Abstract
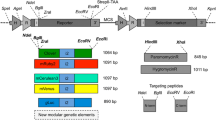
For the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a codon-adapted gene variant of the extracellular luciferase of Gaussia princeps was generated as a sensitive molecular tool to study gene expression from the nuclear genome. In the past, monitoring promoter activity in Chlamydomonas employing the commonly used luciferase encoded by Renilla reniformis was hampered due to the detection limit of the reporter assay, especially if analyzing weak promoters. In this work, the expression of Gaussia-luciferase from such promoters resulted in an average luminescent activity at least 500 times higher than that detected for the Renilla enzyme. The wildtype signal peptide of Gaussia princeps efficiently mediated the export of the luciferase into the culture medium of Chlamydomonas strain cw15arg −, and the characterization of the secreted protein showed an unexpected temperature instability, probably arising from post-translational modifications made by the algae. To further test the utility of Gaussia-luciferase, promoter sequences originating from different viral genomes were analyzed for their ability to drive transgene expression in Chlamydomonas. Solely, the 35S-promoter of the Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) displayed a significant transcriptional activity and this happened only when the shunting region of the 5′-untranslated region of the 35S-sequence was omitted from the luciferase expression cassette. Gaussia-luciferase proved to be a superior quantifiable reporter gene for the analysis of constitutive promoter sequences in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babinger K, Hallmann A, Schmitt R (2006) Translational control of regA, a key gene controlling cell differentiation in Volvox carteri. Development 133:4045–4051
Battraw MJ, Hall TC (1990) Histochemical analysis of CaMV 35S promoter-beta-glucuronidase gene expression in transgenic rice plants. Plant Mol Biol 15:527–538
Blankenship JE, Kindle KL (1992) Expression of chimeric genes by the light-regulated cabII–1 promoter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: a cabII-1/nit1 gene functions as a dominant selectable marker in a nit1- nit2- strain. Mol Cell Biol 12:5268–5279
Croft MT, Moulin M, Webb ME, Smith AG (2007) Thiamine biosynthesis in algae is regulated by riboswitches. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20770–20775
Davies JP, Weeks DP, Grossman AR (1992) Expression of the arylsulfatase gene from the beta 2-tubulin promoter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res 20:2959–2965
Day A, Debuchy R, van Dillewijn J, Purton S, Rochaix JD (1990) Studies on the maintenance and expression of cloned DNA fragments in the nuclear genome of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Physiol Plant 78:254–260
de Hostos EL, Togasaki RK, Grossman A (1988) Purification and biosynthesis of a derepressible periplasmic arylsulfatase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol 106:29–37
Fuhrmann M (2002) Expanding the molecular toolkit for Chlamydomonas reinhardtii—from history to new frontiers. Protist 153:357–364
Fuhrmann M, Hausherr A, Ferbitz L, Schodl T, Heitzer M, Hegemann P (2004) Monitoring dynamic expression of nuclear genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a synthetic luciferase reporter gene. Plant Mol Biol 55:869–881
Fuhrmann M, Oertel W, Hegemann P (1999) A synthetic gene coding for the green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a versatile reporter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 19:353–361
Griffiths CM, Page MJ (1997) Production of heterologous proteins using the baculovirus/insect expression system. Methods Mol Biol 75:427–440
Harris EH (1989) The Chlamydomonas sourcebook: a comprehensive guide to biology and laboratory use. Academic Press, San Diego
Harris EH (2001) Chlamydomonas as a model organism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:363–406
Hasnain SE, Manavathu EK, Leung WC (1985) DNA-mediated transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardi cells: use of aminoglycoside 3′-phosphotransferase as a selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol 5:3647–3650
Heitzer M, Zschoernig B (2007) Construction of modular tandem expression vectors for the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using the Cre/lox-system. Biotechniques 43:324, 326, 328 passim
Inouye S, Sahara Y (2008) Identification of two catalytic domains in a luciferase secreted by the copepod Gaussia princeps. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:96–101
Julenius K, Molgaard A, Gupta R, Brunak S (2005) Prediction, conservation analysis, and structural characterization of mammalian mucin-type O-glycosylation sites. Glycobiology 15:153–164
Kang M, Duncan DD, van Etten JL (2005) Chlorovirus: a genus of Phycodnaviridae that infects certain chlorella-like green algae. Mol Plant Pathol 6:213–224
Kang M, Han JG, Liu PF, Ye Y, Tien P (2000) [The regulation activity of Chlorella virus gene 5′ upstream sequence in Escherichia coli and eucaryotic alage]. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 16:443–446
Kiaulehn S, Voytsekh O, Fuhrmann M, Mittag M (2007) The presence of UG-repeat sequences in the 3′-UTRs of reporter luciferase mRNAs mediates circadian expression and can determine acrophase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Rhythms 22:275–277
Kindle KL, Schnell RA, Fernandez E, Lefebvre PA (1989) Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas using the Chlamydomonas gene for nitrate reductase. J Cell Biol 109:2589–2601
Kobayashi K, Tsuge S, Stavolone L, Hohn T (2002) The Cauliflower mosaic virus virion-associated protein is dispensable for viral replication in single cells. J Virol 76:9457–9464
Kutish GF, Li Y, Lu Z, Furuta M, Rock DL, Van Etten JL (1996) Analysis of 76 kb of the chlorella virus PBCV-1 330-kb genome: map positions 182 to 258. Virology 223:303–317
Matsuo T, Onai K, Okamoto K, Minagawa J, Ishiura M (2006) Real-time monitoring of chloroplast gene expression by a luciferase reporter: evidence for nuclear regulation of chloroplast circadian period. Mol Cell Biol 26:863–870
Mayfield SP, Kindle KL (1990) Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a C. reinhardtii gene as the selectable marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2087–2091
Mayfield SP, Schultz J (2004) Development of a luciferase reporter gene, luxCt, for Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. Plant J 37:449–458
Minko I, Holloway SP, Nikaido S, Carter M, Odom OW, Johnson CH, Herrin DL (1999) Renilla luciferase as a vital reporter for chloroplast gene expression in Chlamydomonas. Mol Gen Genet 262:421–425
Narva KE, Wendell DL, Skrdla MP, Van Etten JL (1987) Molecular cloning and characterization of the gene encoding the DNA methyltransferase, M.CviBIII, from Chlorella virus NC-1A. Nucleic Acids Res 15:9807–9823
Ow DW, Jacobs JD, Howell SH (1987) Functional regions of the Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA promoter determined by use of the firefly luciferase gene as a reporter of promoter activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4870–4874
Pooggin MM, Futterer J, Skryabin KG, Hohn T (2001) Ribosome shunt is essential for infectivity of Cauliflower mosaic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:886–891
Rajam MV, Kumar SV (2006) Green Alga (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii). Methods Mol Biol 344:421–433
Rochaix JD (1995) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as the photosynthetic yeast. Annu Rev Genet 29:209–230
Ryabova LA, Hohn T (2000) Ribosome shunting in the Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA leader is a special case of reinitiation of translation functioning in plant and animal systems. Genes Dev 14:817–829
Schroda M (2006) RNA silencing in Chlamydomonas: mechanisms and tools. Curr Genet 49:69–84
Shao N, Krieger-Liszkay A, Schroda M, Beck CF (2007) A reporter system for the individual detection of hydrogen peroxide and singlet oxygen: its use for the assay of reactive oxygen species produced in vivo. Plant J 50:475–487
Southern PJ, Berg P (1982) Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet 1:327–341
Stevens DR, Rochaix JD, Purton S (1996) The bacterial phleomycin resistance gene ble as a dominant selectable marker in Chlamydomonas. Mol Gen Genet 251:23–30
Tabor S, Richardson CC (1985) A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:1074–1078
Tang DK, Qiao SY, Wu M (1995) Insertion mutagenesis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by electroporation and heterologous DNA. Biochem Mol Biol Int 36:1025–1035
Tannous BA, Kim DE, Fernandez JL, Weissleder R, Breakefield XO (2005) Codon-optimized Gaussia luciferase cDNA for mammalian gene expression in culture and in vivo. Mol Ther 11:435–443
Vallon O, Wollman FA (1995) Mutations affecting O-glycosylation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cause delayed cell wall degradation and sex-limited sterility. Plant Physiol 108:703–712
Verhaegent M, Christopoulos TK (2002) Recombinant Gaussia luciferase. Overexpression, purification, and analytical application of a bioluminescent reporter for DNA hybridization. Anal Chem 74:4378–4385
Wiles S, Ferguson K, Stefanidou M, Young DB, Robertson BD (2005) Alternative luciferase for monitoring bacterial cells under adverse conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3427–3432
Wurm F, Bernard A (1999) Large-scale transient expression in mammalian cells for recombinant protein production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10:156–159
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Markus Fuhrmann for designing the cgluc gene and Meike Priesmeier-Gradl for perfect technical assistance. This work was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the Bavarian Ministry of Economic Affairs, Infrastructure, Transport and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Dieckmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruecker, O., Zillner, K., Groebner-Ferreira, R. et al. Gaussia-luciferase as a sensitive reporter gene for monitoring promoter activity in the nucleus of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Genet Genomics 280, 153–162 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0352-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0352-3