mutat 31:1163–1173
Rozen S, Skaletsky H, Marszalek JD, Minx PJ, Cordum HS, Waterston RH, Wilson RK, Page DC (2003) Abundant gene conversion between arms of palindromes in human and ape Y chromosomes. Nature 423:873–876
Saitta SC, Harris SE, Gaeth AP, Driscoll DA, McDonald-McGinn DM, Maisenbacher MK, Yersak JM, Chakraborty PK, Hacker AM, Zackai EH, Ashley T, Emanuel BS (2004) Aberrant interchromosomal exchanges are the predominant cause of the 22q11.2 deletion. Hum Mol Genet 13:417–428
Sibbons C, Morris JK, Crolla JA, Jacobs PA, Thomas NS (2012) De novo deletions and duplications detected by array CGH: a study of parental origin in relation to mechanisms of formation and size of imbalance. Eur J Hum Genet 20:155–160
Sin HS, Kartashov AV, Hasegawa K, Barski A, Namekawa SH (2015) Poised chromatin and bivalent domains facilitate the mitosis-to-meiosis transition in the male germline. BMC Biol 13:53
Steinmann K, Cooper DN, Kluwe L, Chuzhanova NA, Senger C, Serra E, Lazaro C, Gilaberte M, Wimmer K, Mautner VF, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2007) Type 2 NF1 deletions are highly unusual by virtue of the absence of nonallelic homologous recombination hotspots and an apparent preference for female mitotic recombination. Am J Hum Genet 81:1201–1220
Sun Z, Liu P, Jia X, Withers MA, Jin L, Lupski JR, Zhang F (2013) Replicative mechanisms of CNV formation preferentially occur as intrachromosomal events: evidence from Potocki–Lupski duplication syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 22:749–756
Thiede C, Prange-Krex G, Freiberg-Richter J, Bornhäuser M, Ehninger G (2000) Buccal swabs but not mouthwash samples can be used to obtain pretransplant DNA fingerprints from recipients of allogeneic bone marrow transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant 25:575–577
Thomas NS, Durkie M, Van Zyl B, Sanford R, Potts G, Youings S, Dennis N, Jacobs P (2006a) Parental and chromosomal origin of unbalanced de novo structural chromosome abnormalities in man. Hum Genet 119:444–450
Thomas NS, Durkie M, Potts G, Sandford R, Van Zyl B, Youings S, Dennis NR, Jacobs PA (2006b) Parental and chromosomal origins of microdeletion and duplication syndromes involving 7q11.23, 15q11–q13 and 22q11. Eur J Hum Genet 14:831–837
Trost D, Wiebe W, Uhlhaas S, Schwindt P, Schwanitz G (2000) Investigation of meiotic rearrangements in DGS/VCFS patients with a microdeletion 22q11.2. J Med Genet 37:452–454
Upadhyaya M, Ruggieri M, Maynard J, Osborn M, Hartog C, Mudd S, Penttinen M, Cordeiro I, Ponder M, Ponder BA, Krawczak M, Cooper DN (1998) Gross deletions of the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene are predominantly of maternal origin and commonly associated with a learning disability, dysmorphic features and developmental delay. Hum Genet 102:591–597
Urbán Z, Helms C, Fekete G, Csiszár K, Bonnet D, Munnich A, Donis-Keller H, Boyd CD (1996) 7q11.23 deletions in Williams syndrome arise as a consequence of unequal meiotic crossover. Am J Hum Genet 59:958–962
Visser R, Shimokawa O, Harada N, Kinoshita A, Ohta T, Niikawa N, Matsumoto N (2005) Identification of a 3.0-kb major recombination hotspot in patients with Sotos syndrome who carry a common 1.9-Mb microdeletion. Am J Hum Genet 76:52–67
Vogt J, Mussotter T, Bengesser K, Claes K, Högel J, Chuzhanova N, Fu C, van den Ende J, Mautner VF, Cooper DN, Messiaen L, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2012) Identification of recurrent type-2 NF1 microdeletions reveals a mitotic nonallelic homologous recombination hotspot underlying a human genomic disorder. Hum Mutat 33:1599–1609
Vogt J, Bengesser K, Claes KB, Wimmer K, Mautner VF, van Minkelen R, Legius E, Brems H, Upadhyaya M, Högel J, Lazaro C, Rosenbaum T, Bammert S, Messiaen L, Cooper DN, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2014) SVA retrotransposon insertion-associated deletion represents a novel mutational mechanism underlying large genomic copy number changes with non-recurrent breakpoints. Genome Biol 15:R80
Watson CT, Marques-Bonet T, Sharp AJ, Mefford HC (2014) The genetics of microdeletion and microduplication syndromes: an update. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet 15:215–244
Weckselblatt B, Rudd MK (2015) Human structural variation: mechanisms of chromosome rearrangements. Trends Genet 31:587–599
Wilson Sayres MA, Makova KD (2011) Genome analyses substantiate male mutation bias in many species. Bioessays 33:938–945
Zhang J, Tong H, Fu X, Zhang Y, Liu J, Cheng R, Liang J, Peng J, Sun Z, Liu H, Zhang F, Lu W, Li M, Yao Z (2015) Molecular characterization of NF1 and neurofibromatosis type 1 genotype-phenotype correlations in a Chinese population. Sci Rep 5:11291
Zickler D, Kleckner N (2015) Recombination, pairing, and synapsis of homologs during meiosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a016626
Zickler AM, Hampp S, Messiaen L, Bengesser K, Mussotter T, Roehl AC, Wimmer K, Mautner VF, Kluwe L, Upadhyaya M, Pasmant E, Chuzhanova N, Kestler HA, Högel J, Legius E, Claes K, Cooper DN, Kehrer-Sawatzki H (2012) Characterization of the nonallelic homologous recombination hotspot PRS3 associated with type-3 NF1 deletions. Hum Mutat 33:372–383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuhäusler, L., Summerer, A., Cooper, D.N. et al. Pronounced maternal parent-of-origin bias for type-1 NF1 microdeletions. Hum Genet 137, 365–373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-018-1888-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-018-1888-x