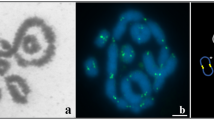
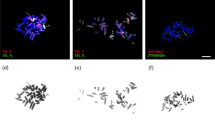
Abstract
Supernumerary B chromosomes (Bs) are dispensable genetic elements widespread in eukaryotes and are poorly understood mainly in relation to mechanisms of maintenance and transmission. The cichlid Astatotilapia latifasciata can harbor Bs in a range of 0 (named B −) and 1–2 (named B +). The B in A. latifasciata is rich in several classes of repetitive DNA sequences, contains protein coding genes, and affects hosts in diverse ways, including sex-biased effects. To advance in the knowledge about the mechanisms of maintenance and transmission of B chromosomes in A. latifasciata, here, we studied the meiotic behavior in males and transmission rates of A. latifasciata B chromosome. We also analyzed structurally and functionally the predicted B chromosome copies of the cell cycle genes separin-like, tubb1-like and kif11-like. We identified in the meiotic structure relative to the B chromosome the presence of proteins associated with Synaptonemal Complex organization (SMC3, SYCP1 and SYCP3) and found that the B performs self-pairing. These data suggest that isochromosome formation was a step during B chromosome evolution and this element is in a stage of diversification of the two arms keeping the self-pairing behavior to protect the A chromosome complement of negative effects of recombination. Moreover, we observed no occurrence of B-drive and confirmed the presence of cell cycle genes copies in the B chromosome and their transcription in encephalon, muscle and gonads, which can indicates beneficial effects to hosts and contribute to B maintenance.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used in the current study are available at SaciBase database (http://186.217.131.253/jbrowse/JBrowse-1.12.1/) and from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- 5mC:
-
5-Methylcytosine
- 5hmC:
-
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine
- AE:
-
Axial elements
- B:
-
B chromosome
- B −:
-
Sample without B chromosome
- B + :
-
Sample with B chromosome
- BncDNA:
-
B chromosome noncoding DNA
- DAPI:
-
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole, dihydrochloride
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- FB −:
-
Female without B chromosome
- FB + :
-
Female with B chromosome
- FISH:
-
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
- GDR:
-
Gene dose ratio
- KCl:
-
Potassium chloride
- kif11-like :
-
Kinesin-like protein
- MB −:
-
Male without B chromosome
- MB + :
-
Male with B chromosome
- LE:
-
Lateral elements
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative PCR
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription PCR
- RT-qPCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
- SMC3:
-
Structural maintenance of chromosomes 3
- SYCP1:
-
Synaptonemal complex protein 1
- SYCP3:
-
Synaptonemal complex protein 3
- tubb1-like :
-
Tubulin beta-1 chain-like
- SaciBase:
-
Search and analysis for cytogenomic integration database
- SC:
-
Synaptonemal complex
- SIM:
-
Structured-illumination microscopy
- SNV:
-
Single nucleotide variation
- SSC:
-
Saline-sodium citrate
- ubce :
-
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme
References
Adams CL, Dimitrova I, Post MD, Gibson L, Spillman MA, Behbakht K, Bradford AP (2019) Identification of a novel diagnostic gene expression signature to discriminate uterine leiomyoma from leiomyosarcoma. Exp Mol Phatol 110:104284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104284
Ahmad SF, Jehangir M, Cardoso AL, Wolf IR, Margarido VP, Cabral-de-Mello DC, O’Neill R, Valente GT, Martins C (2020) B chromosome of multiple species have intense evolutionary dynamics and accumulated genes related to important biological processes. BMC Genom 21:656. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07072-1
Ahmad SF, Martins C (2019) The modern view of B chromosomes under the impact of high scale omics analyses. Cells 8(2):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020156
Aldrich JC, Leibholz A, Cheema MS, Ausió J, Ferree PM (2017) A “selfish” B chromosome induces genome elimination by disrupting the histone code in the jewel wasp Nasonia vitripennis. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42551
Ali I, Yang WC (2020) The functions of kinesin and kinesin-related proteins in eukaryotes. Cell Adh Migr 14(1):139–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336918.2020.1810939
Baier A, Alsheimer M, Benavente R (2007) Synaptonemal complex protein SYCP3: conserved polymerization properties among vertebrates. Biochim Biophys Acta 1774:595–602
Basheva EA, Torgasheva AA, Sakaeva GR, Bidau C, Borodin PV (2010) A- and B-chromosome pairing and recombination in male meiosis of the silver fox (Vulpes vulpes L., 1758, Carnivora, Canidae). Chromosome Res 18:689–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-010-9149-4
Bel Y, Ferré J, Escriche B (2011) Quantitative real-time PCR with SYBR green detection to assess gene duplication in insects: study of gene dosage in Drosophila melanogaster (Diptera) and in Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera). BMC Res Notes 4(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-4-84
Bertollo LAC, Takahashi CS, Moreira-Filho O (1978) Cytotaxonomic consideration on Hoplias lacerdae (Pisces, Erythrinidae). Braz J Genet 1:103–120
Bidau CJ (1986) Effects on cytokinesis and sperm formation of a B-isochromosome in Metaleptea brevicornis adspersa (Acridinae, Acrididae). Caryologia 39(2):165–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.1986.10797778
Blankenberg D, Gordon A, Von-Kuster A, Coraor N, Taylor J, Nekrutenko A (2010) Manipulation of FASTQ data with galaxy. Bioinformatics 26(14):1783–1785. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq281
Camacho JPM, Schmid M, Cabrero J (2011) B chromosomes and sex in animals. Sex Dev 5:155–166. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324930
Camacho JPM, Sharbel TF, Beukeboom LW (2000) B-chromosome evolution. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355:163–178. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2000.0556
Camlin NJ, McLaughlin EA, Holt JE (2017) Motoring through: the role of kinesin superfamily proteins in female meiosis. Hum Reprod Update 23(4):409–420. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmx010
Carchilan M, Delgado M, Ribeiro T, Costa-Nunes P, Caperta A, Morais-Cecílio L, Jones RN, Viegas W, Houben A (2007) Transcriptionally active heterochromatin in rye B chromosomes. Plant Cell 19(6):1738–1749. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.046946
Cardoso AL, Fantinatti BEA, Venturelli NB, Carmello BO, Oliveira RA, Martins C (2019) Epigenetic DNA modifications are correlated with B chromosomes and sex in the cichlid Astatotilapia latifasciata. Front Genet 10:324. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00324
Carmello BO, Coan RLB, Cardoso AL, Ramos E, Fantinatti BEA, Marques D, Oliveira RA, Valente GT, Martins C (2017) The hnRNP Q-like gene is retroinserted into the B chromosomes of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata. Chromosome Res 25:277–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-017-9561-0
Civitelli MV, Consentino P, Capanna E (1989) Inter- and intra-individual chromosome variability in Thamnomys (Grammomys) gazellae (Rodentia, Muridae) B-chromosomes and structural heteromorphisms. Genetica 79:93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00057926
Clark FE, Conte MA, Ferreira-Bravo IA, Poletto AB, Martins C, Kocher TD (2017) Dynamic sequence evolution of a sex-associated B chromosome in Lake Malawi cichlid fish. J Hered 108(1):53–62. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esw059
Clark FE, Conte MA, Kocher TD (2018) Genomic characterization of a B chromosome in Lake Malawi cichlid fishes. Genes 9:610. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9120610
Clark FE, Kocher TD (2019) Changing sex for selfish gain: B chromosomes of Lake Malawi cichlid fish. Sci Rep 9:20213. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55774-8
Coan RLB, Martins C (2018) Landscape of transposable elements focusing on the B chromosome of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata. Genes 9:269. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060269
De Boer E, Lhuissier FG, Heyting C (2009) Cytological analysis of interference in mouse meiosis. In: Keeney S (ed) Meiosis Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols). Humana Press, Ttowa, pp 355–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-103-5_21
Detrich HW, Parker SK (1993) Divergent neural beta tubulin form the Antarctic fish Notothenia coriiceps neglecta: potential sequence contribution to cold adaptation of microtubule assembly. Cell Motil Cytoskel 24:156–166. https://doi.org/10.1002/cm.970240303
Douglas RN, Birchler JA (2017) B chromosomes. In: Bhat T, Wani A (eds) Chromosome structure and aberrations. Springer, New Delhi
Dunce JM, Milburn AE, Gurusaran M, da Cruz I, Sen LT, Benavente R, Davies OR (2018) Structural basis of meiotic telomere attachment to the nuclear envelope by MAJIN-TERB2-TERB1. Nat Commun 9:5355. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07794-7
Fantinatti BEA, Martins C (2016) Development of chromosomal markers based on next-generation sequencing: the B chromosome of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata as a model. BMC Genet 17:119. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0427-9
Fantinatti BEA, Mazzuchelli J, Valente GT, Cabral-De-Mello DC, Martins C (2011) Genomic content and new insights on the origin of the B chromosome of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata. Genetica 139:1273–1282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-012-9629-x
Fraune J, Alsheimer M, Volff JN, Busch K, Fraune S, Bosch TCG, Benavente R (2012) Hydra meiosis reveals unexpected conservation of structural synaptonemal complex proteins across metazoans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(41):16588–16593. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206875109
George CM, Alani E (2012) Multiple cellular mechanism prevent chromosomal rearrangements involving repetitive DNA. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 47(3):297–313. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2012.675644
Grieco ML, Bidau CJ (2000) The dicentric nature of the metacentric B chromosome of Metaleptea brevicornis adspersa (Acridinae, Acrididae). Heredity 84:639–646. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.2000.00688.x
Grishaeva TM, Bogdanov YF (2014) Conservation and variability of synaptonemal complex proteins in phylogenesis of eukaryotes. Int J Evol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/856230
Hamer G, Wang H, Bolcun-Filas E, Cooke HJ, Benavente R, Höög C (2008) Progression of meiotic recombination requires structural maturation of the central element of the synaptonemal complex. J Cell Sci 121:2445–2451. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.033233
Hara-Yokoyama M, Kurihara H, Ichinose S, Matsuda H, Ichinose S, Kurosawa M, Tada N, Iwahara C, Teresawa K, Podyma-Inoue KA, Furukawa K, Iwabuchi K (2019) KIF11 as a potential marker of spermatogenesis within mouse seminiferous tubule cross-sections. J Histochem Cytochem 67(11):813–824. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155419871027
Hashimoto DT, Voltolin TA, Paes ADNVA, Foresti F, Bortolozzi J, Porto-Foresti F (2012) Cytogenetic analysis of B chromosomes in one population of the fish Moenkhausia sanctaefilomenae (Steindachner, 1907) (Teleostei, Characiformes). Com Cytogenet 6(2):141–151. https://doi.org/10.3897/CompCytogen.v6i2.1769
Hauf S, Waizenegger IC, Peters JM (2001) Cohesin cleavage by separase required for anaphase and cytokinesis in human cells. Science 293:1320–1323. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1061376
Hesse S, Zelkowski M, Mikhailova EI, Keijzer CJ, Houben A, Schubert V (2019) Ultrastructure and dynamics of synaptonemal complex components during meiotic pairing and synapsis of standard (A) and accessory (B) rye chromosomes. Front Plant Sci 10:773. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00773
Hong ZJ, Xiao JX, Peng SF, Lin YP, Cheng YM (2020) Novel B-chromosome-specific transcriptionally active sequences are present throughout the maize B chromosome. Mol Genet Genomics 295:313–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01623-2
Houben A (2017) B chromosomes—a matter of chromosome drive. Front Plant Sci 8:210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00210
Hu F, Xu K, Zhou Y, Wu C, Wang S, Xiao J, Wen M, Zhao R, Luo K, Tao M, Duan W, Liu S (2017) Different expression patterns of sperm motility-related genes in testis of diploid and tetraploid cyprinid fish. Biol Reprod 96(4):907–920. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolre/iox010
Huang W, Du Y, Zhao X, Jin W (2016) B chromosome contains active genes and impacts the transcription of A chromosomes in maize (Zea mays L). BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0775-7
Huang YH, Peng SF, Lin YP, Cheng YM (2019) The maize B chromosome is capable of expressing microRNAs and altering the expression of microRNAs derived from A chromosomes. Chromosome Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-019-09620-2
Janke C, Magiera MM (2020) The tubulin code and its role in controlling microtubule properties and functions. Nat Rev 21:307326. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0214-3
Jehangir M, Ahmad SF, Cardoso AL, Ramos E, Valente TG, Martins C (2019) De novo genome assembly of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata reveals a higher level of genomic polymorphism and genes related to B chromosomes. Chromosoma 128:81–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-019-00707-7
Jones N (2017) New species with B chromosomes discovered since 1980. Nucleus 60:263–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-017-0215-6
Jones RN, Rees H (1982) B Chromosomes. Academic Press, London
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9(4):357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25(16):2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li Y, Jing XA, Aldrich JC, Clifford C, Chen J, Akbari OS, Ferree PM (2017) Unique sequence organization and small RNA expression of a “selfish” B chromosome. Chromosoma 126:753–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-0170641-x
Makunin AI, Dementyeva PW, Graphodatsky AS, Volobouev VT, Kukekova AV, Trifonov VA (2014) Genes on B chromosomes of vertebrates. Mol Cytogenet 7:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-014-0099-y
Martins C, Jehangir M (2021) A genomic glimpse of B chromosomes in cichlids. Genes Genom 43:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12919-019-0165-x
Martis MM, Klemme S, Banaei-Moghaddam AM, Blattner FR, Macas J, Schmutzer T, Scholz U, Gundlach H, Wicker T, Simkova H, Novak P, Neumann P, Kubalakova M, Bauer E, Haseneyer G, Fuchs J, Dolezel J, Stein N, Mayer KFX, Houben A (2012) Selfish supernumerary chromosome reveals its origin as a mosaic of host genome and organellar sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:13343–13346. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1204237109
Meyer R, Fofanov V, Panigrahi AK, Merchant F, Zhang N, Pati D (2009) Overexpression and mislocalization of the chromosomal segregation protein separase in multiple human cancers. Clin Cancer Res 15(8):2703–2710. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2454
Muller PY, Janovjak H, Miserez AR, Dobbie Z (2002) Processing of gene expression data generated by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Biotechniques 32:1372–1374
Nakajima RT (2019) Análises em larga escala de proteínas e construção de redes biológicas com foco em estudos de cromossomos B. Doctoral Thesis (In Portuguese). Universidade Estadual Paulista, Instituto de Biociências de Botucatu.
Nascimento-Oliveira JI, Fantinatti BEA, Wolf IR, Cardoso AL, Ramos E, Rieder N, Oliveira RA, Martins C (2021) Differential expression of miRNAs in the presence of B chromosome in the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata. BMC Genom 22:344. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07651-w
Navarro-Domínguez B, Martín-Peciña M, Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Cabrero J, Corral JM, López-León MD et al (2019) Gene expression changes elicited by a parasitic B chromosome in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans are consistent with its phenotypic effects. Chromosoma 128:53–67
Navarro-Domínguez B, Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Cabrero J, Corral JM, López-León MD, Sharbel TF et al (2017) Protein-coding genes in B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45200
Nogales E, Wolf SG, Downing KH (1998) Structure of the alpha beta tubulin dimer by electron crystallography. Nature 391:199–203. https://doi.org/10.1038/34465
Oliveira NL, Cabral-de-Mello DC, Rocha MF, Loreto V, Martins C, Moura RC (2011) Chromosomal mapping of rDNAs and H3 histone sequences in the grasshopper Rhammatocerus brasiliensis (Acrididae, Gomphocerinae): extensive chromosomal dispersion and co-localization of 5S rDNA/H3 histone clusters in the A complement and B chromosome. Mol Cytogenet 4:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8166-4-24
Oliver-Bonet M (2008) FISH on sperms, spermatocytes and oocytes. In: Liehr T (ed) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)—application guide. Springer Protocols Handbooks, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 157–172
Page SL, Hawley RS (2003) Chromosome choreography: the meiotic ballet. Science 301:785. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1086605
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW (1986) Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83(9):2934–2938. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934
Pires LB, Sampaio TR, Dias AL (2015) Mitotic and meiotic behavior of B Chromosomes in Crenicichla lepidota: new report in the family cichlidae. J Hered 106(3):289–295. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esv007
Poletto AB, Ferreia IA, Martins C (2010) The B chromosomes of the African cichlid fish Haplochromis obliquidens harbour 18S rRNA gene copies. BMC Genet 11:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-11-1
Quinlan A, Hall IM (2010) BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 26(6):841–842. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033
Ramos E, Cardoso AL, Brown J, Marques DF, Fantinatti BE, Cabral-de-Mello DC, Oliveira RA, O’Neill RJ, Martins C (2017) The repetitive DNA element BncDNA, enriched in the B chromosome of the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata, transcribes a potentially noncoding RNA. Chromosoma 126:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-016-0601-x
Randazzo D, Khalique U, Belanto JJ, Kenea A, Talsness DM, Olthoff JT, Tran MD, Zaal KJ, Pak K, Pinal-Fernandez I, Mammen AL, Sacket D, Ervasti JM, Ralston E (2019) Persistent upregulation of the β-tubulin tubb6, linked to muscle regeneration, is a source of microtubule disorganization in dystrophic muscle. Hum Mol Genet 28(7):1117–1135. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy418
Rens W, Wallduck MS, Lovell FL, Ferguson-Smith MA, Ferguson-Smith A (2010) Epigenetic modifications on X chromosomes in marsupial and monotreme mammals and implications for evolution of dosage compensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(41):17657–17662. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910322107
Santos JL, Jiménez MM, Díez M (1995) Synaptic patterns of rye B chromosomes IV the B Isochromosomes. Heredity 74:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1995.12
Sciurano R, Pigozzi MI, Benavente R (2019) Disassembly of the synaptonemal complex in chicken oocytes analyzed by super-resolution microscopy. Chromosoma 128:443–451
Silva DMZA, Utsunomia R, Ruiz-Ruano FJ, Daniel SN, Porto-Foresti F, Hashimoto DT, Oliveira C, Camacho JPM, Foresti F (2017) High-throughput analysis unveils a highly shared satellite DNA library among three species of fish genus Astyanax. Sci Rep 7:12726. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12939-7
Simon P (2003) Q-Gene: processing quantitative real-time RT-PCR data. Bioinformatics 19:1439–1440. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg157
Terrenoire E, McRonald F, Halsall JA, Page P, Illingworth RS, Taylor AMR, Davison V, O’Neill LP, Turner B (2010) Immunostaining of modified histones defines high-level features of the human metaphase epigenome. Genome Biol 11:R110. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-11-r110
Valente GT, Conte MA, Fantinatti BEA, Cabral-de-Mello DC, Carvalho RF, Vicari MR, Kocher TD, Martins C (2014) Origin and evolution of B chromosomes in the cichlid fish Astatotilapia latifasciata based on integrated genomic analyses. Mol Biol Evol 31:2061–2072. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu148
Valente GT, Nakajima RT, Fantinatti BEA, Marques DF, Almeida RO, Simões RP, Martins C (2017) B chromosomes: from cytogenetics to systems biology. Chromosoma 126:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-016-0613-6
Venere M, Horbinski C, Crish JF, Jin X, Vasanji A, Major J, Burrows AC, Chang C, Prokop J, Wu Q, Sims PA, Canoll P, Summers MK, Rosenfeld SS, Rich JN (2015) The mitotic kinesin KIF11 is as driver of invasion, proliferation, and self-renewal in gliosblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 7(304):304ra143. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aac6762
White MJD (1973) Animal cytology and evolution, 3d edn. Cambridge University Press, London
Wilson EB (1907) The supernumerary chromosomes of Hemiptera. Science 26:870–871
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden TL (2012) Primer-BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform 13(1):134. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-13-134
Yoshida K, Terai Y, Mizoiri S, Aibara M, Nishihara H, Watanabe M, Kuroiwa A, Hirai H, Hirai Y, Matsuda Y, Okada N (2011) B chromosomes have a functional effect on female sex determination in Lake Victoria cichlid fishes. PLoS Genet 7:e1002203. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002203
Zickler D, Kleckner N (1999) Meiotic chromosomes: integrating structure and function. Annu Rev Genet 33:603–754. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.33.1.603
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (grant numbers 2013/19898-7; 2013/25234-4; 2014/15756-6; 2015/16661-1; 2016/03912-9; 2016/07743-7; 2017/07484-4) and the National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq) (305321/2015-3; 304111/2020-1) to C.M. laboratory team as well as the German Science Foundation (DFG) grant Be1168/8-1 to R.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ALC: performed cytogenetic analyses, sperm-FISH experiments and active B-copies validation, and write the manuscript. NBV: performed immunodetection and crossing experiments, and write the manuscript. IC: performed immunodetection experiments. FMSP: performed bioinformatics analyses. DM: performed sperm-FISH experiments. RAO: performed statistical analyses. RB: designed and contributed to immunodetection experiments. CM: conceived the study and participated in its design and coordination.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Animals were maintained and submitted to scientific procedures in accordance to the protocols of ethics in animal experimentation adopted by the Brazilian College of Experimentation Animal (COBEA) and approved by the animal ethics committee of the Institute of Biosciences-UNESP (protocol nº486).
Consent to participate
All the authors participated in analyses and interpretation of data and read and approved the final manuscript.
Consent for publication
All the authors approved the final manuscript for publication.
Additional information
Communicated by Joan Cerdá.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardoso, A.L., Venturelli, N.B., da Cruz, I. et al. Meiotic behavior, transmission and active genes of B chromosomes in the cichlid Astatotilapia latifasciata: new clues about nature, evolution and maintenance of accessory elements. Mol Genet Genomics 297, 1151–1167 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01911-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01911-4