Abstract
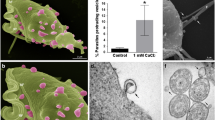
Cytochemical labeling with gold particle-conjugated lectins in combination with transmission and scanning electron microscopy was used to localise specific sugar residues on the Trichomonas vaginalis cell surface. For investigation of the role played by the surface glycoconjugates of T. vaginalis in the process of parasite adhesion to the target cells, selected glycan moieties of parasite surface-bound molecules were removed by treatment with α-mannosidase and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase. For observation of the parasite/epithelial cell interaction, human amnion membrane was employed as an in vitro model. Ultrastructure observations showed that T. vaginalis has distinct binding sites for concanavalin-A and wheat-germ agglutinin. This indicates the presence of mannose or mannose-like residues and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-containing residues on the parasite membrane. The addition of inhibitory sugars to T. vaginalis incubation media diminished the subsequent labeling of the parasite cell coat with lectins. Enzyme treatment caused a significant reduction in the number of sugar residues on the cell surface of the parasite. The majority of the viable, motile, enzyme-treated T. vaginalis cells incubated with amnion membrane were incapable of adhering to the target cells. It was concluded that sugar residues, in particular α-D-mannose and N-acetyl-glucosamine, present in the parasite glycocalyx are involved in the process of T.␣vaginalis attachment to the host's epithelial cells. Removal of the T. vaginalis cell-surface sugars prevented the attachment to and damage of the epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 June 1997 / Accepted: 10 November 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirhaghani, A., Warton, A. Involvement of Trichomonas vaginalis surface-associated glycoconjugates in the parasite/target cell interaction. A quantitative electron microscopy study. Parasitol Res 84, 374–381 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050413
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050413