Abstract
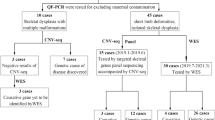
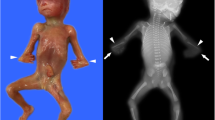
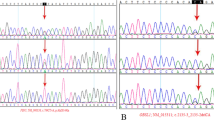
Whole exome sequencing (WES) could yield diagnostic significance in the prenatal diagnosis of skeletal abnormalities. But the phenotypes of fetuses with skeletal abnormalities are heterogenous, and the clinical information we could obtain from an ongoing pregnancy is limited, making the prenatal diagnosis complicated. Therefore, the following interpretation and genetic counseling remain a challenge for clinicians. The aim of this study is to present and investigate the utility of trio-based WES in five fetuses with skeletal anomalies. Five trios with fetal ultrasonic skeletal anomalies were recruited in our study. Fetal specimens and parental peripheral blood were subjected to WES. The fetal skeletal abnormalities were presented through ultrasound scanning images. Fetal WES results showed variants in the PPIB, CHST3, COL1A1, and FGFR3 genes in the five trios. Inherited variants were found in two of the trios, while de novo variants were observed in three of them. Two novel compound heterozygous variants (c.437C > A and c.1044C > G) in CHST3 were identified. We presented five trios with fetal skeletal anomalies, found two novel variants and broadened the spectrum of variants associated with skeletal abnormalities, which would help the establishment of genotype–phenotype relationship in the prenatal setting. Trio-based WES could assist the prenatal diagnosis and genetic counseling of fetuses with skeletal abnormalities.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Albuz B, Cetin GO, Ozhan B, Sarikepe B, Anlas O, Ozturk M, Zeybek S, Sabir N, Bagci G, Semerci Gunduz CN (2020) A novel nonsense mutation in CHST3 in a Turkish patient with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia, Omani type. Clin Dysmorphol 29:61–64
Barbosa-Buck CO, Orioli IM, da Graca DM, Lopez-Camelo J, Castilla EE, Cavalcanti DP (2012) Clinical epidemiology of skeletal dysplasias in South America. Am J Med Genet A 158A:1038–1045
Barkova E, Mohan U, Chitayat D, Keating S, Toi A, Frank J, Frank R, Tomlinson G, Glanc P (2015) Fetal skeletal dysplasias in a tertiary care center: radiology, pathology, and molecular analysis of 112 cases. Clin Genet 87:330–337
Bateman JF, Lamande SR, Dahl HH, Chan D, Cole WG (1988) Substitution of arginine for glycine 664 in the collagen alpha 1(I) chain in lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta. Demonstration of the peptide defect by in vitro expression of the mutant cDNA. J Biol Chem 263:11627–11630
Best S, Wou K, Vora N, Van der Veyver IB, Wapner R, Chitty LS (2018) Promises, pitfalls and practicalities of prenatal whole exome sequencing. Prenat Diagn 38:10–19
Bodian DL, Chan TF, Poon A, Schwarze U, Yang K, Byers PH, Kwok PY, Klein TE (2009) Mutation and polymorphism spectrum in osteogenesis imperfecta type II: implications for genotype-phenotype relationships. Hum Mol Genet 18:463–471
Chang TY, Chung IF, Wu WJ, Chang SP, Lin WH, Ginsberg NA, Ma GC, Chen M (2020) Whole exome sequencing with comprehensive gene set analysis identified a biparental-origin homozygous c.509G>A mutation in PPIB gene clustered in two taiwanese families exhibiting fetal skeletal dysplasia during prenatal ultrasound. Diagnostics (Basel) 10:286
Drury S, Williams H, Trump N, Boustred C, Gosgene LN, Scott RH, Chitty LS (2015) Exome sequencing for prenatal diagnosis of fetuses with sonographic abnormalities. Prenat Diagn 35:1010–1017
Duarte SP, Rocha ME, Bidondo MP, Liascovich R, Barbero P, Groisman B (2019) Bone dysplasias in 1.6 million births in Argentina. Eur J Med Genet 62:103603
Ferretti L, Mellis R, Chitty LS (2019) Update on the use of exome sequencing in the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. Eur J Med Genet 62:103663
Filges I, Friedman JM (2015) Exome sequencing for gene discovery in lethal fetal disorders–harnessing the value of extreme phenotypes. Prenat Diagn 35:1005–1009
French T, Savarirayan R (1993) Thanatophoric Dysplasia. In: Adam MP et al (eds) GeneReviews(®). University of Washington, Seattle
Hafner C, Toll A, Gantner S, Mauerer A, Lurkin I, Acquadro F, Fernández-Casado A, Zwarthoff EC, Dietmaier W, Baselga E, Parera E, Vicente A, Casanova A, Cigudosa J, Mentzel T, Pujol RM, Landthaler M, Real FX (2012) Keratinocytic epidermal nevi are associated with mosaic RAS mutations. J Med Genet 49:249–253
Jiang Y, Pan J, Guo D, Zhang W, Xie J, Fang Z, Guo C, Fang Q, Jiang W, Guo Y (2017) Two novel mutations in the PPIB gene cause a rare pedigree of osteogenesis imperfecta type IX. Clin Chim Acta 469:111–118
Li R, Wang J, Wang L, Lu Y, Wang C (2020) Two novel mutations of COL1A1 in fetal genetic skeletal dysplasia of Chinese. Mol Genet Genomic Med 8:e1105
Logié A, Dunois-Lardé C, Rosty C, Levrel O, Blanche M, Ribeiro A, Gasc JM, Jorcano J, Werner S, Sastre-Garau X, Thiery JP, Radvanyi F (2005) Activating mutations of the tyrosine kinase receptor FGFR3 are associated with benign skin tumors in mice and humans. Hum Mol Genet 14:1153–1160
Lord J, McMullan DJ, Eberhardt RY, Rinck G, Hamilton SJ, Quinlan-Jones E, Prigmore E, Keelagher R, Best SK, Carey GK, Mellis R, Robart S, Berry IR, Chandler KE, Cilliers D, Cresswell L, Edwards SL, Gardiner C, Henderson A, Holden ST, Homfray T, Lester T, Lewis RA, Newbury-Ecob R, Prescott K, Quarrell OW, Ramsden SC, Roberts E, Tapon D, Tooley MJ, Vasudevan PC, Weber AP, Wellesley DG, Westwood P, White H, Parker M, Williams D, Jenkins L, Scott RH, Kilby MD, Chitty LS, Hurles ME, Maher ER (2019) Prenatal exome sequencing analysis in fetal structural anomalies detected by ultrasonography (PAGE): a cohort study. Lancet 393:747–757
Marini JC, Cabral WA, Barnes AM, Chang W (2007) Components of the collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylation complex are crucial for normal bone development. Cell Cycle 6:1675–1681
Milks KS, Hill LM, Hosseinzadeh K (2017) Evaluating skeletal dysplasias on prenatal ultrasound: an emphasis on predicting lethality. Pediatr Radiol 47:134–145
Mortier GR, Cohn DH, Cormier-Daire V, Hall C, Krakow D, Mundlos S, Nishimura G, Robertson S, Sangiorgi L, Savarirayan R, Sillence D, Superti-Furga A, Unger S, Warman ML (2019) Nosology and classification of genetic skeletal disorders: 2019 revision. Am J Med Genet A 179:2393–2419
Naski MC, Wang Q, Xu J, Ornitz DM (1996) Graded activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 by mutations causing achondroplasia and thanatophoric dysplasia. Nat Genet 13:233–237
Ornitz DM, Marie PJ (2002) FGF signaling pathways in endochondral and intramembranous bone development and human genetic disease. Genes Dev 16:1446–1465
Persson M, Cnattingius S, Villamor E, Soderling J, Pasternak B, Stephansson O, Neovius M (2017) Risk of major congenital malformations in relation to maternal overweight and obesity severity: cohort study of 1.2 million singletons. Bmj 357:j2563
Petrovski S, Aggarwal V, Giordano JL, Stosic M, Wou K, Bier L, Spiegel E, Brennan K, Stong N, Jobanputra V, Ren Z, Zhu X, Mebane C, Nahum O, Wang Q, Kamalakaran S, Malone C, Anyane-Yeboa K, Miller R, Levy B, Goldstein DB, Wapner RJ (2019) Whole-exome sequencing in the evaluation of fetal structural anomalies: a prospective cohort study. The Lancet 393:758–767
Price ER, Zydowsky LD, Jin MJ, Baker CH, McKeon FD, Walsh CT (1991) Human cyclophilin B: a second cyclophilin gene encodes a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase with a signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:1903–1907
Pyott SM, Schwarze U, Christiansen HE, Pepin MG, Leistritz DF, Dineen R, Harris C, Burton BK, Angle B, Kim K, Sussman MD, Weis M, Eyre DR, Russell DW, McCarthy KJ, Steiner RD, Byers PH (2011) Mutations in PPIB (cyclophilin B) delay type I procollagen chain association and result in perinatal lethal to moderate osteogenesis imperfecta phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet 20:1595–1609
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American college of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet Med 17:405–424
Schramm T, Gloning KP, Minderer S, Daumer-Haas C, Hörtnagel K, Nerlich A, Tutschek B (2009) Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of skeletal dysplasias. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 34:160–170
Shi J, Ren M, Jia J, Tang M, Guo Y, Ni X, Shi T (2019) Genotype-phenotype association analysis reveals new pathogenic factors for osteogenesis imperfecta disease. Front Pharmacol 10:1200
Steinmann B, Westerhausen A, Constantinou CD, Superti-Furga A, Prockop DJ (1991) Substitution of cysteine for glycine-alpha 1–691 in the pro alpha 1(I) chain of type I procollagen in a proband with lethal osteogenesis imperfecta destabilizes the triple helix at a site C-terminal to the substitution. Biochem J 279(Pt 3):747–752
Superti-Furga A, Unger S (1993) CHST3-Related Skeletal Dysplasia. In: Adam MP et al (eds) GeneReviews(®). University of Washington, Seattle 1993–2022. PMID: 21882400
Tang J, Zhou C, Shi H, Mo Y, Tan W, Sun T, Zhu J, Li Q, Li H, Li Y, Wang S, Hong Y, Li N, Zeng Q, Tan J, Ma W, Luo L (2020) Prenatal diagnosis of skeletal dysplasias using whole exome sequencing in China. Clin Chim Acta 507:187–193
Tavormina PL, Shiang R, Thompson LM, Zhu YZ, Wilkin DJ, Lachman RS, Wilcox WR, Rimoin DL, Cohn DH, Wasmuth JJ (1995) Thanatophoric dysplasia (types I and II) caused by distinct mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3. Nat Genet 9:321–328
Unger S, Lausch E, Rossi A, Megarbane A, Sillence D, Alcausin M, Aytes A, Mendoza-Londono R, Nampoothiri S, Afroze B, Hall B, Lo IF, Lam ST, Hoefele J, Rost I, Wakeling E, Mangold E, Godbole K, Vatanavicharn N, Franco LM, Chandler K, Hollander S, Velten T, Reicherter K, Spranger J, Robertson S, Bonafe L, Zabel B, Superti-Furga A (2010) Phenotypic features of carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3 (CHST3) deficiency in 24 patients: congenital dislocations and vertebral changes as principal diagnostic features. Am J Med Genet A 152A:2543–2549
van Dijk FS, Nesbitt IM, Zwikstra EH, Nikkels PGJ, Piersma SR, Fratantoni SA, Jimenez CR, Huizer M, Morsman AC, Cobben JM, van Roij MHH, Elting MW, Verbeke JIML, Wijnaendts LCD, Shaw NJ, Högler W, McKeown C, Sistermans EA, Dalton A, Meijers-Heijboer H, Pals G (2009) PPIB mutations cause severe osteogenesis imperfecta. The Am J Human Genet 85:521–527
van Dijk FS, Cobben JM, Kariminejad A, Maugeri A, Nikkels PG, van Rijn RR, Pals G (2011) Osteogenesis imperfecta: a review with clinical examples. Mol Syndromol 2:1–20
Van Dijk FS, Sillence DO (2014) Osteogenesis imperfecta: clinical diagnosis, nomenclature and severity assessment. Am J Med Genet A 164a:1470–1481
Waller DK, Correa A, Vo TM, Wang Y, Hobbs C, Langlois PH, Pearson K, Romitti PA, Shaw GM, Hecht JT (2008) The population-based prevalence of achondroplasia and thanatophoric dysplasia in selected regions of the US. Am J Med Genet A 146a:2385–2389
Wapner RJ, Martin CL, Levy B, Ballif BC, Eng CM, Zachary JM, Savage M, Platt LD, Saltzman D, Grobman WA, Klugman S, Scholl T, Simpson JL, McCall K, Aggarwal VS, Bunke B, Nahum O, Patel A, Lamb AN, Thom EA, Beaudet AL, Ledbetter DH, Shaffer LG, Jackson L (2012) Chromosomal microarray versus karyotyping for prenatal diagnosis. N Engl J Med 367:2175–2184
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y:Y drafted the manuscript. MW: acquired the clinic data. HW: analyzed and interpreted the patient data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of Interest.
Ethical approval
This retrospective chart review study involving human participants was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hangzhou Maternity and Child Care Hospital and was in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from the parents.
Consent to publication
The patients had provided their consent for publication.
Additional information
Communicated by Shuhua Xu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Wang, M. & Wang, H. Prenatal trio-based whole exome sequencing in fetuses with abnormalities of the skeletal system. Mol Genet Genomics 297, 1017–1026 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01899-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01899-x