Abstract
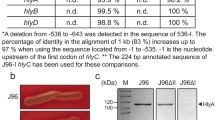
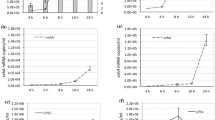
Here we investigate the expression of cylL L and cylL S , the genes that encode the structural subunits of the cytolysin/haemolysin of Enterococcus faecalis, in response to aerobiosis conditions. Haemolysis assays of E. faecalis strains cultured under aerobic and anaerobic conditions revealed three different haemolytic phenotypes, one of which exhibited greater haemolysis under anaerobic conditions than under aerobic conditions, and was shown to be associated with the presence of the cyl genes. Reporter gene studies revealed that cylL L L S promoter activity was significantly greater (up to 8.6-fold) under anaerobic compared to aerobic conditions throughout batch growth, demonstrating that these genes are regulated in response to the degree of aerobiosis. Band shift assays confirmed the binding of a protein factor to the region between 202 and 37 bp upstream of the cylL L start codon, and a higher level of binding was observed with anaerobically derived cell-free extracts than with extracts of aerobically grown cells. This is the first report of an oxygen-regulated virulence factor in E. faecalis (that is distinct from the quorum-sensing regulatory system reported previously), and may be of in vivo relevance for the bacterium in biofilms and other environments characterised by oxygen gradients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DG, McKay LL (1983) Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:549–552
Basinger SF, Jackson RW (1968) Bacteriocine (hemolysin) of Streptococcus zymogenes. J Bacteriol 96:1895–1902
Booth MC, Hatter KL, Miller D, Davis J, Kowalski R, Parke DW, Chodosh J, Jett BD, Callegan MC, Penland R, Gilmore MS (1998) Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in endophthalmitis. Infect Immun 66:356–360
Coburn PS, Hancock LE, Booth MC, Gilmore MS (1999) A novel means of self-protection, unrelated to toxin activation, confers immunity to the bactericidal effects of the Enterococcus faecalis cytolysin. Infect Immun 67:3339–3347
Costerton JW, Lewandowski Z, Caldwell DE, Korber DR, Lappin-Scott HM (1995) Microbial biofilms. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:711–745
Cruz-Rodz AL, Gilmore MS (1990) High efficiency introduction of plasmid DNA into glycine treated Enterococcus faecalis by electroporation. Mol Gen Genet 224:152–154
Day AM, Sandoe JAT, Cove JH, Phillips-Jones MK (2001) Evaluation of a biochemical test scheme for identifying clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:392–396
Dunny GM, Lee LN, LeBlanc DJ (1991) Improved electroporation and cloning vector system for Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1194–1201
Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study Group (1996) Microbiologic factors and visual outcome in the endophthalmitis vitrectomy study. Am J Ophthalmol 122:830–846
Facklam RR, Collins MD (1989) Identification of Enterococcus species isolated from human infections by a conventional test scheme. J Clin Microbiol 27:731–734
Facklam RR, Sahm DF (1995) Enterococcus. In: Murray PR, Baron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover FC, Yolken RH (eds) Manual of clinical microbiology (6th edn). American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 308–314
Facklam RR, Teixeira LM (1998) Enterococcus. In: Collier L, Balows A, Sussman M (eds) Topley and Wilson's Microbiology and microbial infections. Arnold, London, pp 669–682
Gilmore MS, Segarra RA, Booth MC, Bogie C, Hall LR, Clewell DB (1994) Genetic structure of the Enterococcus faecalis cytolytic toxin system and its relationship to lantibiotic determinants. J Bacteriol 176:7335–7344
Haas W, Gilmore MS (1999) Molecular nature of a novel bacterial toxin: the cytolysin of Enterococcus faecalis. Med Microbiol Immunol 187:183–190
Haas W, Shepard BD, Gilmore MS (2002) Two-component regulator of Enterococcus faecalis cytolysin responds to quorum-sensing autoinduction. Nature 415:84–87
Heim R, Prasher DC, Tsien RY (1994) Wavelength mutations and posttranslational autoxidation of green fluorescent protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12501–12504
Huycke MM, Spiegel CA, Gilmore MS (1991) Bacteremia caused by hemolytic, high-level gentamicin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 35:1626–1634
Ike Y, Hashimoto H, Clewell DB (1984) Hemolysis of Streptococcus faecalis subspecies zymogenes contributes to virulence in mice. Infect Immun 45:528–530
Ike Y, Hashimoto H, Clewell DB (1987) High incidence of hemolysin production by Enterococcus (Streptococcus) faecalis strains associated with human parental infections. J Clin Microbiol 25:1524–1528
Ike Y, Clewell DB, Segarra RA, Gilmore MS (1990) Genetic analysis of the pAD1 hemolysin/bacteriocine determinant in Enterococcus faecalis: Tn917 insertional mutagenesis and cloning. J Bacteriol 172:155–163
Joyanes PA, Pascual A, Martínez-Martínez L, Hevia A, Perea EJ (2000) In vitro adherence of Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium to urinary catheters. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 19:124–127
Keane PF, Bonner MC, Johnston SR, Zafar A, Gorman SP (1994) Characterization of biofilm and encrustation on ureteric stents in vivo. Br J Urol 73:687–691
Leclerq R (1997) Enterococci acquire new kinds of resistance. Clin Infect Dis 24 (Suppl 1):S80–S84
MacInnes JI, Kim JE, Lian CJ-, Soltes GA (1990) Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae hlyX gene homology with the fnr gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 172:4587–4592
Macrina FL, Ash Tobian J, Jones KR, Evans RP, Clewell DB (1982) A cloning vector able to replicate in Escherichia coli and Streptococcus sanguis. Gene 19:345–353
McGlynn P, Hunter CN (1992) Isolation and characterisation of a putative transcription factor involved in the regulation of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides pucBA operon. J Biol Chem 267:11098–11103
Megran DW (1992) Enterococcal endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis 15:63–71
Miyazaki S, Ohno A, Kobayashi I, Uji T, Yamaguchi K, Goto S (1993) Cytotoxic effect of hemolytic culture supernatant from Enterococcus faecalis on mouse polymorphonuclear neutrophils and macrophages. Microbiol Immunol 37:265–270
Moellering RC Jr (1992) Emergence of Enterococcus as a significant pathogen. Clin Infect Dis 14:1173–1178
Phillips-Jones MK (2000) Use of a lux reporter system for monitoring rapid changes in α-toxin gene expression in Clostridium perfringens during growth. FEMS Microbiol Lett 188:29–33
Ralph ET, Guest JR, Green J (1998) Altering the anaerobic transcription factor FNR confers a haemolytic phenotype on Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10449–10452
Ritchey TW, Seeley HW Jr (1974) Cytochromes in Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes grown in a haematin-containing medium. J Gen Microbiol 85:220–228
Ross RP, Claiborne A (1997) Evidence for regulation of the NADH peroxidase gene (npr) from Enterococcus faecalis by OxyR. FEMS Microbiol Lett 151:177–183
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd edn). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Scott KP, Mercer DK, Glover LA, Flint HJ (1998) The green fluorescent protein as a visible marker for lactic acid bacteria in complex ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26:219–230
Shephard BD, Gilmore MS (1999) Identification of aerobically and anaerobically induced genes in Enterococcus faecalis by random arbitrarily primed PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1470–1476
Spiro S, Guest JR (1990) FNR and its role in oxygen-related gene expression in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev 75:399–428
Terzaghi BE, Sandine WE (1975) Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol 29:807–813
Todd EW (1934) A comparative serological study of streptolysins derived from human and from animal infections, with notes on pneumococcal haemolysin tetanolysin and staphylococcus toxin. J Pathol Bacteriol 39:299–321
Whitehead TR, Flint HJ (1995) Heterologous expression of an endoglucanase gene (endA) from the ruminal anaerobe Ruminococcus flavefaciens 17 in Streptococcus bovis and Streptococcus sanguis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 126:165–170
Winstedt LL, Frankenberg L, Hederstedt L, von Wachenfeldt C (2000) Enterococcus faecalis V583 contains a cytochrome bd-type respiratory oxidase. J Bacteriol 182:3863–3866
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. P. Duggan for provision of plasmid pVACMC1 and Dr. J. A. T. Sandoe for provision of previously described E. faecalis clinical isolates. AMD was supported by an Emma and Leslie Reid Scholarship from the University of Leeds
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. Goebel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Day, A.M., Cove, J.H. & Phillips-Jones, M.K. Cytolysin gene expression in Enterococcus faecalis is regulated in response to aerobiosis conditions. Mol Gen Genomics 269, 31–39 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0819-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0819-1