Abstract
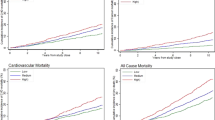
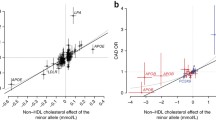
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are hypothesized to explain the genetic predisposition to ischemic heart disease (IHD) in the general population. Lack of evidence for a role of such variation is fostering pessimism about the utility of genetic information in the practice of medicine. In this study we determined the utility of exonic and 5′ SNPs in apolipoprotein E (APOE) and lipoprotein lipase (LPL) when considered singly and in combination for predicting incidence of IHD in 8,456 individuals from the general population during 24 years of follow-up. In men, LPL D9N improved prediction of IHD (P = 0.03) beyond smoking, diabetes and hypertension. The group of men heterozygous and homozygous for the rare D9N variant had a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.69 (95% confidence interval = 1.10–2.58) relative to the most common genotype. Pairwise combinations of D9N with −219G > T in APOE and N291S and S447X in LPL significantly improved the prediction of IHD (P = 0.05 in women, P = 0.04 in men, P = 0.03 in men, respectively) beyond smoking, diabetes and hypertension, and identified subgroups of individuals (n = 6–94) with highly significant HRs of 1.92–4.35. These results were validated in a case-control study (n = 8,806). In conclusion, we present evidence that combinations of SNPs in APOE and LPL identify subgroups of individuals at substantially increased risk of IHD beyond that associated with smoking, diabetes and hypertension.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15:539–553
Anderson KM, Odell PM, Wilson PWF, Kannel WB (1990) Cardiovascular disease risk profiles. Am Heart J 121:293–298
Appleyard M, Hansen AT, Jensen G, Schnohr P, Nyboe J (1989) The Copenhagen City Heart Study. Østerbroundersøgelsen. A book of tables with data from the first examination (1976–78) and a five year follow-up (1981–83). The Copenhagen City Heart Study Group. Scand J Soc Med Suppl 41:1–160
Artiga MJ, Bullido MJ, Sastre I, Recuero M, Garcia MA, Aldudo J, Vazquez J, Valdivieso F (1998) Allelic polymorphisms in the transcriptional regulatory region of apolipoprotein E gene. FEBS Lett 421:105–108
Brodie ED III (2000) Why evolutionary genetics does not always add up. In: Wolf JB, Brodie ED III, Wade MJ (eds) Epistasis and the evolutionary process, 1st edn. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 3–19
Brunzell JD, Deeb SS (2001) Familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency, apoC-II deficiency, and hepatic lipase deficiency. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The Metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 2789–2816
Chakravarti A, Little P (2003) Nature, nurture and human disease. Nature 421:412–414
Clark AG, Boerwinkle E, Hixson JE, Sing CF (2005) Determinants of the success of whole-genome association testing. Genome Res 15:1463–1467
Collins FS (2004) The case for a US prospective cohort study of genes and environment. Nature 429:475–477
Conroy RM, Pyörälä K, Fitzgerald AP, Sans S, Menotti A, De Backer G, De Bacquer D, Ducimetiere P, Jousilahti P, Keil U, Njølstad I, Oganov RG, Thomsen T, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Tverdal A, Wedel H, Whincup P, Wilhelmsen L, Graham IM (2003) Estimation of ten-year risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in Europe: the SCORE project. Eur Heart J 24:987–1003
Cordell HJ (2002) Epistasis: what it means, what it doesn’t mean, and statistical methods to detect it in humans. Hum Mol Genet 11:2463–2468
Cullen P, Cignarella A, Brennhausen B, Mohr S, Assmann G, von Eckardstein A (1998) Phenotype-dependent differences in apolipoprotein E metabolism and in cholesterol homeostasis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Clin Invest 101:1670–1677
Davignon J, Gregg RE, Sing CF (1988) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 8:1–21
de Visser JA, Hermisson J, Wagner GP, Ancel ML, Bagheri-Chaichian H, Blanchard JL, Chao L, Cheverud JM, Elena SF, Fontana W, Gibson G, Hansen TF, Krakauer D, Lewontin RC, Ofria C, Rice SH, von Dassow G, Wagner A, Whitlock MC (2003) Perspective: evolution and detection of genetic robustness. Evol Int J Org Evol 57:1959–1972
den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE (2001) Nomenclature for the description of human sequence variations. Hum Genet 109:121–124
European Society of Hypertension—European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension (2003) Eur Heart J 21:1011–1053
Frikke-Schmidt R, Nordestgaard BG, Agerholm-Larsen B, Schnohr P, Tybjærg-Hansen A (2000) Context dependent and invariant associations between lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins, and apolipoprotein E genotype. A study of 9,060 women and men from the population at large. J Lipid Res 41:1812–1822
Frikke-Schmidt R, Sing CF, Nordestgaard BG, Tybjærg-Hansen A (2004) Gender- and age-specific contributions of additional DNA sequence variation in the 5′ regulatory region of the APOE gene to prediction of measures of lipid metabolism. Hum Genet 115:331–345
Gerdes LU, Klausen IC, Sihm I, Færgeman O (1992) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in a Danish population compared to findings in 45 other study populations around the world. Genet Epidemiol 9:155–167
Gerdes C, Fisher RM, Nicaud V, Boer J, Humphries SE, Talmud PJ, Færgeman O (1997) Lipoprotein lipase variants D9N and N291S are associated with increased plasma triglyceride and lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations: studies in the fasting and postprandial states: The European Atherosclerosis Research Studies. Circulation 96:733–740
Gerdes LU, Jeune B, Ranberg KA, Nybo H, Vaupel JW (2000) Estimation of apolipoprotein E genotype-specific relative mortality risks from the distribution of genotypes in centenarians and middle-aged men: Apolipoprotein E gene is a “frailty gene,” not a “longevity gene”. Genet Epidemiol 19:202–210
Gliemann J (1998) Receptors of the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family in man. Multiple functions of the large family members via interaction with complex ligands. Biol Chem 379:951–964
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA (2004) Living with the past: evolution, development, and patterns of disease. Science 305:1733–1736
Hixson JE, Vernier DT (1990) Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res 31:545–548
Keavney B, Palmer A, Parish S, Clark S, Youngman L, Danesh J, McKenzie C, Delepine M, Lathrop M, Peto R, Collins R (2004) Lipid-related genes and myocardial infarction in 4685 cases and 3460 controls: discrepancies between genotype, blood lipid concentrations, and coronary disease risk. Int J Epidemiol 33:1002–1013
Khot UN, Khot MB, Bajzer CT, Sapp SK, Ohman EM, Brener SJ, Ellis SG, Lincoff AM, Topol EJ (2003) Prevalence of conventional risk factors in patients with coronary heart disease. JAMA 290:898–904
Klein JP, Moeschberger ML (2003) Refinements of the semiparametric proportional hazards model. Survival analysis. Techniques for censored and truncated data, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 295–328
Lambert JC, Brousseau T, Defosse V, Evans A, Arveiler D, Ruidavets JB, Haas B, Cambou JP, Luc G, Ducimetiere P, Cambien F, Chartier-Harlin MC, Amouyel P (2000) Independent association of an APOE gene promoter polymorphism with increased risk of myocardial infarction and decreased apoE plasma concentrations—the ECTIM Study. Hum Mol Genet 9:57–61
Mahley RW, Rall SC Jr (2001) Type III hyperlipoproteinemia (dysbetalipoproteinemia): the role of apolipoprotein E in normal and abnormal lipoprotein metabolism. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds). The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 2835–2862
Moore JH, Williams SM (2005) Traversing the conceptual divide between biological and statistical epistasis: systems biology and a more modern synthesis. BioEssays 27:637–646
National Cholesterol Education Program National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (2002) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. NIH Publication No. 02–5215, September
Nickerson DA, Taylor SL, Weiss KM, Clark AG, Hutchinson RG, Stengard J, Salomaa V, Vartiainen E, Boerwinkle E, Sing CF (1998) DNA sequence diversity in a 9.7-kb region of the human lipoprotein lipase gene. Nat Genet 19:233–240
Nickerson DA, Taylor SL, Fullerton SM, Weiss KM, Clark AG, Stengard JH, Salomaa V, Boerwinkle E, Sing CF (2000) Sequence diversity and large-scale typing of SNPs in the human apolipoprotein E gene. Genome Res 10:1532–1545
Nordestgaard BG, Abildgaard S, Wittrup HH, Steffensen R, Jensen G, Tybjærg-Hansen A (1997) Heterozygous lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Frequency in the general population, effect on plasma lipid levels, and risk of ischemic heart disease. Circulation 96:1737–1744
Olivecrona G, Olivecrona T (1995) Triglyceride lipases and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol 6:291–305
Payami H, Zhu M, Montimurro J, Keefe R, McCulloch CC, Moses L (2005) One step closer to fixing association studies: evidence for age-and gender-specific allele frequency variations and deviations from Hardy–Weinberg expectations in controls. Hum Genet 118:322–330
Pembrey M (2004) Genetic epidemiology: some special contributions of birth cohorts. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 18:3–7
Pritchard JK, Przeworski M (2001) Linkage disequilibrium in humans: models and data. Am J Hum Genet 69:1–14
Rea T, Brown CM, Sing CF (2006) Complex adaptive system models and the genetic analysis of plasma HDL-cholesterol levels. Perspect Biol Med (in press)
Reilly SL, Ferrell RE, Kottke BA, Kamboh MI, Sing CF (1991) The gender-specific apolipoprotein E genotype influence on the distribution of lipids and apolipoproteins in the population of Rochester, MN. I. Pleiotropic effects on means and variances. Am J Hum Genet 49:1155–1166
Schnohr P, Jensen JS, Scharling H, Nordestgaard BG (2002) Coronary heart disease risk factors ranked by importance for the individual and community. A 21 year follow-up of 12000 men and women from The Copenhagen City Heart Study. Eur Heart J 23:620–626
Sing CF, Stengard JH, Kardia SL (2003) Genes, Environment, and Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:1190–1196
Song Y, Stampfer MJ, Liu S (2004) Meta-analysis: Apolipoprotein E genotypes and risk for coronary heart disease. Ann Intern Med 141:137–147
Stannard AK, Riddell DR, Sacre SM, Tagalakis AD, Langer C, von Eckardstein A, Cullen P, Athanasopoulos T, Dickson G, Owen JS (2001) Cell-derived apolipoprotein E (apoE) particles inhibit vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 276:46011–46016
Stengard JH, Clark AG, Weiss KM, Kardia S, Nickerson DA, Salomaa V, Ehnholm C, Boerwinkle E, Sing CF (2002) Contributions of 18 additional DNA sequence variations in the gene encoding apolipoprotein E to explaining variation in quantitative measures of lipid metabolism. Am J Hum Genet 71:501–517
Stengard JH, Kardia SL, Hamon SC, Frikke-Schmidt R, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Salomaa V, Boerwinkle E, Sing CF (2006) Contribution of regulatory and structural variations in APOE to predicting dyslipidemia. J Lipid Res 47:318–328
Task force of the European Society of Cardiology (1997) Management of stable angina pectoris recommendations. Eur Heart J 18:394–413
Weiss LA, Pan L, Abney M, Ober C (2006) The sex-specific genetic architecture of quantitative traits in humans. Nat Genet 38:218–222
Wittrup HH, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Abildgaard S, Steffensen R, Schnohr P, Nordestgaard BG (1997) A common substitution (asn291ser) in lipoprotein lipase is associated with increased risk of ischemic heart disease. J Clin Invest 99:1606–1613
Wittrup HH, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Steffensen R, Deeb SS, Brunzell JD, Jensen G, Nordestgaard BG (1999a) Mutations in the lipoprotein lipase gene associated with ischemic heart disease in men: The Copenhagen City Heart Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:1535–1540
Wittrup HH, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG (1999b) Lipoprotein lipase mutations, plasma lipids and lipoproteins, and risk of ischemic heart disease: a meta-analysis. Circulation 99:2901–2907
Wittrup HH, Nordestgaard BG, Steffensen R, Jensen G, Tybjærg-Hansen A (2002) Effect of gender on phenotypic expression of the S447X mutation in LPL: the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Atherosclerosis 165:119–126
Acknowledgments
We thank Kenneth G. Weiss for his persistent attention to the data analyses. Mette Refstrup, Pia T. Petersen and Hanne Dam are greatly thanked for their excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by Chief Physician Johan Boserup and Lise Boserup’s Fund, The Danish Heart Foundation, The Danish Medical Research Council, Ingeborg and Leo Dannin’s Grant, The Research Fund at Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital, National Institute of Health HL039107 and National Institute of General Medical Science grant GM065509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frikke-Schmidt, R., Sing, C.F., Nordestgaard, B.G. et al. Subsets of SNPs define rare genotype classes that predict ischemic heart disease. Hum Genet 120, 865–877 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0233-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0233-y