Abstract
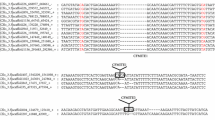
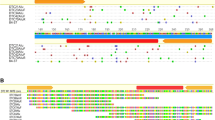
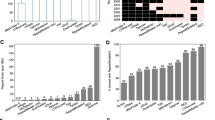
Transposable elements (TEs) are discrete DNA sequences which are able to replicate and jump into different genomic locations. Miniature inverted-repeats TEs (MITEs) are non-autonomous DNA elements whose origin is still poorly understood. Recently, some MITEs were found to contain core repeats that can be arranged in tandem arrays; in some instances, these arrays have even given rise to satellite DNAs in the (peri)centromeric region of the host chromosomes. I report the discovery and analysis of three new MITEs found in the genome of several termite species (hence the name terMITEs) in two different families. For two of the MITEs (terMITE1—Tc1/mariner superfamily; terMITE2—piggyBac superfamily), evidence of past mobility was retrieved. Moreover, these two MITEs contained core repeats, 16 bp and 114 bp long respectively, exhibiting copy number variation. In terMITE2, the tandem duplication appeared associated with element degeneration, in line with a recently proposed evolutionary model on MITEs and the origin of tandem arrays. Concerning their genomic distribution, terMITE1 and terMITE3 appeared more frequently inserted close to coding regions while terMITE2 was mostly associated with TEs. Although MITEs are commonly distributed in coding regions, terMITE2 distribution is in line with that of other insects’ piggyBac-related elements and of other small TEs found in termite genomes. This has been explained through insertional preference rather than through selective processes. Data presented here add to the knowledge on the poorly exploited polyneopteran genomes and will provide an interesting framework in which to study TEs’ evolution and host’s life history traits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bachtrog D (2003) Accumulation of Spock and Worf, two novel non-LTR retrotransposons, on the neo-Y chromosome of Drosophila miranda. Mol Biol Evol 20:173–181
Bartolome C, Maside X, Charlesworth B (2002) On the abundance and distribution of transposable elements in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 19:926–937
Bergamaschi S, Dawes-Gromadzki TZ, Scali V, Marini M, Mantovani B (2007) Karyology, mitochondrial DNA and the phylogeny of Australian termites. Chromosome Res 15:735–753
Coates BS, Kroemer JA, Sumerford DV, Hellmich RL (2011) A novel class of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs) that contain hitchhiking (GTCY)n microsatellites. Insect Mol Biol 20:15–27
Craig N (1997) Target site selection in transposition. Annu Rev Biochem 66:437–474
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190
Crothers DM (2006) Sequence-dependent properties of DNA and their role in function. In: Caporale LH (ed) The implicit genome. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 23–38
Dias GB, Svartman M, Delprat A, Ruiz A, Khun GCS (2014) Tetris is a Foldback transposon that provided the building blocks for an emerging satellite DNA of Drosophila virilis. Genome Biol Evol 6:1302–1313
Dolgin ES, Charlesworth B (2008) The effects of recombination rate on the distribution and abundance of transposable elements. Genetics 178:2169–2177
Engel MS, Grimaldi DA, Krishna K (2009) Termites (Isoptera): their phylogeny, classification, and rise to ecological dominance. Am Mus Novitat 3650:1–27
Fattash I, Rooke R, Wong A, Hui C, Luu T, Bhardway P, Yang G (2013) Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements: discovery, distribution, and activity. Genome 56:475–486
Feschotte C, Pritham E (2007) DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes. Annu Rev Genet 41:331–368
Feschotte C, Zhang X, Wessler SR (2002) Miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) and their relationship with established DNA transposons. In: Craig N, Craigie R, Gellert M, Lambowitz A (eds) Mobile DNA II. A.S.M. Press, Washington D.C., pp 1147–1158
Feschotte C, Swamy L, Wessler SR (2003) Genome-wide analysis of mariner-like transposable elements in rice reveals complex relationships with Stowaway miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs). Genetics 163:747–758
Gaffney PM, Pierce JC, Mackinley AG, Titchen DA, Glenn WK (2003) Pearl, a novel family of putative transposable elements in bivalve mollusks. J Mol Evol 56:308–316
Gao D, Chen J, Chen M, Meyers BC, Jackson S (2012) A highly conserved, small LTR retrotransposon that preferentially targets genes in grass genomes. PLoS One 7:e32010
Gentles AJ, Wakefield MJ, Kohany O, Gu W, Batzer MA, Pollok DD, Jurka J (2007) Evolutionary dynamics of transposable elements in the short-tailed opossum Monodelphis domestica. Genome Res 17:992–1004
Han M-J, Shen Y-H, Gao Y-H, Chen L-Y, Xiang Z-H, Zhang Z (2010) Burst expansion, distribution and diversification of MITEs in the silkworm genome. BMC Genom 11:520
Hirakawa M, Nishihara H, Kanehisa M, Okada N (2009) Characterization and evolutionary landscape of AmnSINE1 in Amniota genomes. Gene 441:100–110
International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860–921
Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, Walichiewicz J (2005a) Repbase Update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:462–467
Jurka J, Kohany O, Pavlicek A, Kapitonov VV, Jurka MV (2005b) Clustering, duplication and chromosomal distribution of mouse SINE retrotransposons. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:117–123
Kramerov DA, Vassetzky NS (2011) Origin and evolution of SINEs in eukaryotic genomes. Heredity 107:487–495
Kuhn GCS, Heslop-Harrison JS (2011) Characterization and genomic organization of PERI, a repetitive DNA in the Drosophila buzzatii cluster related to DINE-1 transposable elements and highly abundant in the sex chromosomes. Cytogenet Genome Res 132:79–88
Le Rouzic A, Deceliere G (2005) Models of the population genetics of transposable elements. Genet Res 85:171–181
Lenoir A, Lavie L, Prieto J-L, Goubely C, Côté J-C, Pélissier T, Deragon J-M (2001) The evolutionary origin and genomic organization of SINEs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biol Evol 18:2315–2322
Liu G, Geurts AM, Yae K, Srinivasan AR, Fahrenkrug SC, Largaespada DA, Takeda J, Horie K, Olson WK, Hackett PB (2005) Target-site preferences of Sleeping Beauty transposons. J Mol Biol 346:161–173
Lo N, Kitade O, Miura T, Constantino R, Matsumoto T (2004) Molecular phylogeny of the Rhinotermitidae. Insectes Soc 51:365–371
Lu C, Chen J, Zhang Y, Hu Q, Su W, Kuang H (2012) Miniature inverted–repeat transposable elements (MITEs) have been accumulated through amplification bursts and play important roles in gene expression and species diversity in Oryza sativa. Mol Biol Evol 29:1005–1017
Luchetti A, Mantovani B (2009) Talua SINE biology in the genome of the Reticulitermes subterranean termites (Isoptera, Rhinotermitidae). J Mol Evol 69:589–600
Luchetti A, Mantovani B (2011) Molecular characterization, genomic distribution and evolutionary dynamics of Short INterspersed Elements (SINEs) in the termite genome. Mol Genet Genomics 285:175–184
Luchetti A, Mantovani B (2013) Conserved domains and SINE diversity during animal evolution. Genomics 102:296–300
Luchetti A, Velonà A, Mueller M, Mantovani B (2013) Breeding systems and reproductive strategies in Italian Reticulitermes colonies (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Insectes Soc 60:203–211
Marzo M, Liu D, Ruiz A, Chalmers R (2013) Identification of multiple binding sites for the THAP domain of the Galileo transposase in the long terminal inverted-repeats. Gene 525:84–91
Matsuura K (2011) Sexual and asexual reproduction in termites. In: Bignell DE, Roisin Y, Lo N (eds) Biology of termites: a modern synthesis. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 255–277
Matsuura K, Vargo EL, Kawatsu K, Labadie PE, Nakano H et al (2009) Queen succession through asexual reproduction in termites. Science 323:1687
Mayer C (2006–2010) Phobos 3.3.11. http://www.ruhr-uni-bochum.de/ecoevo/cm/cm_phobos.htm [accessed 24 October 2014]
Miller WJ, Nagel A, Bachmann J, Bachmann L (2000) Evolutionary dynamics of the SGM transposon family in the Drosophila obscura species group. Mol Biol Evol 17:1597–1609
Naito K, Cho E, Yang G, Campbell MA, Yano K, Okumoto Y, Tanisaka T, Wessler SR (2006) Dramatic amplification of a rice transposable element during recent domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17620–17625
Ohshima K, Okada N (2005) SINEs and LINEs: symbionts of eukaryotic genomes with a common tail. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:475–490
Petrov DA, Fiston-Lavier AS, Lipatov M, Lenkov K, González J (2011) Population genomics of transposable elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 28:1633–1644
Plohl M, Luchetti A, Meštrović N, Mantovani B (2008) Satellite DNAs between selfishness and functionality: structure, genomics and evolution of tandem repeats in centromeric (hetero)chromatin. Gene 409:72–82
Ricci M, Luchetti A, Bonandin L, Mantovani B (2013) Random DNA libraries from three species of the stick insect genus Bacillus (Insecta: Phasmida): repetitive DNA characterization and first observation of polyneopteran MITEs. Genome 56:729–735
Šatović E, Plohl M (2013) Tandem repeat-containing MITEs in the clam Donax trunculus. Genome Biol Evol 5:2549–2559
Scalvenzi T, Pollet N (2014) Insights on genome size evolution from a miniature inverted repeat transposon driving a satellite DNA. Mol Phylogenet Evol 81:1–9
Surzycki SA, Belknap WR (2000) Repetitive-DNA elements are similarly distributed on Caenorhabditis elegans autosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:245–249
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Terrapon N, Li C, Robertson HM, Ji L, Meng X et al (2014) Molecular traces of alternative social organization in a termite genome. Nature Commun 5:3636
Tu Z (1997) Three novel families of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements are associated with genes of the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7475–7480
Tu Z (2001) Eight novel families of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1699–1704
Tu Z (2012) Insect transposable elements. In: Lawrence IG (ed) Insect molecular biology and Biochemistry. Elsevier, London, pp 57–89
Vargo EL, Husseneder C (2011) Genetic structure of termite colonies and populations. In: Bignell DE, Roisin Y, Lo N (eds) Biology of termites: a modern synthesis. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 321–347
Vargo EL, Labadie PE, Matsuura K (2012) Asexual queen succession in the subterranean termite Reticulitermes virginicus. Proc R Soc B 279:813–819
Vigdal TJ, Kaufman CD, Izsvac Z, Voytas DF, Ivics Z (2002) Common physical properties of DNA affecting target site selection of Sleeping Beauty and other Tc1/mariner transposable elements. J Mol Biol 323:441–452
Wallau GL, Capy P, Loreto E, Hua-Van A (2014) Genomic landscape and evolutionary dynamics of mariner transposable elements within the Drosophila genus. BMC Genom 15:727
Wang J, Du Y, Wang S, Brown SJ, Park Y (2008) Large diversity of the piggyBac-like elements in the genome of Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:490–498
Wang J, Wang A, Han Z, Zhang Z, Li F et al (2012) Characterization of Three Novel SINE Families with Unusual Features in Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS One 7:e31355
Wessler SR (2006) Eukaryotic transposable elements: teaching old genomes new tricks. In: Caporale LH (ed) The implicit genome. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 138–162
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P et al (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8:973–982
Wright SI, Schoen DJ (1999) Transposon dynamics and the breeding system. Genetica 107:139–148
Yang H-P, Barbash DA (2008) Abundant and species-specific DINE-1 transposable elements in 12 Drosophila genomes. Genome Biol 9:R39
Yang G, Nagel DH, Feschotte C, Hancock CN, Wessler SR (2009) Tuned for transposition: molecular determinants underlying the hyperactivity of a Stowaway MITE. Science 325:1391–1394
Zhou Y, Cahan SH (2012) A novel family of terminal-repeat retrotransposon in miniature (TRIM) in the genome of the red harvester ant, Pogonomyrmex barbatus. PLoS One 7:e53401
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by RFO-University of Bologna and Canziani funding. I wish to thank Barbara Mantovani and Miroslav Plohl for their suggestions and fruitful discussions. I am grateful to Danna G. Eickbush for the critical reading and the language editing of the manuscript. I wish also to thank two anonymous Reviewers, whose criticisms and suggestions helped to substantially improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luchetti, A. terMITEs: miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) in the termite genome (Blattodea: Termitoidae). Mol Genet Genomics 290, 1499–1509 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1010-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1010-1