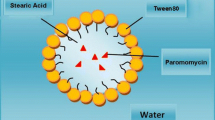
Abstract
Human le ishmaniasis is a vector-borne, neglected infectious disease that is widely distributed in America, Africa, Europe, and Asia. Current therapy is based on old and toxic drugs, including antimonials, aminoglycosides, and amphotericin. As a neglected disease, investment in the development of new therapeutic molecules is scarce. Considering these aspects, the optimization of treatment through novel delivery systems for current therapeutic agents is an attractive alternative. The encapsulation into liposomes of drugs used in treating leishmaniasis increases the concentration of these molecules in macrophages, which may not only increase the chance of cure but also expand their therapeutic spectrum to include resistant Leishmania, as well as reducing toxicity since the drug is less exposed to healthy cells. The classical example is the liposomal formulation of amphotericin B, a well-established therapeutic option that uses liposomes to decrease the progression of renal failure in patients. However, loading other leishmanicidal drugs into liposomes, such as pentavalent antimonials, presents an opportunity for innovative and cheaper therapeutic options for the treatment of human leishmaniasis. This review aims to discuss liposomes as a drug delivery system for leishmanicidal drugs.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available in a repository and can be accessed via a DOI link.
References
Altamura F, Rajesh R, Catta-Preta CMC, Moretti NS, Cestari I (2022) The current drug discovery landscape for trypanosomiasis and leishmaniasis: Challenges and strategies to identify drug targets. Drug Dev Res 83(2):225–252. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21664
Alvar J et al (2012) Leishmaniasis worldwide and global estimates of its incidence. PLoS ONE 7(5):e35671. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035671
Amato VS, Tuon FF, Bacha HA, Neto VA, Nicodemo AC (2008) Mucosal leishmaniasis Current scenario and prospects for treatment. Acta Trop 105(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2007.08.003
Amato VS, Tuon FF, Camargo RA, Souza RM, Santos CR, Nicodemo AC (2011) Can we use a lower dose of liposomal amphotericin B for the treatment of mucosal American leishmaniasis? Am J Trop Med Hyg 85(5):818–819. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2011.11-0287
Amato VS et al (2007) Treatment of mucosal leishmaniasis with a lipid formulation of amphotericin B. Clin Infect Dis 44(2):311–312. https://doi.org/10.1086/510494
Amato VS et al (2009) Immunohistochemistry and polymerase chain reaction on paraffin-embedded material improve the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Amazon region. Int J Dermatol 48(10):1091–1095. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04099.x
Amato VS, Tuon FF, Imamura R, Abegao de Camargo R, Duarte MI, Neto VA (2009) Mucosal leishmaniasis: description of case management approaches and analysis of risk factors for treatment failure in a cohort of 140 patients in Brazil. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 23(9):1026–1034. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03238.x
Amato VS, Tuon FF, Siqueira AM, Nicodemo AC, Neto VA (2007) Treatment of mucosal leishmaniasis in Latin America: systematic review. Am J Trop Med Hyg 77(2):266–274
Amer EI, Eissa MM, Mossallam SF (2016) Oral azithromycin versus its combination with miltefosine for the treatment of experimental Old World cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Parasit Dis 40(2):475–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-014-0529-0
Azevedo EG et al (2014) Mixed formulation of conventional and pegylated liposomes as a novel drug delivery strategy for improved treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 11(10):1551–1560. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2014.932347
Bacha HA et al (2011) Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis identification by PCR in the state of Para, Brazil. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 105(3):173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2010.11.010
Basu MK, Lala S (2004) Macrophage specific drug delivery in experimental leishmaniasis. Curr Mol Med 4(6):681–689. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566524043360186
Belo VS et al (2014) Risk factors for adverse prognosis and death in American visceral leishmaniasis: a meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(7):e2982. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002982
Berman JD, Waddell D, Hanson BD (1985) Biochemical mechanisms of the antileishmanial activity of sodium stibogluconate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27(6):916–920. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.27.6.916
Borborema SE, Schwendener RA, Osso JA Jr, de Andrade HF Jr, do Nascimento N (2011) Uptake and antileishmanial activity of meglumine antimoniate-containing liposomes in Leishmania (Leishmania) major-infected macrophages. Int J Antimicrob Agents 38(4):341–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.05.012
Borborema SET, Osso Junior JA, Tempone AG, de Andrade Junior HF, do Nascimento N (2018) Pharmacokinetic of meglumine antimoniate encapsulated in phosphatidylserine-liposomes in mice model: A candidate formulation for visceral leishmaniasis. Biomed Pharmacother 103:1609–1616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.004
Burza S, Croft SL, Boelaert M (2018) Leishmaniasis Lancet 392(10151):951–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31204-2
Calvo A, Moreno E, Larrea E, Sanmartin C, Irache JM, Espuelas S (2020) Berberine-loaded liposomes for the treatment of leishmania infantum-infected BALB/c mice. Pharmaceutics 12(9):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090858
Camargo RA et al (2010) Mucosal leishmaniasis and abnormalities on computed tomographic scans of paranasal sinuses. Am J Trop Med Hyg 83(3):515–518. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2010.10-0081
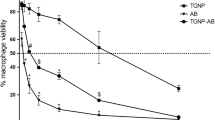
Carneiro G et al (2010) Topical delivery and in vivo antileishmanial activity of paromomycin-loaded liposomes for treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Liposome Res 20(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.3109/08982100903015025
Carvalheiro M et al (2015) Hemisynthetic trifluralin analogues incorporated in liposomes for the treatment of leishmanial infections. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 93:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.04.018
Cauchetier E, Paul M, Rivollet D, Fessi H, Astier A, Deniau M (2000) Therapeutic evaluation of free and liposome-encapsulated atovaquone in the treatment of murine leishmaniasis. Int J Parasitol 30(6):777–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(00)00053-9
Chan MM, Fong D (1990) Inhibition of leishmanias but not host macrophages by the antitubulin herbicide trifluralin. Science 249(4971):924–926. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2392684
Chan-Bacab MJ, Hernandez-Nunez E, Navarrete-Vazquez G (2009) Nitazoxanide, tizoxanide and a new analogue [4-nitro-N-(5-nitro-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)benzamide; NTB] inhibit the growth of kinetoplastid parasites (Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana) in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother 63(6):1292–1293. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkp117
Cogo J et al (2018) Quinoxaline derivatives as potential antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial agents. Bioorg Med Chem 26(14):4065–4072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2018.06.033
Craft N et al (2014) Topical resiquimod protects against visceral infection with Leishmania infantum chagasi in mice. Clin Vaccine Immunol 21(9):1314–1322. https://doi.org/10.1128/CVI.00338-14
Croft SL, Hogg J, Gutteridge WE, Hudson AT, Randall AW (1992) The activity of hydroxynaphthoquinones against Leishmania donovani. J Antimicrob Chemother 30(6):827–832. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/30.6.827
Croft SL, Sundar S, Fairlamb AH (2006) Drug resistance in leishmaniasis. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(1):111–126. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.19.1.111-126.2006
Cury TA et al (2015) Cinnamic acid derived compounds loaded into liposomes: antileishmanial activity, production standardisation and characterisation. J Microencapsul 32(5):467–477. https://doi.org/10.3109/02652048.2015.1046518
Dar MJ, Din FU, Khan GM (2018) Sodium stibogluconate loaded nano-deformable liposomes for topical treatment of leishmaniasis: macrophage as a target cell. Drug Deliv 25(1):1595–1606. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2018.1494222
Dar MJ, Khalid S, Varikuti S, Satoskar AR, Khan GM (2020) Nano-elastic liposomes as multidrug carrier of sodium stibogluconate and ketoconazole: A potential new approach for the topical treatment of cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Eur J Pharm Sci 145:105256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105256
de Almeida L et al (2017) Nanotechnological Strategies for Treatment of Leishmaniasis–A Review. J Biomed Nanotechnol 13(2):117–133. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2017.2349
de Barros NB et al (2016) Liposomes containing an ASP49-phospholipase A2 from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom as experimental therapy against cutaneous leishmaniasis. Int Immunopharmacol 36:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.025
de Camargo RA et al (2014) Facial structure alterations and abnormalities of the paranasal sinuses on multidetector computed tomography scans of patients with treated mucosal leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8(7):e3001. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003001
Dos Santos CCP, Ramos GS, De Paula RC, Faria KF, Moreira POL, Pereira RA, Melo MN, Tafuri WL, Demicheli C, Ribeiro RR, Azevedo EG, Monte-Neto RD, Da Silva SM, Frézard F (2020) Therapeutic efficacy of a mixed formulation of conventional and pegylated liposomes containing meglumine antimoniate, combined with allopurinol, in dogs naturally infected with leishmania infantum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 64(7):e00234-20. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00234-20
Emami T et al (2018) The role of MPL and imiquimod adjuvants in enhancement of immune response and protection in BALB/c mice immunized with soluble Leishmania antigen (SLA) encapsulated in nanoliposome. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(sup2):324–333. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1457042
Fattahi Bafghi A, Haghirosadat BF, Yazdian F, Mirzaei F, Pourmadadi M, Pournasir F, Hemati M, Pournasir S (2021) A novel delivery of curcumin by the efficient nanoliposomal approach against Leishmania major. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 51(10):990–997. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2021.1885045
Ferreira FM et al (2014) Association of water extract of green propolis and liposomal meglumine antimoniate in the treatment of experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Parasitol Res 113(2):533–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3685-8
Ferreira LS, Ramaldes GA, Nunan EA, Ferreira LA (2004) In vitro skin permeation and retention of paromomycin from liposomes for topical treatment of the cutaneous leishmaniasis. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 30(3):289–296. https://doi.org/10.1081/ddc-120030423
Fuentes-Nava G, Tirado-Sanchez A, Fernandez-Figueroa EA, Sanchez-Montes S, Becker I, Bonifaz A (2021) Efficacy of imiquimod 5% cream as first-line management in cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania mexicana. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 54:e0305-2020. https://doi.org/10.1590/0037-8682-0305-2020
Gardner DM et al (2010) Association of acenaphthoporphyrins with liposomes for the photodynamic treatment of leishmaniasis. Photochem Photobiol 86(3):645–652. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.2010.00705.x
Gebreyohannes EA, Bhagvathula AS, Abegaz TM, Seid MA (2018) Treatment outcomes of visceral leishmaniasis in Ethiopia from 2001 to 2017: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Dis Poverty 7(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-018-0491-7
Gharbi M et al (2020) Current status of tropical theileriosis in Northern Africa: A review of recent epidemiological investigations and implications for control. Transbound Emerg Dis 67(Suppl 1):8–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.13312
Grover R, Wolt JD, Cessna AJ, Schiefer HB (1997) Environmental fate of trifluralin. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 153:1–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-2302-3_1
Hussain Z, Khan S, Imran M, Sohail M, Shah SWA, de Matas M (2019) PEGylation: a promising strategy to overcome challenges to cancer-targeted nanomedicines: a review of challenges to clinical transition and promising resolution. Drug Deliv Transl Res 9(3):721–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-019-00631-4
Karimkhani C, Wanga V, Coffeng LE, Naghavi P, Dellavalle RP, Naghavi M (2016) Global burden of cutaneous leishmaniasis: a cross-sectional analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Infect Dis 16(5):584–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00003-7
Karimkhani C, Wanga V, Naghavi P, Dellavalle RP, Naghavi M (2017) Global burden of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Lancet Infect Dis 17(3):264. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30217-1
Khalil EA, Ahmed AE, Musa AM, Hussein MH (2006) Antimony-induced cerebellar ataxia. Saudi Med J 27(1):90–92
Lala S, Pramanick S, Mukhopadhyay S, Bandyopadhyay S, Basu MK (2004) Harmine: evaluation of its antileishmanial properties in various vesicular delivery systems. J Drug Target 12(3):165–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/10611860410001712696
Lasic DD (1998) Novel applications of liposomes. Trends Biotechnol 16(7):307–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-7799(98)01220-7
Lopes RM et al (2016) Lipid-based nanoformulations of trifluralin analogs in the management of Leishmania infantum infections. Nanomedicine (lond) 11(2):153–170. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.15.190
Mantyla A et al (2004) Synthesis, in vitro evaluation, and antileishmanial activity of water-soluble prodrugs of buparvaquone. J Med Chem 47(1):188–195. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm030868a
Marti-Marti I, Alsina M, Giavedoni P, Fuertes I (2021) Cutaneous leishmaniasis of the face treated with imiquimod 3.75. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin (Engl Ed) 39(2):108–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eimc.2020.04.005
Matlashewski G et al (2011) Visceral leishmaniasis: elimination with existing interventions. Lancet Infect Dis 11(4):322–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70320-0
McHardy N, Wekesa LS, Hudson AT, Randall AW (1985) Antitheilerial activity of BW720C (buparvaquone): a comparison with parvaquone. Res Vet Sci 39(1):29–33
Medda S, Mukhopadhyay S, Basu MK (1999) Evaluation of the in-vivo activity and toxicity of amarogentin, an antileishmanial agent, in both liposomal and niosomal forms. J Antimicrob Chemother 44(6):791–794. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/44.6.791
Medkour H et al (2020) Potential of Artesunate in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis in dogs naturally infected by Leishmania infantum: Efficacy evidence from a randomized field trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 14(12):e0008947. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0008947
Mesquita JT, Pinto EG, Taniwaki NN, Galisteo AJ Jr, Tempone AG (2013) Lethal action of the nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative nitazoxanide via induction of oxidative stress in Leishmania (L.) infantum. Acta Trop 128(3):666–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.09.018
Minodier P, Zambelli L, Mary C, Faraut F, Garnier JM, Berbis P (2008) Cutaneous leishmaniasis treated with azithromycin in a child. Pediatr Infect Dis J 27(1):80–81. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0b013e3181506683
Monteiro LM, Lobenberg R, Cotrim PC, Barros de Araujo GL, Bou-Chacra N (2017) Buparvaquone Nanostructured Lipid Carrier: Development of an Affordable Delivery System for the Treatment of Leishmaniases. Biomed Res Int 2017:9781603. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9781603
Moosavian SA, Fallah M, Jaafari MR (2019) The activity of encapsulated meglumine antimoniate in stearylamine-bearing liposomes against cutaneous leishmaniasis in BALB/c mice. Exp Parasitol 200:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2019.03.004
Neal RA, van Bueren J, Hooper G (1988) The activity of nitrofurazone and furazolidone against Leishmania donovani, L. major and L. enriettii in vitro and in vivo. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 82(5):453–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/00034983.1988.11812275
Oliveira MC, Amorim RF, Freitas Rde A, Costa Ade L (2005) A fatal case of mucocutaneous leishmaniasis after pentavalent antimonial use. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 38(3):258–260. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0037-86822005000300011
Owais M, Gupta CM (2005) Targeted drug delivery to macrophages in parasitic infections. Curr Drug Deliv 2(4):311–318. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720105774370177
Pal S, Ravindran R, Ali N (2004) Combination therapy using sodium antimony gluconate in stearylamine-bearing liposomes against established and chronic Leishmania donovani infection in BALB/c Mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(9):3591–3593. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.48.9.3591-3593.2004
Passos SR, de Rodrigues TA, Madureira AP, Giunchetti RC, Zanini MS (2014) Clinical treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis in dogs with furazolidone and domperidone. Int J Antimicrob Agents 44(5):463–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.07.011
Peine KJ et al (2014) Liposomal resiquimod for the treatment of Leishmania donovani infection. J Antimicrob Chemother 69(1):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkt320
Pinto EG, Barbosa LRS, Mortara RA, Tempone AG (2020) Targeting intracellular Leishmania (L.) infantum with nitazoxanide entrapped into phosphatidylserine-nanoliposomes: An experimental study. Chem Biol Interact 332:109296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109296
Pokharel P, Ghimire R, Lamichhane P (2021) Efficacy and Safety of Paromomycin for Visceral Leishmaniasis: A Systematic Review. J Trop Med 2021:8629039. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8629039
Proulx ME, Desormeaux A, Marquis JF, Olivier M, Bergeron MG (2001) Treatment of visceral leishmaniasis with sterically stabilized liposomes containing camptothecin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45(9):2623–2627. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.45.9.2623-2627.2001
Raay B, Medda S, Mukhopadhyay S, Basu MK (1999) Targeting of piperine intercalated in mannose-coated liposomes in experimental leishmaniasis. Indian J Biochem Biophys 36(4):248–251
Rajabi O, Layegh P, Hashemzadeh S, Khoddami M (2016) Topical liposomal azithromycin in the treatment of acute cutaneous leishmaniasis. Dermatol Ther 29(5):358–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.12357
Ramos GS et al (2021) Antileishmanial activity of fullerol and its liposomal formulation in experimental models of visceral leishmaniasis. Biomed Pharmacother 134:111120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111120
Reimao JQ, Colombo FA, Pereira-Chioccola VL, Tempone AG (2012) Effectiveness of liposomal buparvaquone in an experimental hamster model of Leishmania (L.) infantum chagasi. Exp Parasitol 130(3):195–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2012.01.010
Reimao JQ, Taniwaki NN, Tempone AG (2010) Furazolidone is a selective in vitro candidate against Leishmania (L.) chagasi: an ultrastructural study. Parasitol Res 106(6):1465–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1826-x
Reis LES, de Brito RCF, de Oliveira Cardoso JM, Mathias FAS, Soares RDOA, Carneiro CM, de Abreu Vieira PM, Ramos GS, Frézard FJG, Roatt BM, Reis AB (2017) Mixed formulation of conventional and pegylated meglumine antimoniate-containing liposomes reduces inflammatory process and parasite burden in leishmania infantum-infected BALB/c mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61(11):e00962-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00962-17
Reis PG, Abreu AT, Guimaraes AG, Teixeira MC, de Souza J, Silva-Barcellos NM (2013) Development and validation of an analytical method for quantification of arsenic and antimony in liposomes using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. J AOAC Int 96(4):771–775. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.10-263
Rocio C, Amato VS, Camargo RA, Tuon FF, Nicodemo AC (2014) Liposomal formulation of amphotericin B for the treatment of mucosal leishmaniasis in HIV-negative patients. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 108(3):176–178. https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/tru011
Romanelli MM et al (2019) Sertraline Delivered in Phosphatidylserine Liposomes Is Effective in an Experimental Model of Visceral Leishmaniasis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:353. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00353
Roychoudhury J, Sinha R, Ali N (2011) Therapy with sodium stibogluconate in stearylamine-bearing liposomes confers cure against SSG-resistant Leishmania donovani in BALB/c mice. PLoS ONE 6(3):e17376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017376
Sanna V, Pala N, Sechi M (2014) Targeted therapy using nanotechnology: focus on cancer. Int J Nanomedicine 9:467–483. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S36654
Santos J, Rivero A, Marquez M (2000) Acute pancreatitis with a fatal evolution due to antimonials in patients with visceral leishmaniasis and HIV infection. An Med Interna 17(10):562–563
Schettini DA et al (2006) Improved targeting of antimony to the bone marrow of dogs using liposomes of reduced size. Int J Pharm 315(1–2):140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.01.048
Schwendener RA (2007) Liposomes in biology and medicine. Adv Exp Med Biol 620:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-76713-0_9
Sen R, Ganguly S, Saha P, Chatterjee M (2010) Efficacy of artemisinin in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.03.008
Smith L, Serrano DR, Mauger M, Bolas-Fernandez F, Dea-Ayuela MA, Lalatsa A (2018) Orally Bioavailable and Effective Buparvaquone Lipid-Based Nanomedicines for Visceral Leishmaniasis. Mol Pharm 15(7):2570–2583. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00097
Sundar S, Chakravarty J (2010) Liposomal amphotericin B and leishmaniasis: dose and response. J Glob Infect Dis 2(2):159–166. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-777X.62886
Tavares GSV et al (2018) Antileishmanial Activity, Cytotoxicity and Mechanism of Action of Clioquinol Against Leishmania infantum and Leishmania amazonensis Species. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 123(3):236–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12990
Tavares GSV et al (2019) A Pluronic(R) F127-based polymeric micelle system containing an antileishmanial molecule is immunotherapeutic and effective in the treatment against Leishmania amazonensis infection. Parasitol Int 68(1):63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2018.10.005
Taylor VM et al (2011) In vitro and in vivo studies of the utility of dimethyl and diethyl carbaporphyrin ketals in treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(10):4755–4764. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00671-11
Teixeira AC, Paes MG, Guerra Jde O, Prata A, Silva-Vergara ML (2008) Failure of both azithromycin and antimony to treat cutaneous leishmaniasis in Manaus, AM, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 50(3):157–160. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0036-46652008000300005
Tempone AG, Mortara RA, de Andrade HF Jr, Reimao JQ (2010) Therapeutic evaluation of free and liposome-loaded furazolidone in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36(2):159–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.04.006
Tuon FF, Amato VS (2007) Mucosal leishmaniasis and miltefosine. Clin Infect Dis 44(11):1525–6. https://doi.org/10.1086/517848 (author reply 1526-7)
Tuon FF, Amato VS (2008) Neglected tropical diseases: beyond the wars. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 50(5):313–314. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0036-46652008000500013
Tuon FF, Amato VS (2009) Systematic review of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis: few points to be applied to Old World leishmaniasis. Int J Dermatol 48(2):201–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.03982.x
Tuon FF, Amato VS, Graf ME, Siqueira AM, Nicodemo AC, Amato Neto V (2008) Treatment of New World cutaneous leishmaniasis–a systematic review with a meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol 47(2):109–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03417.x
Valentim Silva JR et al (2020) A natural cell-penetrating nanopeptide combined with pentavalent antimonial as experimental therapy against cutaneous leishmaniasis. Exp Parasitol 217:107934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2020.107934
Valladares JE, Freixas J, Alberola J, Franquelo C, Cristofol C, Arboix M (1997) Pharmacokinetics of liposome-encapsulated meglumine antimonate after intramuscular and subcutaneous administration in dogs. Am J Trop Med Hyg 57(4):403–406. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1997.57.403
Varma DM, Redding EA, Bachelder EM, Ainslie KM (2021) Nano- and Microformulations to Advance Therapies for Visceral Leishmaniasis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 7(5):1725–1741. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01132
Vennerstrom JL, Lovelace JK, Waits VB, Hanson WL, Klayman DL (1990) Berberine derivatives as antileishmanial drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34(5):918–921. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.34.5.918
Want MY et al (2017) Nanoliposomal artemisinin for the treatment of murine visceral leishmaniasis. Int J Nanomedicine 12:2189–2204. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S106548
Wolf B (1998) Hydrophilic-lipophilic drug carrier systems of bead cellulose and isopropyl myristate. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 24(11):1007–1015. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639049809089944
Wyllie S, Cunningham ML, Fairlamb AH (2004) Dual action of antimonial drugs on thiol redox metabolism in the human pathogen Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem 279(38):39925–39932. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405635200
Yang DM, Liew FY (1993) Effects of qinghaosu (artemisinin) and its derivatives on experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. Parasitology 106(Pt 1):7–11. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000074758
Yesilova Y et al (2016) Meglumine antimoniate is more effective than sodium stibogluconate in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Dermatolog Treat 27(1):83–87. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2015.1054778
Zhang R et al (2010) In vitro and in vivo antileishmanial efficacy of nitazoxanide against Leishmania donovani. Parasitol Res 107(2):475–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1906-y
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Felipe Francisco Tuon—literature review and manuscript draft
Leticia Ramos Dantas—literature review and manuscript draft
Regina Maia de Souza—manuscript review
Victoria Stadler Tasca Ribeiro—manuscript review
Valdir Sabbaga Amato—manuscript review
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
N/A.
Consent to Participate
N/A.
Consent for Publication
N/A.
Conflicts of Interest
F. F. Tuon is a CNPq researcher. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Una Ryan
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tuon, F.F., Dantas, L.R., de Souza, R.M. et al. Liposomal drug delivery systems for the treatment of leishmaniasis. Parasitol Res 121, 3073–3082 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07659-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07659-5