Abstract
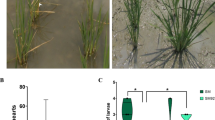
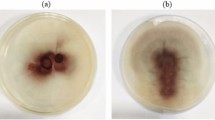
Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum causes bacterial wilt in ginger, reducing ginger production worldwide. We sequenced the whole genome of a highly virulent phylotype I, race 4, biovar 3 Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum strain GRsMep isolated from a severely infected ginger field in India. R. pseudosolanacearum GRsMep genome is organised into two replicons: chromosome and megaplasmid with a total genome size of 5,810,605 bp. This strain encodes approximately 72 effectors which include a combination of core effectors as well as highly variable, diverse repertoire of type III effectors. Comparative genome analysis with GMI1000 identified conservation in the genes involved in the general virulence mechanism. Our analysis identified type III effectors, RipBJ and RipBO as present in GRsMep but absent in the reported genomes of other strains infecting Zingiberaceae family. GRsMep contains 126 unique genes when compared to the pangenome of the Ralstonia strains that infect the Zingiberaceae family. The whole-genome data of R. pseudosolanacearum strain will serve as a resource for exploring the evolutionary processes that structure and regulate the virulence determinants of the strain. Pathogenicity testing of the transposon insertional mutant library of GRsMep through virulence assay on ginger plants identified a few candidate virulence determinants specific to bacterial wilt in ginger.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The whole genome of R.pseudosolanacearum GRsMep has been deposited in NCBI under Bioproject accession number PRJNA772165. The Biosample accession number is SAMN22367847.
References
Angot A, Peeters N, Lechner E et al (2006) Ralstonia solanacearum requires F-box-like domain-containing type III effectors to promote disease on several host plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14620–14625. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0509393103
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A et al (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W16-21. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw387
Asolkar T, Ramesh R (2020) The involvement of the type six secretion system (T6SS) in the virulence of Ralstonia solanacearum on brinjal. 3 Biotech 10:324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02311-4
Aznar A, Dellagi A (2015) New insights into the role of siderophores as triggers of plant immunity: what can we learn from animals? J Exp Bot 66:3001–3010. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv155
Backert S, Meyer TF (2006) Type IV secretion systems and their effectors in bacterial pathogenesis. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:207–217
Barrangou R, Fremaux C, Deveau H et al (2007) CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science 315:1709–1712. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1138140
Bernal P, Llamas MA, Filloux A (2018) Type VI secretion systems in plant-associated bacteria. Environ Microbiol 20:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13956
Bertelli C, Laird MR, Williams KP et al (2017) IslandViewer 4: expanded prediction of genomic islands for larger-scale datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W30–W35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx343
Bhatt G, Denny TP (2004) Ralstonia solanacearum iron scavenging by the siderophore staphyloferrin B is controlled by PhcA, the global virulence regulator. J Bacteriol 186:7896–7904. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.23.7896-7904.2004
Bocsanczy AM, Espindola AS, Norman DJ (2019) Whole-genome sequences of Ralstonia solanacearum strains P816, P822, and P824, emerging pathogens of blueberry in Florida. Microbiol Resour Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01316-18
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Buddenhagen IW, Sequeira L, Kelman A (1962) Designation of races in Pseudomonas solanacearum. Phytopathology 52:726
Chang JH, Desveaux D, Creason AL (2014) The ABCs and 123s of bacterial secretion systems in plant pathogenesis. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52:317–345. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-011014-015624
Chaudhari NM, Gupta VK, Dutta C (2016) BPGA—an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci Rep 6:24373. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24373
Chen L, Shirota M, Zhang Y et al (2014) Involvement of HLK effectors in Ralstonia solanacearum disease development in tomato. J Gen Plant Pathol 80:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-013-0490-2
Cianciotto NP, White RC (2017) Expanding Role of Type II Secretion in Bacterial Pathogenesis and Beyond. Infect Immun. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00014-17
Clough SJ, Lee KE, Schell MA, Denny TP (1997) A two-component system in Ralstonia (Pseudomonas) solanacearum modulates production of PhcA-regulated virulence factors in response to 3-hydroxypalmitic acid methyl ester. J Bacteriol 179:3639–3648. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.11.3639-3648.1997
Cohan FM (2002) What are bacterial species? Annu Rev Microbiol 56:457–487
Coll NS, Valls M (2013) Current knowledge on the Ralstonia solanacearum type III secretion system. Microb Biotechnol 6:614–620. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12056
Craig L, Li J (2008) Type IV pili: paradoxes in form and function. Curr Opin Struct Biol 18:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2007.12.009
Dake G (1995) Diseases of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) and their management. J Spices Aromat Crop 4:40–48
de Lange O, Schreiber T, Schandry N et al (2013) Breaking the DNA-binding code of Ralstonia solanacearum TAL effectors provides new possibilities to generate plant resistance genes against bacterial wilt disease. New Phytol 199:773–786
Denny T (2007) Plant pathogenic Ralstonia species. Plant-associated bacteria. Springer, Berlin, pp 573–644
Dillon MM, Almeida RND, Laflamme B et al (2019) Molecular evolution of Pseudomonas syringae type III secreted effector proteins. Front Plant Sci 10:418. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00418
Dohroo NP (2016) Diseases of ginger. Ginger. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 325–360
Fegan M, Prior P (2005) How complex is the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. In: Bact wilt Dis Ralstonia solanacearum species complex, vol 1, p 449–461
Flavier AB, Clough SJ, Schell MA, Denny TP (1997) Identification of 3-hydroxypalmitic acid methyl ester as a novel autoregulator controlling virulence in Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol Microbiol 26:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.5661945.x
Genin S, Boucher C (2004) Lessons learned from the genome analysis of Ralstonia solanacearum. Annu Rev Phytopathol 42:107–134. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.42.011204.104301
Genin S, Denny TP (2011) Pathogenomics of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. Annu Rev Phytopathol 50:67–89. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173000
González ET, Allen C (2003) Characterization of a Ralstonia solanacearum operon required for polygalacturonate degradation and uptake of galacturonic acid. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:536–544. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.6.536
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W181–W184. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn179
Green B, Bouchier C, Fairhead C et al (2012) Insertion site preference of Mu, Tn5, and Tn7 transposons. Mob DNA 3:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1759-8753-3-3
Guerra GS, Balan A (2020) Genetic and structural determinants on iron assimilation pathways in the plant pathogen Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri and Xanthomonas sp. Brazilian J Microbiol [publication Brazilian Soc Microbiol 51:1219–1231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00207-x
Guidot A, Elbaz M, Carrère S et al (2009) Specific genes from the potato brown rot strains of Ralstonia solanacearum and their potential use for strain detection. Phytopathology 99:1105–1112. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-99-9-1105
Hayward AC (1964) Characteristics of Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Appl Bacteriol 27:265–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1964.tb04912.x
Hayward AC (1991) Biology and epidemiology of bacterial wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum. Annu Rev Phytopathol 29:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.29.090191.000433
Hayward AC (1994) Systematics and phylogeny of Pseudomonas solanacearum and related bacteria. In: Hayward AC, Hartman GL (eds) Bacterial wilt: the disease and its causative agent, Pseudomonas solanacearum. CAB INTERNATIONAL, Wallingford (United Kingdom), pp 123–135, ISBN 0-85198-875-X
Iiyama K, Kodama S, Kusakabe H et al (2021) Complete genome sequences of Ralstonia solanacearum strains isolated from Zingiberaceae plants in Japan. Microbiol Resour Announc 10:e01303-e1320. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01303-20
Ishii M, Aragaki M (1963) Ginger wilt caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum E. F Smith Plant Dis Report 47:710–713
Kang Y, Liu H, Genin S et al (2002) Ralstonia solanacearum requires type 4 pili to adhere to multiple surfaces and for natural transformation and virulence. Mol Microbiol 46:427–437. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03187.x
Kumar A, Hayward AC (2016) Bacterial diseases of ginger and their control. ginger. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 361–386
Kumar A, Sarma YR (2004) Characterization of Ralstonia solanacearum causing bacterial wilt in ginger. Indian Phytopathol 57:12–17
Kumar A, Sarma YR, Anandaraj M (2004) Evaluation of genetic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum causing bacterial wilt of ginger using REP-PCR and PCR-RFLP. Curr Sci 87:1555–1561
Kumar A, Prameela TP, Bhai RS et al (2012) Small cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum Maton.) and ginger (Zingiber officinale Roxb) bacterial wilt is caused by same strain of Ralstonia solanacearum: a result revealed by multilocus sequence typing (MLST). Eur J Plant Pathol 132:477–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9903-2
Kumar A, Munjal V, Sheoran N et al (2017) Draft genome sequence of highly virulent race 4/biovar 3 of Ralstonia solanacearum CaRs_Mep causing bacterial wilt in Zingiberaceae plants in India. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01420-16
Kumar A, Bhai RS, Sasikumar B, et al (2006) Roxb. a bacterial wilt evading species in Zingiberaceae: a potential source for valuable genes for bacterial wilt resistance. In: Absracts of 4 international bacterial wilt symposium. CSL, p 85
Landry D, González-Fuente M, Deslandes L, Peeters N (2020) The large, diverse, and robust arsenal of Ralstonia solanacearum type III effectors and their in planta functions. Mol Plant Pathol 21:1377–1388. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12977
Langille MGI, Hsiao WWL, Brinkman FSL (2010) Detecting genomic islands using bioinformatics approaches. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2350
Le Roux C, Huet G, Jauneau A et al (2015) A receptor pair with an integrated decoy converts pathogen disabling of transcription factors to immunity. Cell 161:1074–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.025
Lee I, Ouk Kim Y, Park S-C, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Lei N, Chen L, Kiba A et al (2020) Super-multiple deletion analysis of type III effectors in Ralstonia solanacearum OE1–1 for full virulence toward host plants. Front Microbiol 11:1683
Li X, Huang X, Chen G et al (2018) Complete genome sequence of the sesame pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain SEPPX 05. Genes Genom 40:657–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0667-3
Liu H, Zhang S, Schell MA, Denny TP (2005) Pyramiding unmarked deletions in Ralstonia solanacearum shows that secreted proteins in addition to plant cell-wall-degrading enzymes contribute to virulence. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:1296–1305. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-18-1296
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S et al (2012) Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:614–629. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00804.x
Mao Y-H, Ma J-C, Li F et al (2015) Ralstonia solanacearum RSp0194 encodes a novel 3-keto-acyl carrier protein synthase III. PLoS One 10:e0136261
Moffett ML, Hayward AC (2011) The role of weed species in the survival of Pseudomonas solanacearum in tomato cropping land. Australas Plant Pathol 9:6–8
Morel A, Guinard J, Lonjon F et al (2018) The eggplant AG91-25 recognizes the Type III-secreted effector RipAX2 to trigger resistance to bacterial wilt (Ralstonia solanacearum species complex). Mol Plant Pathol 19:2459–2472. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12724
Nahar K, Matsumoto I, Taguchi F et al (2014) Ralstonia solanacearum type III secretion system effector Rip36 induces a hypersensitive response in the nonhost wild eggplant Solanum torvum. Mol Plant Pathol 15:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12079
Nakano M, Mukaihara T (2019) The type III effector RipB from Ralstonia solanacearum RS1000 acts as a major avirulence factor in Nicotiana benthamiana and other Nicotiana species. Mol Plant Pathol 20:1237–1251. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12824
Ochman H, Lawrence JG, Groisman EA (2000) Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 405:299–304
Peeters N, Carrère S, Anisimova M et al (2013) Repertoire, unified nomenclature and evolution of the Type III effector gene set in the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. BMC Genom 14:859. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-859
Perrier A, Barberis P, Genin S (2018) Introduction of genetic material in Ralstonia solanacearum through natural transformation and conjugation. Methods Mol Biol 1734:201–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7604-1_16
Poueymiro M, Cunnac S, Barberis P et al (2009) Two type III secretion system effectors from Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 determine host-range specificity on tobacco. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22:538–550. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-22-5-0538
Prameela TP, Suseela Bhai R (2020) Bacterial wilt of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) incited by Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum—a review based on pathogen diversity, diagnostics and management. J Plant Pathol 102:709–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-020-00487-5
Prior P, Ailloud F, Dalsing BL et al (2016) Genomic and proteomic evidence supporting the division of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum into three species. BMC Genom 17:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2413-z
Quinon VL, Aragaki M, Ishii M (1964) Pathogenicity+ serological relationship of 3 strains of Pseudomonas solanacearum in Hawaii. Phytopathology 54:1096
Remenant B, Coupat-Goutaland B, Guidot A et al (2010) Genomes of three tomato pathogens within the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex reveal significant evolutionary divergence. BMC Genom 11:379. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-379
Remenant B, de Cambiaire J-C, Cellier G et al (2011) Ralstonia syzygii, the blood disease bacterium and some Asian R. solanacearum strains form a single genomic species despite divergent lifestyles. PLoS One 6:e24356
Remenant B, Babujee L, Lajus A et al (2012) Sequencing of K60, type strain of the major plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum. J Bacteriol 194:2742–2743
Safni I, Cleenwerck I, De Vos P et al (2014) Polyphasic taxonomic revision of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex: proposal to emend the descriptions of Ralstonia solanacearum and Ralstonia syzygii and reclassify current R. syzygii strains as Ralstonia syzygii subsp. syzygii subsp. nov. R Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3087–3103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.066712-0
Salanoubat M, Genin S, Artiguenave F et al (2002) Genome sequence of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum. Nature 415:497–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/415497a
Schandry N, de Lange O, Prior P, Lahaye T (2016) TALE-like effectors are an ancestral feature of the Ralstonia solanacearum species complex and converge in DNA targeting specificity. Front Plant Sci 7:1225. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01225
Schell MA (2000) Control of virulence and pathogenicity genes of Ralstonia Solanacearum by an elaborate sensory network. Annu Rev Phytopathol 38:263–292. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.38.1.263
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30:2068–2069
Shan W, Yang X, Ma W et al (2013) Draft genome sequence of Ralstonia solanacearum race 4 biovar 4 strain SD54. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00890-13
She X, Tang Y, He Z, Lan G (2015) Genome sequencing of Ralstonia solanacearum race 4, biovar 4, and phylotype I, strain YC45, isolated from Rhizoma kaempferiae in southern China. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01110-15
Soto MJ, Sanjuan J, Olivares J (2006) Rhizobia and plant-pathogenic bacteria: common infection weapons. Microbiology 152:3167–3174
Sun L, Ge Y, Sparks JA et al (2019) TDNAscan: a software to identify complete and truncated T-DNA insertions. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00685
Tan X, Qiu H, Li F et al (2019) Complete genome sequence of sequevar 14M ralstonia solanacearum strain HA4–1 reveals novel type III effectors acquired through horizontal gene transfer. Front Microbiol 10:1893
Tatusov RL, Natale DA, Garkavtsev IV et al (2001) The COG database: new developments in phylogenetic classification of proteins from complete genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 29:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.1.22
Wairuri CK, van der Waals JE, van Schalkwyk A, Theron J (2012) Ralstonia solanacearum needs Flp pili for virulence on potato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 25:546–556. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-06-11-0166
Wang K, Remigi P, Anisimova M et al (2016) Functional assignment to positively selected sites in the core type III effector RipG 7 from Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol Plant Pathol 17:553–564
Wroblewski T, Caldwell KS, Piskurewicz U et al (2009) Comparative large-scale analysis of interactions between several crop species and the effector repertoires from multiple pathovars of Pseudomonas and Ralstonia. Plant Physiol 150:1733–1749. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.140251
Wu D, von Roepenack-Lahaye E, Buntru M et al (2019) A plant pathogen type III effector protein subverts translational regulation to boost host polyamine levels. Cell Host Microbe 26:638-649.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2019.09.014
Xu J, Zheng H-J, Liu L, Pan Z-C, Prior P, Tang B, Xu J-S, Zhang H, Tian Q, Zhang L-Q, Feng J (2011) Complete Genome Sequence of the Plant Pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum Strain Po82. J Bacteriol 193(16):4261–4262. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05384-11
Yoshihara A, Shimatani M, Sakata M et al (2020) Quorum sensing inhibition attenuates the virulence of the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum species complex. ACS Chem Biol 15:3050–3059. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.0c00752
Zehr EI (1969) Studies of the distribution and economic importance of Pseudomonas solanacearum EF Smith in certain crops in the Philippines. Philipp Agric 53:218–223
Zhang L, Xu J, Xu J et al (2012) TssM is essential for virulence and required for type VI secretion in Ralstonia solanacearum. J Plant Dis Prot 119:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356431
Zhang L, Xu J, Xu J et al (2014) TssB is essential for virulence and required for type VI secretion system in Ralstonia solanacearum. Microb Pathog 74:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2014.06.006
Zhang F, Zhao S, Ren C et al (2018) CRISPRminer is a knowledge base for exploring CRISPR-Cas systems in microbe and phage interactions. Commun Biol 1:180. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-018-0184-6
Zheng X, Li X, Wang B et al (2019) A systematic screen of conserved Ralstonia solanacearum effectors reveals the role of RipAB, a nuclear-localized effector that suppresses immune responses in potato. Mol Plant Pathol 20:547–561. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12774
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by National Post-Doctoral Fellowship (PDF/2016/003228/LS), awarded to Suraby E. J. by Science, Engineering and Research Board (SERB), India and Central University of Kerala (internal funding) to Ginny Antony. The authors acknowledge the Director, ICAR-Indian Institute of Spices Research for providing the R. pseudosolanacearum cultures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Martine Collart.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

438_2022_1925_MOESM9_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file9 Fig. S1. The distribution of genomic islands and prophages in GRsMep genome a) Chromosome, b) Megaplasmid. The regions in different colours indicate GIs predicted by different prediction methods such as integrated (red), IslandPath-DIMOB (blue), SIGI-HMM (orange) and Island Pick (green) (JPG 737 KB)

438_2022_1925_MOESM10_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file10 Fig. S2. KEGG distribution of core, accessory, and unique genes of Ralstonia strains infecting members of Zingiberaceae family. The bar diagram represents the distribution of core, accessory and unique genes in a) major category and b) sub-category (JPG 959 KB)

438_2022_1925_MOESM11_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file11 Fig. S3. Phylogenetic tree comparing GRsMep with Ralstonia strains from other phylotypes based on OrthoANI values. The heat map was generated with orthoANI values calculated from OAT software. Ralstonia strains used in the analysis is detailed in Table 1. All the strains used for the comparison based on OrthoANI values are non-pathogenic to ginger. (JPG 478 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suraby, E.J., Sruthi, K.B. & Antony, G. Genome-wide identification of type III effectors and other virulence factors in Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum causing bacterial wilt in ginger (Zingiber officinale). Mol Genet Genomics 297, 1371–1388 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01925-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01925-y