Abstract
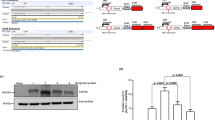
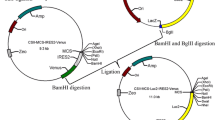
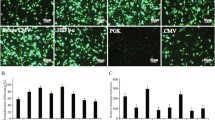
The regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells by combining various cis-regulatory features has rarely been discussed. In this study, we constructed expression vectors containing various combinations of regulatory elements to examine the regulation of gene expression by different combinations of cis-regulatory elements. The effects of four promoters (CMV promoter, PGK promoter, Polr2a promoter, and EF-1α core promoter), two enhancers (CMV enhancer and SV40 enhancer), two introns (EF-1α intron A and hybrid intron), two terminators (CYC1 terminator and TEF terminator), and their different combinations on downstream gene expression were compared in various mammalian cells using fluorescence microscopy to observe fluorescence, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), and western blot. The receptor binding domain (RBD) sequence from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein was used to replace the eGFP sequence in the expression vector and the RBD expression was detected by qRT-PCR and western blot. The results showed that protein expression can be regulated by optimizing the combination of cis-acting elements. The vector with the CMV enhancer, EF-1α core promoter, and TEF terminator was found to express approximately threefold higher eGFP than the unmodified vector in different animal cells, as well as 2.63-fold higher recombinant RBD protein than the original vector in HEK-293T cells. Moreover, we suggest that combinations of multiple regulatory elements capable of regulating gene expression do not necessarily exhibit synergistic effects to enhance expression further. Overall, our findings provide insights into biological applications that require the regulation of gene expression and will help to optimize expression vectors for biosynthesis and other fields. Additionally, we provide valuable insights into the production of RBD proteins, which may aid in developing reagents for diagnosis and treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files. The data and materials generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. We understand the importance of data sharing and are committed to promoting transparency and reproducibility. Interested researchers can contact the corresponding author to request access to the data and materials associated with this study. We will make every effort to respond to data requests promptly and provide the necessary information to facilitate further research and collaboration.
References
Andersson R, Sandelin A (2020) Determinants of enhancer and promoter activities of regulatory elements. Nat Rev Genet 21:71–87
Baier T, Jacobebbinghaus N, Einhaus A, Lauersen KJ, Kruse O (2020) Introns mediate post-transcriptional enhancement of nuclear gene expression in the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. PLoS Genet 16:e1008944
Bergman DT, Jones TR, Liu V, Ray J, Jagoda E, Siraj L, Kang HY, Nasser J, Kane M, Rios A, Nguyen TH, Grossman SR, Fulco CP, Lander ES, Engreitz JM (2022) Compatibility rules of human enhancer and promoter sequences. Nature 607:176–184
Boshart M, Weber F, Jahn G, Dorsch-Häsler K, Fleckenstein B, Schaffner W (1985) A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell 41:521–530
Cambray G, Guimaraes JC, Mutalik VK, Lam C, Mai QA, Thimmaiah T, Carothers JM, Arkin AP, Endy D (2013) Measurement and modeling of intrinsic transcription terminators. Nucleic Acids Res 41:5139–5148
Consortium AA (2020) Structural and functional comparison of SARS-CoV-2-spike receptor binding domain produced in Pichia pastoris and mammalian cells. Sci Rep 10:21779
Crook NC, Freeman ES, Alper HS (2011) Re-engineering multicloning sites for function and convenience. Nucleic Acids Res 39:e92
Curran KA, Karim AS, Gupta A, Alper HS (2013) Use of expression-enhancing terminators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to increase mRNA half-life and improve gene expression control for metabolic engineering applications. Metab Eng 19:88–97
Dhillon N, Shelansky R, Townshend B, Jain M, Boeger H, Endy D, Kamakaka R (2020) Permutational analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae regulatory elements. Synth Biol (oxf) 5:ysaa007
Diamos AG, Mason HS (2018) Chimeric 3’ flanking regions strongly enhance gene expression in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1971–1982
Gallegos JE, Rose AB (2015) The enduring mystery of intron-mediated enhancement. Plant Sci 237:8–15
Ito Y, Kitagawa T, Yamanishi M, Katahira S, Izawa S, Irie K, Furutani-Seiki M, Matsuyama T (2016) Enhancement of protein production via the strong DIT1 terminator and two RNA-binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci Rep 6:36997
Jin E, Wong L, Jiao Y, Engel J, Holdridge B, Xu P (2017) Rapid evolution of regulatory element libraries for tunable transcriptional and translational control of gene expression. Synth Syst Biotechnol 2:295–301
Kikuta H, Goto S, Kondo M, Akada R, Hoshida H (2022) Identification of essential intron sequences that enhance gene expression independently of splicing in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1865:194784
Mariati HSC, Yap MG, Yang Y (2012) Post-transcriptional regulatory elements for enhancing transient gene expression levels in mammalian cells. Methods Mol Biol 801:125–135
Martinez-Ara M, Comoglio F, van Arensbergen J, van Steensel B (2022) Systematic analysis of intrinsic enhancer-promoter compatibility in the mouse genome. Mol Cell 82:2519-2531.e2516
Melcher R, Grosch HW, Hasilik A (2002) Plasmid vectors with a 5′-hybrid intron facilitate high-level glycoprotein expression in CHO-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1575:49–53
Ramakrishnan K, Prattipati M, Samuel P, Sankaranarayanan M (2020) Transcriptional control of gene expression in Pichia pastoris by manipulation of terminators. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:7841–7851
Santos-Moreno J, Schaerli Y (2019) A framework for the modular and combinatorial assembly of synthetic gene circuits. ACS Synth Biol 8:1691–1697
Shang J, Ye G, Shi K, Wan Y, Luo C, Aihara H, Geng Q, Auerbach A, Li F (2020) Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 581:221–224
Shaul O (2017) How introns enhance gene expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 91:145–155
Tai W, He L, Zhang X, Pu J, Voronin D, Jiang S, Zhou Y, Du L (2020) Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell Mol Immunol 17:613–620
Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D (2020) Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 181:281–292 (e286)
Wang X, Xu Z, Tian Z, Zhang X, Xu D, Li Q, Zhang J, Wang T (2017) The EF-1α promoter maintains high-level transgene expression from episomal vectors in transfected CHO-K1 cells. J Cell Mol Med 21:3044–3054
Wang W, Guo X, Li YM, Wang XY, Yang XJ, Wang YF, Wang TY (2018) Enhanced transgene expression using cis-acting elements combined with the EF1 promoter in a mammalian expression system. Eur J Pharm Sci 123:539–545
Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF (2020) A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 395:470–473
Weintraub AS, Li CH, Zamudio AV, Sigova AA, Hannett NM, Day DS, Abraham BJ, Cohen MA, Nabet B, Buckley DL, Guo YE, Hnisz D, Jaenisch R, Bradner JE, Gray NS, Young RA (2017) YY1 is a structural regulator of enhancer-promoter loops. Cell 171:1573-1588.e1528
West S, Proudfoot NJ (2009) Transcriptional termination enhances protein expression in human cells. Mol Cell 33:354–364
Xu N, Wei L, Liu J (2019) Recent advances in the applications of promoter engineering for the optimization of metabolite biosynthesis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:33
Xu P, Xu S, He C, Khetan A (2020) Applications of small molecules in modulating productivity and product quality of recombinant proteins produced using cell cultures. Biotechnol Adv 43:107577
Yamanishi M, Ito Y, Kintaka R, Imamura C, Katahira S, Ikeuchi A, Moriya H, Matsuyama T (2013) A genome-wide activity assessment of terminator regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae provides a “terminatome” toolbox. ACS Synth Biol 2:337–347
Yang J, Wang W, Chen Z, Lu S, Yang F, Bi Z, Bao L, Mo F, Li X, Huang Y, Hong W, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Ye F, Lin S, Deng W, Chen H, Lei H, Zhang Z, Luo M, Gao H, Zheng Y, Gong Y, Jiang X, Xu Y, Lv Q, Li D, Wang M, Li F, Wang S, Wang G, Yu P, Qu Y, Yang L, Deng H, Tong A, Li J, Wang Z, Yang J, Shen G, Zhao Z, Li Y, Luo J, Liu H, Yu W, Yang M, Xu J, Wang J, Li H, Wang H, Kuang D, Lin P, Hu Z, Guo W, Cheng W, He Y, Song X, Chen C, Xue Z, Yao S, Chen L, Ma X, Chen S, Gou M, Huang W, Wang Y, Fan C, Tian Z, Shi M, Wang FS, Dai L, Wu M, Li G, Wang G, Peng Y, Qian Z, Huang C, Lau JY, Yang Z, Wei Y, Cen X, Peng X, Qin C, Zhang K, Lu G, Wei X (2020) A vaccine targeting the RBD of the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces protective immunity. Nature 586:572–577
Yew NS, Wysokenski DM, Wang KX, Ziegler RJ, Marshall J, McNeilly D, Cherry M, Osburn W, Cheng SH (1997) Optimization of plasmid vectors for high-level expression in lung epithelial cells. Hum Gene Ther 8:575–584
Yuan L, Janes L, Beeler D, Spokes KC, Smith J, Li D, Jaminet SC, Oettgen P, Aird WC (2013) Role of RNA splicing in mediating lineage-specific expression of the von Willebrand factor gene in the endothelium. Blood 121:4404–4412
Zabidi MA, Stark A (2016) Regulatory enhancer-core-promoter communication via transcription factors and cofactors. Trends Genet 32:801–814
Zhang XM, Zha GM, Wang J, Wang XJ, Song S, Shu JC, Chu BB, Yang GY (2016) Comparation of the effects of different 5’-untranslated regions (UTRs) on gene expression in HEK293 cells. Biotechnol Lett 38:2051–2057
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Grants from the Doctoral Foundation of Henan Agricultural University (30501221) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFD1301200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Martine Collart.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, LY., Zhang, S., Li, LY. et al. Optimization of mammalian expression vector by cis-regulatory element combinations. Mol Genet Genomics 298, 1121–1133 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02042-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02042-0