Abstract
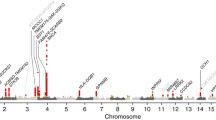
Previous evidence has shown that Parkinson disease (PD) has a heritable component, but only a small proportion of the total genetic contribution to PD has been identified. Genetic heterogeneity complicates the verification of proposed PD genes and the identification of new PD susceptibility genes. Our approach to overcome the problem of heterogeneity is to study a population isolate, the mid-western Amish communities of Indiana and Ohio. We performed genome-wide association and linkage analyses on 798 individuals (31 with PD), who are part of a 4,998 member pedigree. Through these analyses, we identified a region on chromosome 5q31.3 that shows evidence of association (p value < 1 × 10−4) and linkage (multipoint HLOD = 3.77). We also found further evidence of linkage on chromosomes 6 and 10 (multipoint HLOD 4.02 and 4.35 respectively). These data suggest that locus heterogeneity, even within the Amish, may be more extensive than previously appreciated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002) Merlin–rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30:97–101
Agarwala R, Biesecker LG, Schaffer AA (2003) Anabaptist genealogy database. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 121:32–37
Bem D, Yoshimura S, Nunes-Bastos R, Bond FC, Kurian MA, Rahman F, Handley MT, Hadzhiev Y, Masood I, Straatman-Iwanowska AA, Cullinane AR, McNeill A, Pasha SS, Kirby GA, Foster K, Ahmed Z, Morton JE, Williams D, Graham JM, Dobyns WB, Burglen L, Ainsworth JR, Gissen P, Müller F, Maher ER, Barr FA, Aligianis IA (2011) Loss-of-function mutations in RAB18 cause Warburg micro syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 88:499–507
Boyles AL, Scott WK, Martin ER, Schmidt S, Li YJ, Ashley-Koch A, Bass MP, Schmidt M, Pericak-Vance MA, Speer MC, Hauser ER (2005) Linkage disequilibrium inflates type I error rates in multipoint linkage analysis when parental genotypes are missing. Hum Hered 59:220–227
Cummings AC, Jiang L, Velez Edwards DR, McCauley JL, Laux R, McFarland LL, Fuzzell D, Knebusch C, Caywood L, Reinhart-Mercer L, Nations L, Gilbert JR, Konidari I, Tramontana M, Cuccaro ML, Scott WK, Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL (2012) Genome-wide association and linkage study in the amish detects a novel candidate late-onset Alzheimer disease gene. Ann Hum Genet 76:342–351
Cummings AC, Lee SL, McCauley JL, Jiang L, Crunk A, McFarland LL, Gallins PJ, Fuzzell D, Knebusch C, Jackson CE, Scott WK, Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL (2011) A genome-wide linkage screen in the Amish with Parkinson disease points to chromosome 6. Ann Hum Genet 75:351–358
Cummings AC, Torstenson E, Davis MF, D'Aoust LN, Scott WK, Pericak-Vance MA, Bush WS, Haines JL (2013) Evaluating power and type 1 error in large pedigree analyses of binary traits. PLoS One 8(5):e62615. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062615
Fahn S, Elton R, members of the UPDRS Development Committee (1987) Recent developments in Parkinson’s disease. In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Jenner P, Teychenne P (eds) Recent developments in Parkinson’s disease. Raven Press, New York, 153–163
Foltynie T, Hicks A, Sawcer S, Jonasdottir A, Setakis E, Maranian M, Yeo T, Lewis S, Brayne C, Stefansson K, Compston A, Gulcher J, Barker RA (2005) A genome wide linkage disequilibrium screen in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 252:597–602
Foroud T, Pankratz N, Martinez M (2006) Chromosome 5 and Parkinson disease. Eur J Hum Genet 14:1106–1110
Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S (1999) Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 56:33–39
Hamza TH, Chen H, Hill-Burns EM, Rhodes SL, Montimurro J, Kay DM, Tenesa A, Kusel VI, Sheehan P, Eaaswarkhanth M, Yearout D, Samii A, Roberts JW, Agarwal P, Bordelon Y, Park Y, Wang L, Gao J, Vance JM, Kendler KS, Bacanu SA, Scott WK, Ritz B, Nutt J, Factor SA, Zabetian CP, Payami H (2011) Genome-wide gene-environment study identifies glutamate receptor gene GRIN2A as a Parkinson’s disease modifier gene via interaction with coffee. PLoS Genet 7:e1002237
Hancock DB, Martin ER, Stajich JM, Jewett R, Stacy MA, Scott BL, Vance JM, Scott WK (2007) Smoking, caffeine, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in families with Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 64:576–580
Hancock DB, Martin ER, Mayhew GM, Stajich JM, Jewett R, Stacy MA, Scott BL, Vance JM, Scott WK (2008) Pesticide exposure and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a family-based case-control study. BMC Neurol 8:6
Hicks AA, Petursson H, Jonsson T, Stefansson H, Johannsdottir HS, Sainz J, Frigge ML, Kong A, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K, Sveinbjornsdottir S (2002) A susceptibility gene for late-onset idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 52:549–555
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1998) Parkinsonism: onset, progression, and mortality. 1967. Neurology 50:318
International Parkinson Disease Genomics Consortium, Nalls MA, Plagnol V, Hernandez DG, Sharma M, Sheerin UM, Saad M, Simon-Sanchez J, Schulte C, Lesage S, Sveinbjornsdottir S, Stefansson K, Martinez M, Hardy J, Heutink P, Brice A, Gasser T, Singleton AB, Wood NW (2011) Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet 377:641–649
International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC) & Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2) (2011) A two-stage meta-analysis identifies several new loci for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS Genet 7:e1002142
Katzman R, Brown T, Fuld P, Peck A, Schechter R, Schimmel H (1983) Validation of a short Orientation-Memory-Concentration Test of cognitive impairment. Am J Psychiatry 140:734–739
Klein C, Westenberger A (2012) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a008888
Krygowska-Wajs A, Kachergus JM, Hulihan MM, Farrer MJ, Searcy JA, Booij J, Berendse HW, Wolters ECh, Wszolek ZK (2005) Clinical and genetic evaluation of 8 Polish families with levodopa-responsive Parkinsonism. J Neural Transm 112:1487–1502
Lai BC, Marion SA, Teschke K, Tsui JK (2002) Occupational and environmental risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 8:297–309
Lee SL, Murdock DG, McCauley JL, Bradford Y, Crunk A, McFarland L, Jiang L, Wang T, Schnetz-Boutaud N, Haines JL (2008) A genome-wide scan in an Amish pedigree with Parkinsonism. Ann Hum Genet 72:621–629
Li YJ, Scott WK, Hedges DJ, Zhang F, Gaskell PC, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Allen FA Jr, Goetz CG, Mastaglia F, Stajich JM, Gibson RA, Middleton LT, Saunders AM, Scott BL, Small GW, Nicodemus KK, Reed AD, Schmechel DE, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Conneally PM, Roses AD, Gilbert JR, Vance JM, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (2002) Age-of-onset in two common neurodegenerative diseases is genetically controlled. Am J Hum Genet 70:985–993
Lill CM, Roehr JT, McQueen MB, Kavvoura FK, Bagade S, Schjeide BM, Schjeide LM, Meissner E, Zauft U, Allen NC, Liu T, Schilling M, Anderson KJ, Beecham G, Berg D, Biernacka JM, Brice A, DeStefano AL, Do CB, Eriksson N, Factor SA, Farrer MJ, Foroud T, Gasser T, Hamza T, Hardy JA, Heutink P, Hill-Burns EM, Klein C, Latourelle JC, Maraganore DM, Martin ER, Martinez M, Myers RH, Nalls MA, Pankratz N, Payami H, Satake W, Scott WK, Sharma M, Singleton AB, Stefansson K, Toda T, Tung JY, Vance J, Wood NW, Zabetian CP; 23andMe Genetic Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease Consortium; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium; Parkinson’s Disease GWAS Consortium; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2; Young P, Tanzi RE, Khoury MJ, Zipp F, Lehrach H, Ioannidis JP, Bertram L (2012) Comprehensive research synopsis and systematic meta-analyses in Parkinson’s disease genetics: the PDGene database. PLoS Genet 8:e1002548
Litvan I, Agid Y, Calne D (1996) Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear gaze palsy. Neurology 47:1–9
Liu F, Kirichenko A, Axenovich TI, van Duijn CM, Aulchenko YS (2008) An approach for cutting large and complex pedigrees for linkage analysis. Eur J Hum Genet 16:854–860
Maraganore DM, Farrer MJ, Lesnick TG, de Andrade M, Bower JH, Hernandez D, Hardy JA, Rocca WA (2003) Case-control study of the alpha-synuclein interacting protein gene and Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:1233–1239
Maraganore DM, de Andrade M, Lesnick TG, Strain KJ, Farrer MJ, Rocca WA, Pant PV, Frazer KA, Cox DR, Ballinger DG (2005) High-resolution whole-genome association study of Parkinson disease. Am J Hum Genet 77:685–693
Marras C, Goldman SM (2011) Genetics meets environment: evaluating gene-environment interactions in neurologic diseases. Semin Neurol 31:553–561
Martinez M, Brice A, Vaughan JR, Zimprich A, Breteler MM, Meco G, Filla A, Farrer MJ, Bétard C, Hardy J, De Michele G, Bonifati V, Oostra B, Gasser T, Wood NW, Dürr A; French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group; European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson’s Disease (2004) Genome-wide scan linkage analysis for Parkinson’s disease: the European genetic study of Parkinson’s disease. J Med Genet 41:900–907
Marx FP, Holzmann C, Strauss KM, Li L, Eberhardt O, Gerhardt E, Cookson MR, Hernandez D, Farrer MJ, Kachergus J, Engelender S, Ross CA, Berger K, Schols L, Schulz JB, Riess O, Kruger R (2003) Identification and functional characterization of a novel R621C mutation in the synphilin-1 gene in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 12:1223–1231
Myhre R, Klungland H, Farrer MJ, Aasly JO (2008) Genetic association study of synphilin-1 in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. BMC Med Genet 9:19
Pankratz N, Nichols WC, Uniacke SK, Halter C, Rudolph A, Shults C, Conneally PM, Foroud T; Parkinson Study Group (2002) Genome screen to identify susceptibility genes for Parkinson disease in a sample without parkin mutations. Am J Hum Genet 71:124–135
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identifed in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276:2045–2047
Rosenberger A, Sharma M, Muller-Myhsok B, Gasser T, Bickeboller H (2007) Meta analysis of whole-genome linkage scans with data uncertainty: an application to Parkinson’s disease. BMC Genet 8:44
Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Lyons K, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Colcher A, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Ondo WG, Allen FH Jr, Goetz CG, Small GW, Masterman D, Mastaglia F, Laing NG, Stajich JM, Slotterbeck B, Booze MW, Ribble RC, Rampersaud E, West SG, Gibson RA, Middleton LT, Roses AD, Haines JL, Scott BL, Vance JM, Pericak-Vance MA (2001) Complete genomic screen in Parkinson disease: evidence for multiple genes. JAMA 286:2239–2244
Thiele H, Nurnberg P (2005) HaploPainter: a tool for drawing pedigrees with complex haplotypes. Bioinformatics 21:1730–1732
Thornton T, McPeek MS (2007) Case-control association testing with related individuals: a more powerful quasi-likelihood score test. Am J Hum Genet 81:321–337
Van Den Eeden SK, Tanner CM, Bernstein AL, Fross RD, Leimpeter A, Bloch DA, Nelson LM (2003) Incidence of Parkinson’s disease: variation by age, gender, and race/ethnicity. Am J Epidemiol 157:1015–1022
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the participants of this study who have so graciously allowed us to visit with them and have participated in studies with us for over 10 years. We would like to acknowledge additional work for this study that was performed using the Vanderbilt Center for Human Genetics Research Core facilities: the Genetic Studies Ascertainment Core, the DNA Resources Core, and the Computation Genomics Core. This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants AG019085 (to JLH and MAP-V) and AG019726 (to WKS), and a grant from the Michael J. Fox Foundation (to JLH). Some of the samples used in this study were collected while WKS, JRG, and MAP-V were faculty members at Duke University. The authors would like to thank L. L. McFarland, C. Knebusch, and the late C. E. Jackson for their contributions to the overall Amish projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2013_1316_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Figure 2 Possible haplotypes and co-inheritance pattern on chromosome 5.Sub-pedigree 4 is shown with possible haplotype combinations for the peak region of co-inheritance on chromosome 5. The six SNPs in this haplotype are at the location of the maximum HLOD score. Genders have been randomized to protect privacy (TIFF 24 kb)
439_2013_1316_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Figure 3 Possible haplotypes and co-inheritance pattern on chromosome 6. Sub-pedigree 9 is shown with possible haplotype combinations for the peak region of co-inheritance on chromosome 6. The four SNPs in this haplotype are at the location of the maximum HLOD score. Genders have been randomized to protect privacy (TIFF 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, M.F., Cummings, A.C., D’Aoust, L.N. et al. Parkinson disease loci in the mid-western Amish. Hum Genet 132, 1213–1221 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1316-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1316-1