Abstract
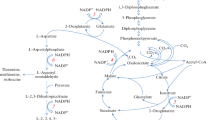
The biosynthesis and catabolism of lysine in Penicillium chrysogenum is of great interest because these pathways provide 2-aminoadipic acid, a precursor of the tripeptide δ-L-2-aminoadipyl-L-cysteinyl-D-valine that is an intermediate in penicillin biosynthesis. In vivo conversion of labelled L-lysine into two different intermediates was demonstrated by HPLC analysis of the intracellular amino acid pool. L-lysine is catabolized to 2-aminoadipic acid by an ω-aminotransferase and to saccharopine by a lysine-2-ketoglutarate reductase. In lysine-containing medium both activities were expressed at high levels, but the ω-aminotransferase activity, in particular, decreased sharply when ammonium was used as the nitrogen source. The ω-aminotransferase was partially purified, and found to accept L-lysine, L-ornithine and, to a lesser extent, N-acetyl-L-lysine as amino-group donors. 2-Ketoglutarate, 2-ketoadipate and, to a lesser extent, pyruvate served as amino group acceptors. This pattern suggests that this enzyme, previously designated as a lysine-6-aminotransferase, is actually an ω-aminotransferase. When 2-ketoadipate is used as substrate, the reaction product is 2-aminoadipic acid, which contributes to the pool of this intermediate available for penicillin biosynthesis. The N-terminal end of the purified 45-kDa ω-aminotransferase was sequenced and was found to be similar to the corresponding segment of the OAT1 protein of Emericella (Aspergillus) nidulans. This information was used to clone the gene encoding this enzyme.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonowitz Y et al (1993) Delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase, the multienzyme integrating the four primary reactions in beta-lactam biosynthesis, as a model peptide synthetase. Biotechnology 11:807–810
Aharonowitz Y, Cohen G, Martín JF (1992) Penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthetic genes: structure, organisation, regulation, and evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol 46:461–495
Albrecht AM, Vogel HJ (1964) Acetylornithine δ-transaminase. Partial purification and repression behavior. J Biol Chem 239:1872–1876
Arruda P, Kemper EL, Papes F, Leite A (2000) Regulation of lysine catabolism in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci 5:324–330
Bañuelos O, Casqueiro J, Fierro F, Hijarrubia MJ, Gutiérrez S, Martín JF (1999) Characterization and lysine control of expression of the lys1 gene of Penicillium chrysogenum encoding homocitrate synthase. Gene 226:51–59
Bañuelos O, Casqueiro J, Gutiérrez S, Martín JF (2000) Overexpression of the lys1 gene in Penicillium chrysogenum: Homocitrate synthase levels, α-aminoadipic acid pool and penicillin production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:69–77
Bhattacharjee JK (1985) α-Aminoadipate pathway for the biosynthesis of lysine in lower eukaryotes. Crit Rev Microbiol 12:131–151
Casqueiro J, Gutiérrez S, Bañuelos O, Fierro F, Velasco J, Martín JF (1998) Characterization of the lys2 gene of Penicillium chrysogenum encoding α-aminoadipic acid reductase. Mol Gen Genet 259:549–556
Casqueiro J, Gutiérrez S, Bañuelos O, Hijarrubia MJ, Martín JF (1999) Gene targeting in Penicillium chrysogenum: Disruption of the lys2 gene leads to penicillin overproduction. J Bacteriol 181:1181–1188
Chang YF, Adams E (1971) Induction of separate catabolic pathways for L- and D-lysine in Pseudomonas putida. Biochem Biophys Acta 45:570–576
Chang YF, Adams E (1974) D-lysine catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas putida: interrelations with L-lysine catabolism. J Bacteriol 117:753–764
Coque JJR, Liras P, Láiz L, Martín JF (1991) A gene encoding lysine 6-aminotransferase, which forms the β-lactam precursor α-aminoadipic acid, is located in the cluster of cephamycin biosynthetic genes in Nocardia lactamdurans. J Bacteriol 173:6258–6264
Díez B, Gutiérrez S, Barredo JL, van Solingen P, van der Voort Lucia HM, Martín JF (1990) The cluster of penicillin biosynthetic genes. J Biol Chem 265:16358–16365
Diez B, Mellado E, Rodríguez M, Bernasconi E, Barredo JL (1999) The NADP-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase gene from Penicillium chrysogenum and the construction of expression vectors for filamentous fungi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:196–207
Dzikowska A, Swianiewicz M, Talarczyk A, Wisniewska M, Goras M, Scazzocchio C, Weglenski P (1999) Cloning, characterisation and regulation of the ornithine transaminase (otaA) gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Curr Genet 35:118–126
Esmahan C, Álvarez E, Montenegro E, Martín JF (1994) Catabolism of lysine in Penicillium chrysogenum leads to formation of a-aminoadipic acid, a precursor of penicillin biosynthesis. Appl Enviroment Microbiol 60:1705–1710
Fangmeier N, Leistner E (1980) A 15N NMR study on D-lysine metebolism in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem 255:10205–10209
Fierro F, Barredo JL, Díez B, Gutiérrez S, Fernández FJ, Martín JF (1995) The penicillin gene cluster is amplified in tandem repeats linked by conserved hexanucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6200–6204
Fothergill JC, Guest JR (1977) Catabolism of L-lysine by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol 99:139–155
Friedrich GC, Demain AL (1978) Uptake and metabolism of (-aminoadipate by Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Microbiol 119:43–47
Hijarrubia MJ, Aparicio JF, Martín JF (2002) Nitrate regulation of α-Aminoadipate reductase formation and lysine inhibition of its activity in Penicillium chrysogenum and Acremonium chrysogenum. Appl Microb Biotechnol 59:270–277
Hönlinger C, Kubicek CP (1989) Regulation of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine and isopenicillin N biosynthesis in Penicillium chrysogenum by the alpha-aminoadipate pool size. FEMS Microbiol Lett 53:71–75
Kern BA, Hendlin D, Inamine E (1980) L-lysine ε-aminotransferase involved in cephamycin C synthesis in Streptomyces luctamdurans. Antimicrob Agents Chemoter 17:679–685
Kinzel JJ, Winston MK, Bhattacharjee JK (1983) Role of L-lysine-α-ketoglutarate aminotransferase in catabolism of lysine as a nitrogen source for Rhodotorula glutinis. J Bacteriol 155:417–419
Madduri K, Shapiro S, DeMarco AC, White RL, Stuttard C, Vining C (1991) Lysine catabolism and α-Aminoadipate synthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:358–363
Markovitz PJ, Chuang DT, Cox RP (1984) Familial hyperlysinemias : purification and characterization of the bi-functional aminoadipic acid semialdehyde synthase with lysine-ketoglutarate reductase and saccharopine dehydrogenase activities. J Biol Chem 259:11643–11646
Martín JF (1998) New aspects of genes and enzymes for ß-lactam antibiotic biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:1–15
Martín JF (2000) α-Aminoadipyl-cysteinyl-valine synthetases in ßlactam producing organisms. From Abraham’s discoveries to novel concepts of non-ribosomal peptide synthesis. J Antibiot 53:1008–1021
Naranjo L et al (2005)
Naranjo L, Martín de Valmaseda E, Bañuelos O, López P, Riaño J, Casqueiro J, Martín JF (2001) Conversion of pipecolic acid into lysine in Penicillium chrysogenum requires pipecolate oxidase and saccharopine reductase: characterization of the lys7 gene encoding saccharopine reductase. J Bacteriol 183:7165–7172
Nishida H, Nishiyama M (2000) What is characteristic of fungal lysine synthesis through the α-Aminoadipate pathway? J Mol Evol 51:299–302
Novak J, Kopecky J, Vanek Z (1997) Nitrogen source regulates expression of alanine dehydrogenase isoenzymes in Streptomyces avermitilis in a chemically defined medium. Can J Microbiol 43:189–193
Papes F, Kemper EL, Cord-Neto G, Langone F, Arruda P (1999) Lysine degradation through the saccharopine pathway in mammals: involvement of both bifunctional and monofunctional lysine-degrading enzymes in mouse. Biochem J 344:555–563
Perez-Llarena FJ, Rodríguez-García A, Enguita FJ, Martín JF, Liras P (1998) The pcd gene encoding piperideine-6-carboxylate dehydrogenase involved in biosynthesis of α-aminoadipic acid is located in the cephamycin cluster of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Bacteriol 180:4753–4756
Schmidt H, Bode R, Birnbaum D (1988) A novel enzyme, L-lysine:pyruvate aminotransferase, catalyses the first step of lysine catabolism in Pichia guilliermondii. FEMS Microbiol Lett 49:203–206
Shapiro S (1989) Nitrogen assimilation in actinomycetes and the influence of nitrogen nutrition on actinomycete secondary metabolism. In: Shapiro S (ed) Regulation of secondary metabolism in actinoycetes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 135–211
Sim KL, Perry D (1997) Analysis of swainsonine and its early metabolic precursors in cultures of Metarhizium anisopliae. Glycoconj J 14:661–668
Soda K, Misono H (1971) L-lysine-a-ketoglutarate aminotransferase. Methods Enzymol 17B:222–228
Soda K, Misono H, Yamamoto T (1968) L-Lysine:alpha-ketoglutarate aminotransferase. I. Identification of a product, delta-1-piperideine-6-carboxylic acid. Biochemistry 7:4102–4109
Tanizawa K, Yoshimura T, Asada Y, Sawada S, Misono H, Soda K (1982) Stereochemistry of proton abstraction catalyzed by lysine and ornithine ω-aminotransferases. Biochemistry 21:1104–1108
Wade M, Thomson DM, Miflin BJ (1980) Saccharopine: an intermediate of L-lysine biosynthesis and degradation in Pyriculia oryzae. J Gen Microbiol 120: 11–20
Yonaha K, Nishie M, Aibara S (1992) The primary structure of w-amino acid: pyruvate aminotransferase. J Biol Chem 267:12506–12510
Zabriskie TM, Jackson MD (2000) Lysine biosynthesis and metabolism in fungi. Nat Prod Rep 17:85–97
Zhu X, Tang G, Galili G (2000) Characterization of the two saccharopine dehydrogenase isozymes of lysine catabolism encoded by the single composite AtLKR/SDH locus of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:1363–1371
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the CICYT (BIO2000-1729-C02-02 and FIT-01000-2001-130). L. Naranjo was a Fellow of the AECI Programme (Ministerio de Asuntos Exteriores, Madrid)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valmaseda, E.M.M.d., Campoy, S., Naranjo, L. et al. Lysine is catabolized to 2-aminoadipic acid in Penicillium chrysogenum by an omega-aminotransferase and to saccharopine by a lysine 2-ketoglutarate reductase. Characterization of the omega-aminotransferase. Mol Genet Genomics 274, 272–282 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0018-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0018-3