Abstract
Mixed infections of Toxoplasma gondii and Eimeria tenella are likely to occur frequently due to the high prevalence of both pathogens in free-ranging chickens. In this study, we investigated the co-occurrence of the two parasites in the same immune-competent host cell towards altered patterns of parasite-host interactions. Chicken blood monocyte–derived macrophages were co-infected with T. gondii RH tachyzoites and E. tenella Houghton sporozoites in vitro for 24 h. Through monitoring the uptake of pH-sensitive pHrodo™ Zymosan BioParticles (“Zymosan”) by macrophages, we created a three-dimensional model and to analyze quantitatively phagocytosis using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Assessments of parasite populations were performed by qPCR at 2, 6, 12, and 24 h post-infection (hpi). At 6 hpi, phagocytosis was inhibited in the E. tenella–infected cultures while no inhibition of phagocytosis was observed due to T. gondii. Phagocytosis activity revealed more complex interactions during co-infection. At 12 and 24 hpi, phagocytosis response to “Zymosan” was distinctly weaker in co-infected cells than in all other groups except for cells mono-infected with high doses of E. tenella at 24 hpi. By qPCR, significantly reduced numbers of both intracellular parasites were recorded (10-fold) in all infected groups at 2 hpi. At 12 hpi, the T. gondii population reached lowest values but dramatically increased by 24 hpi. Our data confirm that macrophage phagocytosis is involved in the control of invasion by apicomplexan parasites in chicken which particularly applies to E. tenella infection and it was able to be altered by the co-existing parasites.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Toxoplasma (T.) gondii and Eimeria (E.) tenella are two ubiquitous intracellular parasites in poultry and are both representatives of parasitic coccidia. T. gondii infection is often asymptomatic and reported in almost all the warm-blood animals (Harker et al. 2015). Chicken are considered as resistant host with high seroprevalence of T. gondii worldwide (Dubey 2010). In contrast, E. tenella is one of the most pathogenic protozoan parasites in chicken and may cause severe enteric diseases and lethality. Even sub-clinical enteric coccidiosis reduces economic productivity in chickens (Dalloul and Lillehoj 2006).
Chicken macrophages play an important role as part of the first barrier of the innate immune response against T. gondii and E. tenella (Hériveau et al. 2000; Unno et al. 2008; Vervelde et al. 1995; Zhou et al. 2013). Macrophages mainly contribute to the clearance and destruction of both intracellular and extracellular pathogens through phagocytosis (Dalloul et al. 2007). However, T. gondii can survive by forming a specialized parasitophorous vacuole (PV) in phagocytes such as macrophages (Sibley 1995). There is evidence that protozoan within human or murine macrophages block phagosome-endosome fusion by Leishmania or phagosome acidification by Toxoplasma (Desjardins and Descoteaux 1997; Goren 1977). Additionally, T. gondii within the PV block lipopolysaccharide (LPS)–triggered IL-12 and TNF-α during macrophage phagocytosis (Butcher and Denkers 2002). Regarding Eimeria, a previous study into E. bovis infection in bovine calves indicates significant macrophage infiltration of the intestinal mucosa (Taubert et al. 2009). In chickens, it was shown that the engulfment of sporozoites by macrophages occurred few hours after infection and sporozoites were more often located within or next to macrophages in previously naïve than in E. tenella immune chickens (Challey and Burns 1959; Cox 2001; Vervelde et al. 1996). Chicken macrophages isolated from peritoneal exudates were shown to engulf E. tenella sporozoites at 2–3 h post-infection (hpi) (Long and Rose 1976). Sporozoite-bearing macrophages have been reported to possibly transport Eimeria spp. sporozoites to other host cells (Challey and Burns 1959; Trout and Lillehoi 1993; van Doorninck and Becker 1957).
Several published studies investigated interaction of cells involved in innate immunity and T. gondii or Eimeria spp. during mono-infection, few have referred to mutual host-parasite or parasite-parasite interaction with these two coccidian in co-infection models (Hiob et al. 2017). In fact, mixed infections appear to occur frequently in chickens as prevalence of Eimeria spp. and seroprevalence of T. gondii and. is high, especially in free-ranging chickens (Al-Gawad et al. 2012; Deyab and Hassanein 2005; Lehmann et al. 2006). A recent case reported in Scotland showed co-infection of T. gondii and Eimeria stiedae in a wild rabbit (Mason et al. 2015). Field studies on co-infections in chickens are currently lacking; however, an experimental in vivo study points at putative interaction of T. gondii and E. tenella during co-infection (Hiob et al. 2017).
In our recent in vitro study into co-infection of chicken macrophages with T. gondii and E. tenella, destruction of parasites mainly occurred before 24 hpi (Zhang et al. 2018). E. tenella displayed a tendency to increase replication during co-infection with T. gondii at 72 hpi in chicken primary macrophage cultures. Besides, at 2 hpi, more intracellular sporozoites of E. tenella than T. gondii tachyzoites—if by phagocytosis or invasion—were detected (Zhang et al. 2018). The current study aims at enhancing our understanding in host-pathogen and pathogen-pathogen interaction in co-infected chicken primary macrophage cultures. By generating a 3D model, we studied the capacity of macrophage phagocytosis in co-infected and mono-infected cultures. In addition, the invasion and reproduction of both E. tenella and T. gondii which are likely related to phagocytosis were investigated in the early phase of in vitro infection.
Methods
Chicken primary macrophage isolation and culture
Chicken peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were isolated from heparinized whole blood of adult female chickens (6-week old), based on the established protocols (Malkwitz et al. 2013) kindly provided by Dr. Braukmann, Friedrich-Loeffler-Institute Jena, Germany. The animal experiments related to the blood sampling were approved by the responsible authorities (Landesdirektion Sachsen, Germany, trial registration number V13/10). Two-milliliter blood was mixed gently with 2-mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 1 mg/mL gentamicin (Life technologies, Darmstadt, Germany). Two-milliliter Biocoll® separating solution (density 1077 g/ml; Biochrom AG, Berlin, Germany) was used to separate the PBMCs by centrifugation at 250×g for 45 min. Afterwards, the isolated PBMCs were washed with 5-mL PBS once, followed by centrifugation at 350×g for 30 min. The resulting pellet was washed and centrifuged (350×g, 20 min) once with 5-mL pre-warmed, 41 °C, RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma, Taufkirchen, Germany). Subsequently, 5 × 106 PBMC/well were resuspended in RPMI with 5% chicken serum and 5% fetal bovine serum, penicillin (100 U/mL, PAA), streptomycin (0.1 mg/mL, PAA), and amphotericin B (0.0025 mg/mL, PAA), and incubated in 24-well plates for 96 h (41 °C, 5% CO2). The macrophages were purified by rinsing off non-adherent cells twice in PBS at 2 h, 24 h, and 96 h after seeding PBMC cultures for infection.
Parasites
Genetically modified T. gondii RH-GFP tachyzoites (type I strain, kindly provided by Professor Dominique Soldati-Favre, University of Geneva Medical School, Switzerland) were harvested from infected human foreskin fibroblast (HFF) cultures. E. tenella Houghton-YFP strain (kindly provided by Professor Xun Suo, China Agricultural University, China) sporozoites were gained following an established protocol (Thabet et al. 2017) with slight improvement. Briefly, sporocysts were collected by mechanical destruction of the oocyst wall with 0.5-mm glass beads (BioSpec Products, Bartlesville, OK, USA). Sporocysts were incubated in 0.25% trypsin (w/v) (Carl Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) and 4% sodium taurocholic acid (w/v) (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) at 41 °C for 90 min for excystation. Then, sterile pluriStrainer® 5 μm (pluriSelect Life science, Leipzig, Germany) was used to purify excysted sporozoites with 1% glucose in PBS at pH 7.4 (follow buffer).
Infection
Cell cultures were divided into six groups. Infection groups were performed with a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of certain parasites per cell (Table 1, total infection doses based on the mean population of adherent macrophages/well): Group NC consisted of uninfected negative control PBMC cultures that were seeded 96 h before the start of the experiment. Infection groups were conducted as follows: Groups TH (MOI of 4 T. gondii tachyzoites), TL (MOI of 2 T. gondii tachyzoites), EH (MOI of 4 E. tenella sporozoites), EL (MOI of 2 E. tenella sporozoites), and CI (MOI of 2 T. gondii tachyzoites and 2 E. tenella sporozoites, simultaneous infection). In total, 10 cell cultures from 2 birds were applied repetitively in this study as follows: 6 cultures (3 cultures per bird) for phagocytosis assay and 4 cultures (2 cultures per bird) for qPCR analysis. Groups were observed over a period of 24 h.
Phagocytosis assay
Twenty-four-well plates for cell imaging (Bottom thickness: 170 μm, Cellvis, CA, USA) were used to assess macrophage phagocytosis according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, 500 μg/mL of pHrodo™ Red Zymosan BioParticles (“Zymosan”, Life Technologies, USA) were vortexed and resuspended homogeneously in RPMI (pH = 7.4). Cultures were rinsed off in PBS three times to remove extracellular parasites before activation. Each well was supplemented with dispersed “Zymosan” 200 μL/well at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hpi, and incubated at 37 °C without CO2 supplementation for further 2 h after induction of activation. Infections were repeated 6 times per time point for each culture. The reaction was washed 3 times with PBS. Then, ice-cold PBS was added to stop the reaction for cell imaging. NucBlue™ Live ReadyProbes™ (Life Technoglogies, USA) were used to stain nuclei. In order to test for basic function of phagocytosis by cells treated according to the described conditions, cultures of group NC (n = 6 per observation period) were exposed to activation at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hpi (infection time point for other infection groups). Additionally, uninfected control cultures (n = 3) were stimulated for 1 h by LPS (1 μg/ml) application 96 h after seeding in 24-well plates. Afterwards, cells were rinsed with PBS and activated by dispersed “Zymosan” for further 2 h as well. Non-cell controls were kept in parallel. All incubation steps were performed in a dark chamber.
Confocal laser scanning microscopy
Phagocytosis was determined by cell imaging with × 200 magnification using CLSM (Leica TCS SP8, Wetzlar, Germany). Imaging spots were taken from the central area of six individual wells for each group and observation period. Parasite visualization (× 400 magnifications) was carried out 12 hpi. Stacks were calculated for every 1.5–2 μm and included all attached cells. Defined range of emission for each fluorescence and sequential acquisition (LAS X, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) was used to avoid overlapping. Imaris® software version 9.3 (Bitplane, Abingdon, UK) was used to generate a 3D model from the stacks and to quantify the number of positive cells with intracellular granules of “Zymosan”. The relative inhibition of phagocytosis in infected cultures following 2 h of stimulation by “Zymosan” was calculated as follows:
Intracellular parasite replication
Cultures were trypsinized by Biotase® (Biochrom, Berlin, Germany) at 37 °C for 30 min and collected at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hpi after washing three times gently with PBS. DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit® (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions for cell cultures. T. gondii DNA standard curve was obtained by gradient 10-fold dilutions of 107 tachyzoites. T. gondii replication was analyzed by the 529-bp repeat element in a probe-based qPCR. ITS1 fragment quantification was used to quantify the replication of E. tenella by SYBR Green-based PCR (Kawahara et al. 2008).
According to the chosen infection doses, DNA was extracted from 2.5 × 105 and 5 × 105 E. tenella sporozoites, respectively, to normalize the initial copy numbers of E. tenella (n = 4). The relative copy number of E. tenella DNA was implemented by measurement of pSCA-17 plasmid standard dilution as described before (Thabet et al. 2015). Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) was performed using the CFX Connect Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA).
For T. gondii qPCR, 5 μL of sample DNA eluate was used in a total volume of 25 μL containing 12.5 μL of Master Mix, 3.2 μL of DNase/RNase free water (Gibco™, Life Technologies, USA), 0.9 μL of each 25 μM forward and reverse primer, and 2.5 μL of 2 μM TaqMan probe. The cycling program consisted of 95 °C for 15 min (initial denaturation), followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s (denaturation), 60 °C for 1 min (annealing), and 72 °C for 15 s (extension). Two microliters of sample DNA eluate was used for E. tenella–specific PCR, in a total volume of 20 μL containing 10 μL of SYBR Green master mix, 7.2 μL of water, and 0.9 μL of 25 μM forward and reverse primer. For E. tenella qPCR, the cycling program consisted of heating to 95 °C for 5 min (initial denaturation), followed by 40 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s (denaturation), 55 °C for 20 s (annealing), and 72 °C for 20 s (extension). A subsequent melting curve analysis (95 °C for 1 min, 55 °C for 30 s, 0.5 °C/s) was performed for E. tenella qPCR to create the dissociation curve. Data represent the mean of three replicates with an acceptable standard deviation of less than 0.5 for Ct values.
Data analysis and statistics
The intracellular T. gondii tachyzoites were represented as total DNA copy quantities. For E. tenella, the DNA copy number/μL was assessed for each observation period. RPN was calculated as mean value (n = 3 or 4) with standard deviation (SD) for each group in relation to DNA copy numbers determined for the initial infection dose. Statistical analysis was calculated by SPSS® version 20 (IBM, New York, USA). Differences between groups were determined by the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test and assumed significant at p < 0.05.
Results
Phagocytosis in uninfected macrophages cultures
NC phagocytosis was evaluated at time points corresponding to hpi of the infected cultures that were kept in parallel (Fig. 1). Thus, hpi is also used to describe the effects observed in NC although these cells were not infected. During the 2 h of exposure to “Zymosan,” no detectable changes in morphology or signs of apoptosis were found by light microscopy (data not shown). At 2 hpi, more than 70% of DAPI-positive macrophages incorporated “Zymosan” (Table 2). In contrast, LPS exposure at the beginning of the experiment resulted in a clearly lower proportion of activated cells to 53.7 ± 2.8% of DAPI-positive macrophages. In group NC, 57.6 ± 2.0% of cells were phagocytic until 6 hpi, and 56.9 ± 2.5% cells were revealed “Zymosan” positive at 12 hpi. At 24 hpi, phagocytosis percentage decreased to the lowest observed value with 36.6 ± 1.2% (Table 2).
Phagocytosis activity of primary chicken macrophages at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hpi. Phagocytosis was determined after 2-h exposure to “Zymosan” by cell imaging with. n = 6 cultures, each 3 cultures per bird. Non-positive staining of “Zymosan” and cell nuclei of macrophages was presented in blank culture (negative control) (data not shown). Staining: DAPI (cell nuclei, NucBlue™ Live ReadyProbes™ blue); pHrodo (“Zymosan” bioparticles, red). Confocal laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM), × 200 magnifications; 3D model generated by Imaris®
Phagocytosis in infected macrophage cultures
Cell cultures were finally infected up to 24 h as listed in Table 1. At 2 hpi, all infected groups showed initial inhibition of phagocytosis compared with group NC, however, on variable levels (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Material). Inhibition was most pronounced in groups TH and EH, being significantly higher than in group CI (p < 0.005). No additive effect was seen in phagocytosis inhibition by co-infection as compared with groups TL and EL that were mono-infected with the same dose of the respective parasite as used for co-infection of group CI.
Relative inhibition of “Zymosan” engulfment in chicken macrophages by mono- and co-infection until 24 hpi. Values represent mean values and standard deviation in relation to phagocytosis in group NC (uninfected, n = 6, each 3 cultures per bird). Values of relative inhibition equal 0 in group NC. (a) Relative inhibition at 2 hpi. (b) Relative inhibition at 6 hpi. (c) Relative inhibition at 12 hpi. (d) Relative inhibition at 24 hpi. Asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005) indicate a significant difference between groups (Mann Whitney U test). Denomination of groups: Groups TH (MOI of 4 T. gondii tachyzoites), TL (MOI of 2 T. gondii tachyzoites), EH (MOI of 4 E. tenella sporozoites), EL (MOI of 2 E. tenella sporozoites), and CI (MOI of 2 T. gondii tachyzoites and 2 E. tenella sporozoites, simultaneously infection)
Over the following investigation period, patterns of inhibition varied.
At 6 hpi, compared with group NC, E. tenella infection inhibited macrophage phagocytosis in group EH and, less distinctly, in group EL, whereas T. gondii showed no inhibitory effect in groups TH and TL (Fig. 2b). Likewise, no phagocytosis inhibition was observed in group CI. Compared with group CI, both groups EH and EL displayed significantly higher inhibition values (p < 0.005 and p < 0.05, respectively).
At 12 hpi, Zymosan-induced activation of phagocytosis was similar to group NC in all four mono-infected groups (TH, TL, EH, EL). In contrast, group CI featured a remarkably reduced response to stimulation of phagocytosis compared with group NC, and inhibition values were significantly higher than in all other infection groups (p < 0.005 in comparison with TL, EH, and EL and p < 0.05 in comparison with TH) (Fig. 2c).
At 24 hpi, group CI remained at a high inhibition level compared with group NC although values were significantly lower than in group EH (p < 0.005) (Fig. 2d). In contrast, groups TH and EL did not display reduced phagocytosis, and consequently inhibition values were negative and significantly lower than in group CI (p < 0.005 compared with TH and p < 0.05 compared with EL). Group TL showed only slight inhibition, although a statistical effect was seen in comparison with group CI (p < 0.05). Strikingly, highest phagocytosis inhibition values were observed in group EH, and the respective values were significantly higher than in group CI (p < 0.005).
CLSM
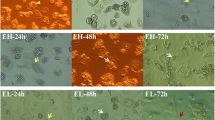
E. tenella meronts and replicating T. gondii tachyzoites were visible in all infected macrophage cultures at 12 hpi (Fig. 3). However, fewer intracellular E. tenella sporozoites or first generation of E. tenella meronts were observed than intracellular T. gondii in the respective cultures. “Zymosan”-positive cell was not visualized inside any co-infected cells of group CI.
Cell imaging of parasite replication by CLSM at 12 hpi. Typical form of T. gondii replication and stage development of E. tenella was seen in co-infection at 12 hpi. However, the “Zymosan” was not visualized positively in single co-infected cell. Cell imaging in group NC is presented in Fig. 1. DAPI: cell nuclei stained blue; pHrodo (Zymosan bioparticles) stain red, white arrows; T. gondii (tachyzoites, GFP, green); E. tenella (sporozoites and meronts, nucleus-stained YFP, yellow)
Parasite replication
T. gondii
Following a rapid initial decrease, low T. gondii DNA copy numbers were observed in groups TH, TL, and CI until 12 hpi. However, the quantity of T. gondii DNA distinctly increased thereafter by 24 hpi. Interestingly, at the end of the experimental period, group CI reached almost the level of the high-dose mono-infected group (TH) although the infection dose applied was similar to group TL which obviously remained on a lower level of reproduction (Fig. 4a). Relative parasite numbers (RPN) amounted to about 5% in group TH and 10% in group TL at 2 hpi (Fig. 4b). At this time, lowest RPN (3.6 ± 0.1%) were observed in group CI, which were significantly lower as compared with group TL (p < 0.05). At 6 hpi, an increase in RPN was observed for group TH (22.9 ± 2.2%), followed by a transient decline at 12 hpi (1.1 ± 0.4%) and finally a steep increase at 24 hpi (65.3 ± 9.8%). In group TL, a similar trend was observed with comparatively low RPN values until 6 hpi (9.3 ± 4.4%) and even a further reduction at 12 hpi (2.1 ± 1.4%), followed by a very distinct increase at 24 hpi (56.4 ± 21.0%).
Assessment of parasite reproduction during infection until 24 hpi. (a) Quantities of intracellular parasite estimated by qPCR. T. gondii tachyzoites and E. tenella (all stages) are represented as DNA copies/μL. Number sign represents DNA quantities of initial infection doses. (b) Relative parasite numbers (RPN) of T. gondii and E. tenella compared with the initial infection doses. RPN = DNA copies per time point/DNA copies of the initial infection doses. RPN were calculated as mean value of parasite DNA copies with standard deviation (n = 3 or 4). *p < 0.05 is considered a statistically significant difference between marked infected groups (based on Mann Whitney U test). Denomination of groups: groups TH (MOI of 4 T. gondii tachyzoites), TL (MOI of 2 T. gondii tachyzoites), EH (MOI of 4 E. tenella sporozoites), EL (MOI of 2 E. tenella sporozoites), and CI (MOI of 2 T. gondii tachyzoites and 2 E. tenella sporozoites, simultaneously infection)
In group CI, low RPN levels comparable with those recorded for the mono-infected groups TH and TL were observed with lowest values at 12 hpi (1.7 ± 0.1%). However, at 24 hpi, RPN values of group CI (100.1 ± 13.1%) clearly exceeded those of both mono-infected groups (p < 0.05). Based on the same initial, T. gondii infection dose replication was almost twice as high in the co-infected group as in the mono-infected group TL at the termination of the experiment.
E. tenella
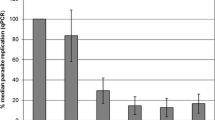
The quantity of intracellular E. tenella stages (sporozoites or first generation meronts) was reduced as compared with the initial dose at 2 hpi and remained low until the end of the experiment irrespective of the applied mono-infection dose (EL, EH) or co-infection (CI; Fig. 4a) without any significant group effects.
Consequently, RPN values were low at 2 hpi with only 13.9 ± 3.6% in group EL and 17.0 ± 2.5% in group EH (Fig. 4b). In both mono-infected groups, RPN levels further decreased until 6 hpi (group EL: 6.7 ± 3.6%; group EH: 6.7 ± 1.1%). Until 12 hpi, RPN moderately increased in these two groups indicating moderately increased reproduction (group EL: 10.4 ± 3.8%; group EH: 14.0 ± 4.4%). This trend continued until 24 hpi in group EH (18.9 ± 4.3%) whereas RPN values had decreased in group EL by then (4.2 ± 2.3%).
Initially, group CI displayed similar RPN (16.0 ± 8.4%) as the mono-infected groups. However, a very distinct peak of RPN values (25.3 ± 6.6%) was noted in group CI at 6 hpi (p < 0.05). At 12 hpi and 24 hpi, RPN of CI cultures were rather similar to those of the EH group (15.3 ± 3.1% and 17.0 ± 4.8% at 12 hpi and 24 hpi, respectively) and, at 24 hpi, RPN of group CI, infected with the same E. tenella dose as cultures of group EL, were 4-fold higher than in the EL group.
Discussion
Macrophages are professional phagocytes and highly efficient at internalizing particles (Aderem and Underhill 1999). Flow cytometry and pH-sensitive fluorescent particles have been broadly used to visualize and quantify phagocytosis by macrophage cell lines (Pérez-Flores et al. 2016) or non-adherent phagocytic cells (Gordon et al. 2017; Neaga et al. 2013). However, a recent study (Kapellos et al. 2016) indicated that primary macrophages showed higher sensitivity to external stimulation and could suffer more from stress than other cells during fluorescent staining or running on a flow cytometer. We made similar observations working with chicken primary macrophages (data not shown). Most phagocytosis assays were carried out in mammalian macrophages, so far. However, direct comparison of data from mammalian macrophage cultures to our study is of limited value because the avian immune system features complex differences to the mammalian immune system, i.e., different antigen receptors (Iqbal et al. 2005), number of cytokines families (Kaufman et al. 1999), and delayed NO production of avian macrophages compared with murine macrophages (Malkwitz et al. 2018). So far, only two recent reports were found on the investigation of phagocytosis by using the same pH-sensitive fluorescent bioparticles in a chicken macrophage cell line (HD11 cells) (Garrido et al. 2018; Lee et al. 2018).
In our experiments, we firstly investigated the capacity of cultured chicken primary macrophages to engulf “Zymosan” at four observation periods up to 24 hpi. Macrophage showed great adaptation without observed apoptosis after applying “Zymosan” following the manufacturer’s instructions. Initial engulfment was efficient with on average 72% of macrophages displaying phagocytosis at 2 hpi. However, macrophage activity decreased to 36.6% until the end of the study period. This finding indicates that primary macrophage phagocytosis is generally declining over time. Compared with a recent study of Garrido et al. (Garrido et al. 2018), showing that about 25% of HD 11 cells retain phagocytic activity induced by pH-sensitive bioparticles after 16-h mock treatment, our observed phagocytosis percentages are in a good range over the whole chosen study period.
The cell density of murine bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs) and the duration of activation played a crucial role in uptake of fluorescent particles (Kapellos et al. 2016). Therefore, for longer-term phagocytosis investigations in primary avian macrophages, optimization of cultivation and assay conditions may be crucial to improve phagocytosis capacity over a longer period of time. In our study, LPS polarization led to a reduction of the uptake of “Zymosan” by about 20%. This is in line with the findings in murine BMDMs, where stated that cytokine expression changes by LPS stimulation may reduce their ability to engulf fluorescent particles (Kapellos et al. 2016). Altogether, the model described here appears to be a suitable model to perform investigations into T. gondii and E. tenella infections including co-infection in chicken macrophages.
Pathogen-pathogen interaction is more and more recognized as an important factor in pathogenesis and disease outcome. For parasites, in vivo studies into enhanced interactions of pathogens co-existing in a host and evidence of competition were shown (Clark et al. 2016; Hiob et al. 2017; Onaga et al. 1983). Regarding coccidia, clinical disease caused by E. maxima is ameliorated by concurrent E. praecox infections in chickens (Jenkins et al. 2008). Eimeria replication in terms of oocyst excretion numbers does not seem to be influenced by co-infections with other Eimeria species in most in vivo studies (Cornelissen et al. 2009). However, a study into experimental E. tenella infections showed significantly lower oocyst excretion in a group co-infected with T. gondii than in an Eimeria mono-infected group (Hiob et al. 2017).
In contrast, our previous long-term in vitro study revealed that both T. gondii and E. tenella were multiplying more effectively in co-infected cultures than in mono-infected cultures over a period of 72 hpi (Zhang et al. 2018). Looking into the related impact on macrophage function as a crucial aspect of the innate immune response, we have identified phagocytosis, which is the major activity of chicken macrophages during pathogen exposure, to be severely impacted by T. gondii and E. tenella co-infections.
With regard to the mode of invasion, it has been demonstrated that a proportion of T. gondii may invade host cells actively while avoiding an efficient phagocytic response through formation of a parasitophorous vacuole (Butcher and Denkers 2002; Morisaki et al. 1995). For E. bovis, active invasion is negligible in bovine primary macrophages (Taubert et al. 2009). For both T. gondii and E. tenella, phagocytosis by the host cell was identified earlier as the major route of pathogen entry (Goren 1977; Rose and Lee 1977).
In our phagocytosis assay, all T. gondii or E. tenella mono-infected groups showed inhibition of “Zymosan” engulfment at 2 hpi. Inhibition of phagocytosis in the high-dose infected groups (TH, EH) was more obvious than in low-dose infection groups (TL, EL). This is in line with a dose-dependent parasite replication (RPN) as observed for both parasites. Interestingly, co-infected macrophage cultures exhibited a significantly lower level of phagocytosis inhibition than seen in all mono-infection groups. Intracellular parasite quantification demonstrated that more than double T. gondii copies were detected in group TL whereas slightly lower E. tenella copy numbers were found in group EL compared with group CI, which shows that parasite replication is affected differently for T. gondii and E. tenella during co-infection. While E. tenella displays a higher initial incorporation rate upon co-infection, T. gondii appears to feature an impaired invasion rate. According to our recent light microscopical study (Zhang et al. 2018) and live cell imaging results (unpublished yet), most E. tenella sporozoites were capable at 2 hpi to enter macrophages while most T. gondii tachyzoites “prefer” to adhere to the surface of a macrophage or stay free in the cell culture medium. One previous in vitro study likewise reported the capacity of chicken macrophages to engulf E. tenella sporozoites at 2–3 hpi (Long and Rose 1976). Another study showed that a high proportion of live T. gondii stayed loosely adherent to host cells without invading and inducing phagocytosis (Morisaki et al. 1995). On the other hand, a previous study showed that most T. gondii tachyzoites remained adherent to murine macrophages followed by phagocytic inhibition treatment (Ryning and Remington 1978). We speculate that the initially reduced T. gondii RPN in group CI compared with mono-infection groups may be that T. gondii endocytosis by macrophages was blocked on the host-cell side by phagocytosis-inhibited macrophages previously entered by E. tenella. However, further evidences need to support it by investigating the signal pathway interactions.
Entry of both T. gondii and E. tenella increased whereas no inhibition was seen on phagocytic capacity of macrophages in co-infection at 6 hpi. Interestingly, co-infection showed distinctly lower phagocytic inhibition but higher RPN of E. tenella than E. tenella mono-infection group. Meanwhile, phagocytic inhibition by mono-infection of both parasites likely revealed biphasic at 6 and 12 hpi in our study. Specifically, inhibition appeared mostly in the E. tenella infection. Due to lack of comparable research, we assumed that significant engulfment of E. tenella was associated possibly to the low phagocytosis-inhibited macrophages modulating by T. gondii infection.
Combining to our data of quantification and visualization, it appears that a small number of both parasites retained their capability to evade from macrophage phagocytosis and developed successfully while most were eliminated at 12 hpi. Similar results were seen before in mono-infected chicken primary macrophage cultures with the lowest parasite DNA copies of T. gondii at the same point (Malkwitz et al. 2017). T. gondii and E. tenella stages were occasionally identified within the same individual macrophages, which is in line with findings from our previous study (Zhang et al. 2018). E. tenella exhibited higher initial infection efficiency than T. gondii as inferred from RPN at 12 hpi in relation to the applied infection dose. However, CLSM suggests that most of E. tenella-YFP failed to show fluorescence and little intracellular sporozoites or meronts were visualized during Eimeria infection. The co-infected cell cultures showed distinctly lower activation by “Zymosan” than mono-infected cultures at 12 hpi. Interestingly, phagocytic activity as measured by “Zymosan” incorporation into macrophages was initially inhibited stronger in both groups EH and TH than in the co-infected group CI which was exposed to both parasites at half the infection dose. This effect reversed at 12 hpi indicating that co-infection leads to more complex effects on a host culture than a mono-infection. Similar to the LPS polarization which was described earlier, co-infection likely triggered immune pathways in the cultures, and stronger so than mono-infections did, which needs to be further discussed.
Relative phagocytosis inhibition values at the end of our study period (24 hpi) were strongly increased in groups EH and CI, while TH cultures displayed significantly higher phagocytosis activity than uninfected cultures. Seemingly, E. tenella appears to be mainly responsible for the reduced macrophage phagocytosis that was observed in group CI. Both studied apicomplexan parasites have similar ways of host cell invasion and intracellular replication. Nevertheless, they exhibit different effects on chicken macrophage function related to innate immunity. It may be hypothesized from our data that parasite stage and replication as well as parasite adaption to its host may be involved in the observed infection-related group differences. Follow-up studies including in vivo studies or immune intervention will be needed to investigate the underlying mechanism of phagocytosis inhibition (E. tenella and co-infections) or enhancement (T. gondii infections towards the end of the study).
Conclusion
This in vitro infection model of primary avian macrophages can provide an efficient and accurate way to further investigate mechanisms of host-parasite and parasite-parasite interaction during co-infections with pathogens such as monoxenous and heteroxenous coccidia. The current findings contribute to our understanding of macrophage modulation by intracellular parasites and functionality at the early stage of infection with T. gondii and/or E. tenella.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Aderem A, Underhill DM (1999) Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol 17:593–623
Al-Gawad AA, Mahdy OA, El-Massry AAN, Al-Aziz MSA (2012) Studies on coccidia of Egyptian Balady breed chickens. Life Sci J 9:568–576
Butcher BA, Denkers EY (2002) Mechanism of entry determines the ability of Toxoplasma gondii to inhibit macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production. Infect Immun 70:5216–5224
Challey JR, Burns WC (1959) The invasion of the cecal mucosa by Eimeria tenella sporozoites and their transport by macrophages. J Protozool 6:238–241
Clark NJ, Wells K, Dimitrov D, Clegg SM (2016) Co-infections and environmental conditions drive the distributions of blood parasites in wild birds. J Anim Ecol 85:1461–1470
Cornelissen JBWJ, Swinkels WJC, Boersma WA, Rebel JMJ (2009) Eimeria praecox infection ameliorates effects of Eimeria maxima infection in chickens. Vet Parasitol 162:58–66
Cox FEG (2001) Concomitant infections, parasites and immune responses. Parasitology 122:S23–S38. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118200001698X
Dalloul RA, Lillehoj HS (2006) Poultry coccidiosis: recent advancements in control measures and vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 5:143–163
Dalloul RA, Bliss TW, Hong Y-H, Ben-Chouikha I, Park DW, Keeler CL, Lillehoj HS (2007) Unique responses of the avian macrophage to different species of Eimeria. Mol Immunol 44:558–566
Desjardins M, Descoteaux A (1997) Inhibition of phagolysosomal biogenesis by the Leishmania lipophosphoglycan. J Exp Med 185:2061–2068
Deyab AK, Hassanein R (2005) Zoonotic toxoplasmosis in chicken. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 35:341–350
Dubey JP (2010) Toxoplasma gondii infections in chickens (Gallus domesticus). Prevalence, clinical disease, diagnosis and public health significance. Zoonoses Public Health 57:60–73
Garrido D, Alber A, Kut E, Chanteloup NK, Lion A, Trotereau A, Dupont J, Tedin K, Kaspers B, Vervelde L (2018) The role of type I interferons (IFNs) in the regulation of chicken macrophage inflammatory response to bacterial challenge. Dev Comp Immunol 86:156–170
Gordon SR, Maute RL, Dulken BW, Hutter G, George BM, McCracken MN, Gupta R, Tsai JM, Sinha R, Corey D (2017) PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity. Nature 545:495–499
Goren MB (1977) Phagocyte lysosomes: interactions with infectious agents, phagosomes, and experimental perturbations in function. Annu Rev Microbiol 31:507–533
Harker KS, Ueno N, Lodoen MB (2015) Toxoplasma gondii dissemination: a parasite's journey through the infected host. Parasite Immunol 37:141–149
Hériveau C, Dimier-Poisson I, Lowenthal J, Naciri M, Quéré P (2000) Inhibition of Eimeria tenella replication after recombinant IFN-γ activation in chicken macrophages, fibroblasts and epithelial cells. Vet Parasitol 92:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4017(00)00275-2
Hiob L, Koethe M, Schares G, Goroll T, Daugschies A, Bangoura B (2017) Experimental Toxoplasma gondii and Eimeria tenella co-infection in chickens. Parasitol Res:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5636-2
Iqbal M, Philbin VJ, Smith AL (2005) Expression patterns of chicken toll-like receptor mRNA in tissues, immune cell subsets and cell lines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 104:117–127
Jenkins M, Allen P, Wilkins G, Klopp S, Miska K (2008) Eimeria praecox infection ameliorates effects of Eimeria maxima infection in chickens. Vet Parasitol 155:10–14
Kapellos TS, Taylor L, Lee H, Cowley SA, James WS, Iqbal AJ, Greaves DR (2016) A novel real time imaging platform to quantify macrophage phagocytosis. Biochem Pharmacol 116:107–119
Kaufman J, Milne S, Göbel TWF, Walker BA, Jacob JP, Auffray C, Zoorob R, Beck S (1999) The chicken B locus is a minimal essential major histocompatibility complex. Nature 401:923–925
Kawahara F, Taira K, Nagai S, Onaga H, Onuma M, Nunoya T (2008) Detection of five avian Eimeria species by species-specific real-time polymerase chain reaction assay. Avian Dis 52:652–656
Lee JH, Hou X, Kummari E, Borazjani A, Edelmann MJ, Ross MK (2018) Endocannabinoid hydrolases in avian HD11 macrophages identified by chemoproteomics: inactivation by small-molecule inhibitors and pathogen-induced downregulation of their activity. Mol Cell Biochem 444:125–141
Lehmann T, Marcet PL, Graham DH, Dahl ER, Dubey JP (2006) Globalization and the population structure of Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:11423–11428
Long PL, Rose ME (1976) Growth of Eimeria tenella in vitro in macrophages from chicken peritoneal exudates. Z Parasitenk 48:291–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380405
Malkwitz I, Berndt A, Daugschies A, Bangoura B (2013) Long-term investigations on Toxoplasma gondii-infected primary chicken macrophages. Parasitol Res 112:3115–3122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3486-0
Malkwitz I, Berndt A, Zhang R, Daugschies A, Bangoura B (2017) Replication of Toxoplasma gondii in chicken erythrocytes and thrombocytes compared to macrophages. Parasitol Res 116:123–131
Malkwitz I, Berndt A, Daugschies A, Bangoura B (2018) Characterisation of susceptibility of chicken macrophages to infection with Toxoplasma gondii of type II and III strains. Exp Parasitol 187:22–29
Mason S, Dubey JP, Smith JE, Boag B (2015) Toxoplasma gondii coinfection with diseases and parasites in wild rabbits in Scotland. Parasitology 142:1415–1421
Morisaki JH, Heuser JE, Sibley LD (1995) Invasion of Toxoplasma gondii occurs by active penetration of the host cell. J Cell Sci 108:2457–2464
Neaga A, Lefor J, Lich KE, Liparoto SF, Xiao YQ (2013) Development and validation of a flow cytometric method to evaluate phagocytosis of pHrodo™ BioParticles® by granulocytes in multiple species. J Immunol Methods 390:9–17
Onaga H, Tajima M, Ishii T (1983) Activation of macrophages by culture fluid of antigen-stimulated spleen cells collected from chickens immunized with Eimeria tenella. Vet Parasitol 13:1–11
Pérez-Flores G, Hernández-Silva C, Gutiérrez-Escobedo G, de Las Peñas A, Castaño I, Arreola J, Pérez-Cornejo P (2016) P2X7 from j774 murine macrophages acts as a scavenger receptor for bacteria but not yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 481:19–24
Rose ME, Lee DL (1977) Interactions in vitro between sporozoites of Eimeria tenella and host peritoneal exudate cells. Electron microscopal observations. Z Parasitenk 54:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380632
Ryning FW, Remington JS (1978) Effect of cytochalasin D on Toxoplasma gondii cell entry. Infect Immun 20:739–743
Sibley LD (1995) Invasion of vertebrate cells by Toxoplasma gondii. Trends Cell Biol 5:129–132
Taubert A, Behrendt JH, Sühwold A, Zahner H, Hermosilla C (2009) Monocyte-and macrophage-mediated immune reactions against Eimeria bovis. Vet Parasitol 164:141–153
Thabet A, Alnassan AA, Daugschies A, Bangoura B (2015) Combination of cell culture and qPCR to assess the efficacy of different anticoccidials on Eimeria tenella sporozoites. Parasitol Res 114:2155–2163
Thabet A, Zhang R, Alnassan A-A, Daugschies A, Bangoura B (2017) Anticoccidial efficacy testing: In vitro Eimeria tenella assays as replacement for animal experiments. Vet Parasitol 233:86–96
Trout JM, Lillehoi HS (1993) Evidence of a role for intestinal CD8+ lymphocytes and macrophages in transport of Eimeria acervulina sporozoites. J Parasitol 79:790–792
Unno A, Suzuki K, Xuan X, Nishikawa Y, Kitoh K, Takashima Y (2008) Dissemination of extracellular and intracellular Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites in the blood flow. Parasitol Int 57:515–518
van Doorninck WM, Becker ER (1957) Transport of sporozoites of Eimeria necatrix in macrophages. J Parasitol 43:40–44
Vervelde L, Vermeulen AN, Jeurissen SH (1995) Eimeria tenella: sporozoites rarely enter leukocytes in the cecal epithelium of the chicken (Gallus domesticus). Exp Parasitol 81:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1006/expr.1995.1089
Vervelde L, Vermelen AN, Jeurissen SHM (1996) In situ characterization of leucocyte subpopulations after infection with Eimeria tenella in chickens. Parasite Immunol 18:247–256
Zhang R, Thabet A, Hiob L, Zheng W, Daugschies A, Bangoura B (2018) Mutual interactions of the apicomplexan parasites Toxoplasma gondii and Eimeria tenella with cultured poultry macrophages. Parasit Vectors 11:453
Zhou Z, Wang Z, Cao L, Hu S, Zhang Z, Qin B, Guo Z, Nie K (2013) Upregulation of chicken TLR4, TLR15 and MyD88 in heterophils and monocyte-derived macrophages stimulated with Eimeria tenella in vitro. Exp Parasitol 133:427–433
Acknowledgments
We thank the Bioimaging Core Facility (BCF) and all members of the Institute of Parasitology, Leipzig University, for technical assistance and support. We are grateful to D. Hu, China Agricultural University, China, for preparing samples. The authors acknowledge support from the German Research Foundation (DFG) and Leipzig University within the program of Open Access Publishing.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. RZ receives research doctoral fellowships from Akademie für Tiergesundheit (AfT) and Karl-Enigk-Stiftung (KES), Germany. The funding of open access publishing was provided from the German Research Foundation (DFG), Germany. The funders had no role in study design, analysis, interpretation of data and writing the manuscripts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ designed the study, wrote the manuscript, performed the experiments, and analyzed partial data. WZ analyzed partial data and helped to draft the manuscript. AD and BB critically revised the study design, data interpretation, and manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The animal experiments related to the blood sampling were approved by the responsible authorities (Landesdirektion Sachsen, Germany, trial registration number V13/10).
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Handling Editor: Julia Walochnik
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Zheng, W., Daugschies, A. et al. Apicomplexan co-infections impair with phagocytic activity in avian macrophages. Parasitol Res 119, 4159–4168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06900-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06900-3