Abstract
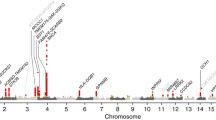
Whole genome screening is increasingly used to identify genetic risk factors for complex diseases. In this study, a genome wide linkage disequilibrium (LD) screen was performed in a cohort of Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients from the UK (n = 195) using pooled DNA to facilitate efficient genotyping of 5546 microsatellite markers. Allele frequencies were compared with those found in 2 previously typed disease free control populations, and the most interesting markers were selected for multiple repeat testing among the 3 pools. Markers were then individually genotyped in our original PD cohort and one of the original control groups, and independently in a second cohort of UK PD patients (n = 179), and additional controls.
Using this 2–stage approach, we have been unable to find evidence for consistent association of any markers with sporadic PD. Subgroup analysis of the most promising marker shows some evidence that microsatellite marker D1S2886 is associated with familial forms of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The International HapMap Project (2003) Nature 426:789–796
Barcellos LF, Klitz W, Field LL, Tobias R, Bowcock AM, Wilson R, Nelson MP, Nagatomi J, Thomson G (1997) Association mapping of disease loci, by use of a pooled DNA genomic screen. Am J Hum Genet 61:734–747
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, van Dongen JW, Vanacore N, van Swieten JC, Brice A, Meco G, van Duijn CM, Oostra BA, Heutink P (2003) Mutations in the DJ–1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early–onset–parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Burn DJ, Mark MH, Playford ED, Maraganore DM, Zimmerman-TR J, Duvoisin RC, Harding AE, Marsden CD, Brooks DJ (1992) Parkinson’s disease in twins studied with 18F–dopa and positron emission tomography. Neurology 42:1894–1900
DeStefano AL, Golbe LI, Mark MH, Lazzarini AM, Maher NE, Saint-Hilaire M, Feldman RG, Guttman M, Watts RL, Suchowersky O, Lafontaine AL, Labelle N, Lew MF, Waters CH, Growdon JH, Singer C, Currie LJ, Wooten GF, Vieregge P, Pramstaller PP, Klein C, Hubble JP, Stacy M, Montgomery E, MacDonald ME, Gusella JF, Myers RH (2001) Genome-wide scan for Parkinson’s disease: The Gene PD Study. Neurology 57:1124–1126
Elbaz A, Grigoletto F, Baldereschi M, Breteler MM, Manubens-Bertran JM, Lopez PS, Dartigues JF, Alperovitch A, Tzourio C, Rocca WA (1999) Familial aggregation of Parkinson’s disease: a population-based case-control study in Europe. EUROPARKINSON Study Group. Neurology 52:1876–1882
Farrer M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Muenter M, DeVrieze FW, Crook R, Perez-Tur J, Lincoln S, Maraganore D, Adler C, Newman S, MacElwee K, McCarthy P, Miller C, Waters C, Hardy J (1999) A chromosome 4p haplotype segregating with Parkinson’s disease and postural tremor. Hum Mol Genet 8:81–85
Fjalldal JB, Sigurdsson J, Benediktsson K, Ellingsson LM (2001) Automated Genotyping: Combining neural networks and decision trees to perform robust allele calling. Proc Int Joint Conf Neural Networks A1–A6
Funayama M, Hasegawa K, Kowa H, Saito M, Tsuji S, Obata F (2002) A new locus for Parkinson’s disease (PARK8) maps to chromosome 12p11. 2-q13. 1. Ann Neurol 51:296–301
Gasser T, Muller MB, Wszolek ZK, Oehlmann R, Calne DB, Bonifati V, Bereznai B, Fabrizio E, Vieregge P, Horstmann RD (1998) A susceptibility locus for Parkinson’s disease maps to chromosome 2p13. Nat Genet 18: 262–265
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51: 745–752
Hicks AA, Petursson H, Jonsson T, Stefansson H, Johannsdottir HS, Sainz J, Frigge ML, Kong A, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K, Sveinbjornsdottir S (2002) A susceptibility gene for late-onset idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 52:549–555
Jorde LB (2000) Linkage disequilibrium and the search for complex disease genes. Genome Res 10: 1435–1444
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Le WD, Xu P, Jankovic J, Jiang H, Appel SH, Smith RG, Vassilatis DK (2003) Mutations in NR4A2 associated with familial Parkinson disease. Nat Genet 33:85–89
Leroy E, Boyer R, Auburger G, Leube B, Ulm G, Mezey E, Harta G, Brownstein MJ, Jonnalagada S, Chernova T, Dehejia A, Lavedan C, Gasser T, Steinbach PJ, Wilkinson KD, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 395: 451–452
Marder K, Tang MX, Mejia H, Alfaro B, Cote L, Louis E, Groves J, Mayeux R (1996) Risk of Parkinson’s disease among first-degree relatives: A community- based study. Neurology 47: 155–160
Palsson B, Palsson F, Perlin M, Gudbjartsson H, Stefansson K, Gulcher J (1999) Using quality measures to facilitate allele calling in high-throughput genotyping. Genome Res 9: 1002–1012
Pankratz N, Nichols WC, Uniacke SK, Halter C, Rudolph A, Shults C, Conneally PM, Foroud T (2002) Genome screen to identify susceptibility genes for Parkinson disease in a sample without parkin mutations. Am J Hum Genet 71:124–135
Piccini P, Burn DJ, Ceravolo R, Maraganore D, Brooks DJ (1999) The role of inheritance in sporadic Parkinson’s disease: evidence from a longitudinal study of dopaminergic function in twins. Ann Neurol 45:577–582
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276: 2045–2047
Risch N, Merikangas K (1996) The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 273: 1516–1517
Sawcer S, Compston A (2003) The genetic analysis of multiple sclerosis in Europeans: concepts and design. J Neuroimmunol 143:13–16
Sawcer S, Maranian M, Setakis E, Curwen V, Akesson E, Hensiek A, Coraddu F, Roxburgh R, Sawcer D, Gray J, Deans J, Goodfellow PN, Walker N, Clayton D, Compston A (2002) A whole genome screen for linkage disequilibrium in multiple sclerosis confirms disease associations with regions previously linked to susceptibility. Brain 125:1337–1347
Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Lyons K, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Colcher A, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Ondo WG, Allen FH Jr, Goetz CG, Small GW, Masterman D, Mastaglia F, Laing NG, Stajich JM, Slotterbeck B, Booze MW, Ribble RC, Rampersaud E, West SG, Gibson RA, Middleton LT, Roses AD, Haines JL, Scott BL, Vance JM, Pericak-Vance MA (2001) Complete Genomic Screen in Parkinson Disease: Evidence for Multiple Genes. JAMA 286:2239–2244
Setakis E (2003) Statistical analysis of the GAMES studies. J Neuroimmunol 143:47–52
Sveinbjornsdottir S, Hicks AA, Jonsson T, Petursson H, Guomundsson G, Frigge ML, Kong A, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K (2000) Familial Aggregation of Parkinson’s Disease in Iceland. N Engl J Med 343:1765–1770
Valente EM, Bentivoglio AR, Dixon PH, Ferraris A, Ialongo T, Frontali M, Albanese A, Wood NW (2001) Localization of a Novel Locus for Autosomal Recessive Early-Onset Parkinsonism, PARK6, on Human Chromosome 1p35-p36. Am J Hum Genet 68:895–900
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foltynie, T., Hicks, A., Sawcer, S. et al. A genome wide linkage disequilibrium screen in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 252, 597–602 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0686-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0686-2