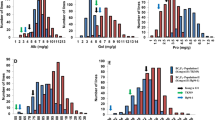
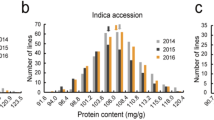
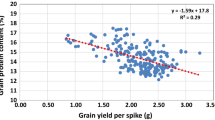
Abstract
Rice is the staple food for majority of the global population. But, rice grain has low protein content (PC). Mapping of QTLs controlling grain PC is essential for enhancement of the trait through breeding programs. A shortlisted panel population for grain protein content was studied for genetic diversity, population structure and association mapping for grain PC. Phenotyping results showed a wide variation for grain PC. The panel population showed a moderate level of genetic diversity estimated through 98 molecular markers. AMOVA and structure analysis indicated linkage disequilibrium for grain PC and deviation of Hardy–Weinberg’s expectation. The analysis showed 15% of the variation among populations and 73% among individuals in the panel population. STRUCTURE analysis categorized the panel population into three subpopulations. The analysis also revealed a common primary ancestor for each subpopulation with few admix individuals. Marker-trait association using 98 molecular markers detected 7 strongly associated QTLs for grain PC by both MLM and GLM analysis. Three novel QTLs qPC3.1, qPC5.1 and qPC9.1 were detected for controlling the grain PC. Four reported QTLs viz., qPC3, QPC8, qPC6.1 and qPC12.1 were validated for use in breeding programs. Reported QTLs, qPC6, qPC6.1 and qPC6.2 may be same QTL controlling PC in rice. A very close marker RM407 near to protein controlling QTL, qProt8 and qPC8, was detected. The study provided clue for simultaneous improvement of PC with high grain yield in rice. The strongly associated markers with grain PC, namely qPC3, qPC3.1, qPC5.1, qPC6.1, qPC8, qPC9.1 and qPC12.1, will be useful for their pyramiding for developing protein rich high yielding rice.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets utilized for reaching at the conclusions are present within the paper.
References
Agrama HA, Eizenga GC (2008) Molecular diversity and genome-wide linkage disequilibrium patterns in a worldwide collection of Oryza sativa and its wild relatives. Euphytica 160(3):339–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9535-y
Agrama HA, Eizenga GC, Yan W (2007) Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Mol Breeding 19(4):341–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9066-6
Aluko G, Martinez C, Tohme J, Castano C, Bergman C, Oard JH (2004) QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa X O. glaberrima. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):630–639
Anandan A, Anumalla M, Pradhan SK, Ali J (2016) Population structure, diversity and trait association analysis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm for early seedling vigor (ESV) using trait linked SSR markers. PLoS One 11(3):406. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152406
Bagchi TB, Sharma SG, Chattopadhyay K (2015) Development of NIRS models to predict protein and amylose content of brown rice and proximate compositions of rice bran. Food Chem 191:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.038
Banerjee S, Chandel G, Mandal Meena NM, Saluja T (2011) Assessment of nutritive value in milled rice grain of some indian rice landraces and their molecular characterization. Bangladesh J Agril Res 36(3):369–380
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635 (PMID: 17586829)
Carnahan HL, Wiser WJ, Rutger JN (1972) Associations between protein content and other characters in rice (abstr.). In: Proc. 14th rice tech. working group, Univ. California, Davis. pp 31–32
Chen H, He H, Zou Y, Chen W, Yu R, Liu X, Yang Y, Gao Y-M, Xu J-L, Fan L-M (2011) Development and application of a set of breeder-friendly SNP markers for genetic analyses and molecular breeding of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 123(6):869–879
Coffman WR, Juliano BO (1987) Rice. In: Olson RA, Frey KJ (eds) Nutritional quality of cereal grains: genetic and agronomic improvement. Agronomy monograph no. 28, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 101–131
Earl DA, Von HBM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4(2):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14(8):2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x (PMID: 15969739)
Faraji F, Esfahani M, Kavousi M, Nahvi M, Forghani A (2013) Effect of nitrogen fertilizer levels on Fe and protein content, grain breakage and grain yield of rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Khazar). Biharean Biol 7(1):25–28
Garris AJ, McCouch SR, Kresovich S (2003) Population structure and its effect on haplotype diversity and linkage disequilibrium surrounding the xa5 locus of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 165(2):759–769
Gearing ME (2015) Good as gold: Can golden rice and other biofortified crops prevent malnutrition? Science in the News, Harvard University. http://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/
Hao HL, Wei YZ, Yang X, Feng Y, Wu CY (2007) Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer levels on Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn concentration in shoot and quality in rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Sci 14(4):289–294
HiileRisLambers D, Rutger JN, Qualset CO, Wiser WJ (1972) Heritability of protein content and its relationship to agronomic characters in rice. In: Proc. 14th rice tech. Working group, Univ. California, Davis. pp 31
Hu Z, Li P, Zhou M, Zhang Z, Wang L, Zhu L, Zhu Y (2004) Mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for rice protein and fat content using doubled haploid lines. Euphytica 135(1):47–54
Huang X, Zhao Y, Wei X, Li C, Wang A, Zhao Q et al (2012) Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat Genet 44(1):32–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.1018
Huang Y, Sun C, Min J, Chen Y, Tong C, Bao J (2015) Association mapping of quantitative trait loci for mineral element contents in whole grain rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 63(50):10885–10892. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04932
Jin L, Lu Y, Shao YF, Zhang G, Xiao P, Shen SQ, Corke H, Bao JS (2010) Molecular marker assisted selection for improvement of the eating, cooking and sensory quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Cereal Sci 51:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2009.11.007
Kumar V, Singh A, Mithra ASV, Krishnamurthy SL, Parida SK, Jain S et al (2015) Genome-wide association mapping of salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa). DNA Res 22:133–145. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsu046
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21(9):2128–2129. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
Mahender A, Anandan A, Pradhan SK, Pandit E (2016) Rice grain nutritional traits and their enhancement using relevant genes and QTLs through advanced approaches. Springplus 5(1):2086. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3744-6
Mohanty A, Marndi BC, Sharma S, Das A (2011) Biochemical characterization of two high protein rice cultivars from Assam rice collections. Oryza 48(2):171–174
N’Goran JAK, Laurent V, Risterucci AM, Lanaud C (2000) The genetic structure of cocoa populations (Theobroma cacao L.) revealed by RFLP analysis. Euphytica 115(2):83–90
NRRI Annual Report (2015) ICAR-national rice research institute (NRRI). Cuttack, India
Oko AO, Ubi BE, Efisue AA, Dambaba N (2012) Comparative analysis of the chemical nutrient composition of selected local and newly introduced rice varieties grown in ebonyi state of nigeria. Int J Agric For 2(2):16–23
Pan Y, Zhang H, Zhang D, Li J, Xiong H, Yu J et al (2015) Genetic analysis of cold tolerance at the germination and booting stages in rice by association mapping. PLoS One 10:e0120590. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120590
Pandit E, Tasleem S, Barik SR, Mohanty DP, Nayak DK, Mohanty SP, Das S, Pradhan SK (2017) Genome-wide association mapping reveals multiple qtls governing tolerance response for seedling stage chilling stress in indica rice. Front Plant Sci 8:552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00552
Patil AH, Premi V, Sahu V, Dubey M, Sahu GR, Chandel G (2014) Identification of elite rice germplasm lines for grain protein content, ssr based genotyping and dna fingerprinting. Int J Agric For 2(2):16–23
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5, Genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 28(19):2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460 (PMID: 22820204)
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin software available at http://darwin.cirad.fr/darwin
Pradhan SK, Barik SR, Sahoo A, Mohapatra S, Nayak DK, Mahender A (2016) Population structure, genetic diversity and molecular marker-trait association analysis for high temperature stress tolerance in rice. PLoS One 11:e0160027. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160027
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959 (PMID: 10835412)
Qin Y, Kim SM, Sohn JK (2009) QTL analysis of protein content in double-haploid lines of rice. Korean J Crop Sci 54(2):165–171
Salgotra RK, Gupta BB, Bhat JA, Sharma S (2015) Genetic diversity and population structure of basmati rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm collected from North Western Himalayas using trait linked SSR markers. PLoS One. 10(7):e0131858. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131858
Swamy BPM, Shamsudin NAA, Rahman SNA, Mauleon R, Ratnam W, Cruz MTS, Kumar A (2017) Association mapping of yield and yield-related traits under reproductive stage drought stress in rice (oryza sativa l.). Rice 10(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-017-0161-6
Tan YF, Sun M, Xing YZ, Hua JP, Sun XL, Zhang QF, Corke H (2001) Mapping quantitative trait loci for milling quality, protein content and color characteristics of rice using a recombinant inbred line population derived from an elite rice hybrid. Theor Appl Genet 103(6,7):1037–1045
Terao T, Hirose T (2014) Control of grain protein contents through SEMIDWARF1 mutant alleles: sd1 increases the grain protein content in Dee-geo-woo-gen but not in Reimei. Mol Genet Genomics 290:939–954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0965-7
Singh N, Choudhury DR, Singh AK, Kumar S, Srinivasan K, Tyagi RK et al (2013) Comparison of SSR and SNP markers in estimation of genetic diversity and population structure of Indian rice varieties. PLoS One. 8(12):e84136. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084136
Uday G, Murthy MK, Hittalmani S (2014) Genetic analysis of recombinant inbred lines for total grain protein content and grain yeild in rice (oryza sativa l). Int J Agric Sci Res 4(2):51–58
Verma DK, Srivastava PP (2017) Proximate composition, mineral content and fatty acids analyses of aromatic and non-aromatic Indian rice. Rice Sci 24(1):21–31
Weng J, Gu S, Wan X, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Zhai H, Wan J (2008) Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res 18:1199–1209
Yang Y, Guo M, Li R, Shen L, Wang W, Liu M, Zhu Q, Hu Z, He Q, Yang X, Tang S, Gu M, Yan C (2015) Identification of quantitative trait loci responsible for rice grain protein content using chromosome segment substitution lines and fine mapping of qPC-1 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 35:130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0328-z
Yu YH, Li G, Fan YY, Zhang KQ, Min J, Zhu ZW, Zhuang JY (2009) Genetic relationship between grain yield and the contents of protein and fat in a recombinant inbred population of rice. J Cereal Sci 50(1):121–125
Yun B, Kim M, Handoyo T, Kim K (2014) Analysis of rice grain quality-associated quantitative trait loci by using genetic mapping. Am J Plant Sci 5(9):1125–1132. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2014.59125
Zhang W, Bi J, Chen L, Zheng L, Ji S, Xia Y, Xie K, Zhao Z, Wang Y, Liu L, Jiang L, Wan J (2008) QTL mapping for crude protein and protein fraction contents in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Cereal Sci 48:539–547
Zhang P, Li J, Li X, Liu X, Zhao X, Lu Y (2011) Population structure and genetic diversity in a rice core collection (Oryza sativa L.) investigated with SSR markers. PLoS One 6:e27565. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.20110027565 (pmid:22164211)
Zhang Y, Zou M, De T (2012) Association analysis of rice cold tolerance at tillering stage with SSR markers in Japonica cultivars in Northeast China. Chin J Rice Sci 26:423–430
Zhao K, Tung CW, Eizenga GC, Wright MH, Ali ML, Price AH (2011) Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa. Nat Commun 13(2):467. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1467
Zhao WG, Jong WC, Soon WK, Jeong HL, Kyung HM, Yong JP (2013) Association analysis of physicochemical traits on eating quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 191:9–21
Zheng L, Zhang W, Liu S, Chen L, Liu X, Chen X, Maa J, Chen W, Zhao Z, Jiang L, Wan J (2012) Genetic relationship between grain chalkiness, protein content, and paste viscosity properties in a backcross inbred population of rice. J Cereal Sci 56:153–160
Zhong M, Wang L, Yuan J, Luo L, Xu C, He YQ (2011) Identification of QTL affecting protein and amino acid contents in rice. Rice Sci 18(3):187–195
Zimmermann MB, Hurrell RF (2002) Improving iron, zinc and vitamin A nutrition through plant biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotech 13(2):142–145
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr.SK Nayak former Editor-In-Chief, Oryza for checking the manuscript. They also thank Director, ICAR-National Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, Odisha for full support in providing facilities for the research work.
Funding
This research work was supported by ICAR-National Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, Odisha, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: SKP EP. Performed the experiments: EP SP KC BB. Analysed the data: EP PD SS. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: SKP JNR. Wrote the paper: SKP EP Editing: SKP JNR.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors declare that this study complies with the current laws of the country in which the experiments were performed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1 (A) Scree plot and eigen values (B) loading values generated for four agro-morphologic component traits for 105 rice genotypes.
Fig. S2 The distribution pattern of (i) alpha-value showing leptokurtic symmetry and (ii-v) distribution of FST values in the sub-populations showing a symmetric shape derived from the studied panel population with K=2 (A) and K=3 (B).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pradhan, S.K., Pandit, E., Pawar, S. et al. Association mapping reveals multiple QTLs for grain protein content in rice useful for biofortification. Mol Genet Genomics 294, 963–983 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01556-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01556-w