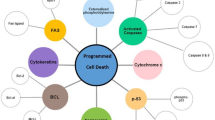
Abstract
Human gnathostomiasis caused by third-stage Gnathostoma spinigerum larvae (G. spinigerum L3) is an important zoonotic disease in tropical areas of the world. The excretory-secretory products (ES) that are excreted by infective larva play a significant role in host immune evasion and tissue destruction. To investigate the poorly understood mechanisms of G. spinigerum L3 pathogenesis, we focused on the potential effect of ES on inducing apoptosis in human immune cells by using human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) as a model. Early and late apoptosis of PBMCs were assessed following the exposure of these cells to G. spinigerum L3 ES (0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 μg/ml) for 6–48 h. The apoptotic cells were identified by flow cytometric staining of PBMC with FITC-annexin V and propidium iodide. The expression of regulatory genes related to apoptosis mechanisms in ES-treated PBMCs was investigated using a Human Apoptosis RT2 Profiler™ PCR Array. The results showed significant levels of early phase apoptosis at 18 h and of late phase apoptosis at 24 h. We speculate that this apoptosis in PBMCs occurs via the extrinsic pathway. Apoptosis in the ES-induced PBMCs was observed as quickly as 90 min after exposure, and the highest effect was observed at 18–24 h. Furthermore, ES can trigger apoptosis lasting for 48 h. Our findings expand the understanding of one of the mechanisms involved, immune-evasive strategy mechanism used by G. spinigerum larvae during human gnathostomiasis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthony RM, Rutitzky LI, Urban JF, Jr., Stadecker MJ, Gause WC (2007) Protective immune mechanisms in helminth infection Nature reviews Immunology 7:975–987 doi:10.1038/nri2199
Babu S, Blauvelt CP, Nutman TB (2007) Filarial parasites induce NK cell activation, type 1 and type 2 cytokine secretion, and subsequent apoptotic cell death. J Immunol 179:2445–2456
Barbosa AP, Campos DM, Semerene AR, Teixeira AR, Santana JM (2006) Lagochilascaris minor third-stage larvae secrete metalloproteases with specificity for fibrinogen and native collagen Microbes and infection/Institut Pasteur 8:2725–2732 doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2006.08.001
Basavaraju SV, Zhan B, Kennedy MW, Liu Y, Hawdon J, Hotez PJ (2003) Ac-FAR-1, a 20 kDa fatty acid- and retinol-binding protein secreted by adult Ancylostoma caninum hookworms: gene transcription pattern, ligand binding properties and structural characterisation Molecular and biochemical parasitology 126:63–71
Benjathummarak S, Kumsiri R, Nuamtanong S, Kalambaheti T, Waikagul J, Viseshakul N, Maneerat Y (2016) Third-stage Gnathostoma spinigerum larva excretory secretory antigens modulate function of Fc gamma receptor I-mediated monocytes in peripheral blood mononuclear cell culture Tropical medicine and health 44:5 doi:10.1186/s41182-016-0005-x
Bennuru S, Semnani R, Meng Z, Ribeiro JM, Veenstra TD, Nutman TB (2009) Brugia malayi excreted/secreted proteins at the host/parasite interface: stage- and gender-specific proteomic profiling PLoS neglected tropical diseases 3:e410 doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000410
Boyum A (1968) Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation Supplementum 97:77–89
Carneiro-Santos P et al (2000) Apoptosis: a mechanism of immunoregulation during human Schistosomiasis mansoni. Parasite Immunol 22:267–277
Chen L, Rao KV, He YX, Ramaswamy K (2002) Skin-stage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni produce an apoptosis-inducing factor that can cause apoptosis of T cells The Journal of biological chemistry 277:34329–34335 doi:10.1074/jbc.M201344200
Chow SC, Brown A, Pritchard D (2000) The human hookworm pathogen Necator americanus induces apoptosis in T lymphocytes Parasite immunology 22:21–29
Colino J, Snapper CM (2003) Two distinct mechanisms for induction of dendritic cell apoptosis in response to intact Streptococcus pneumoniae Journal of immunology 171:2354–2365
Daigneault M et al. (2012) Monocytes regulate the mechanism of T-cell death by inducing Fas-mediated apoptosis during bacterial infection PLoS pathogens 8:e1002814 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002814
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death Toxicologic pathology 35:495–516 doi:10.1080/01926230701320337
Evan G, Littlewood T (1998) A matter of life and cell death. Science 281:1317–1322
Germann R, Schachtele M, Nessler G, Seitz U, Kniehl E (2003) Cerebral gnathostomiasis as a cause of an extended intracranial bleeding Klinische Padiatrie 215:223–225 doi:10.1055/s-2003-41401
Hajiaghalou S, Ebrahimi B, Shahverdi A, Sharbatoghli M, Beigi Boroujeni N (2016) Comparison of apoptosis pathway following the use of two protocols for vitrification of immature mouse testicular tissue Theriogenology 86:2073–2082 doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.06.027
Hingorani A, Ascher E (2011) Part two: against the motion asymptomatic popliteal artery aneurysms (less than 3 cm) should be repaired European journal of vascular and endovascular surgery: the official journal of the European Society for Vascular Surgery 41:448–449; discussion 449 doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2011.02.008
Igney FH, Krammer PH (2002) Death and anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis Nature reviews Cancer 2:277–288 doi:10.1038/nrc776
Iwasa T, Suga S, Qi L, Komada Y (2010) Apoptosis of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by wild-type measles virus infection is induced by interaction of hemagglutinin protein and cellular receptor, SLAM via caspase-dependent pathway Microbiology and immunology 54:405–416 doi:10.1111/j.1348-0421.2010.00231.x
James ER, Green DR (2004) Manipulation of apoptosis in the host-parasite interaction. Trends in parasitology 20:280–287. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2004.04.004
Jenkins SJ, Hewitson JP, Jenkins GR, Mountford AP (2005) Modulation of the host’s immune response by schistosome larvae. Parasite immunology 27:385–393. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.2005.00789.x
Kaewpitoon N, Kaewpitoon SJ, Pengsaa P, Sripa B (2008) Opisthorchis viverrini: the carcinogenic human liver fluke World journal of gastroenterology 14:666–674
Kaneko S, Suzuki N, Koizumi H, Yamamoto S, Sakane T (1997) Rescue by cytokines of apoptotic cell death induced by IL-2 deprivation of human antigen-specific T cell clones Clinical and experimental immunology 109:185–193
Kuroda Y et al (2002) Structural studies on IgG oligosaccharides of patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Glycoconj J 19:23–31
Lee ST, Wong PF, Cheah SC, Mustafa MR (2011) Alpha-tomatine induces apoptosis and inhibits nuclear factor-kappa B activation on human prostatic adenocarcinoma PC-3 cells PloS one 6:e18915 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018915
Metzstein MM, Stanfield GM, Horvitz HR (1998) Genetics of programmed cell death in C. elegans: past, present and future Trends in genetics: TIG 14:410–416
Moore DA, McCroddan J, Dekumyoy P, Chiodini PL (2003) Gnathostomiasis: an emerging imported disease Emerging infectious diseases 9:647–650 doi:10.3201/eid0906.020625
Mulcahy G, O'Neill S, Fanning J, McCarthy E, Sekiya M (2005) Tissue migration by parasitic helminths—an immunoevasive strategy? Trends Parasitol 21:273–277. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2005.04.003
Nono JK, Pletinckx K, Lutz MB, Brehm K (2012) Excretory/secretory-products of Echinococcus multilocularis larvae induce apoptosis and tolerogenic properties in dendritic cells in vitro PLoS neglected tropical diseases 6:e1516 doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001516
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase Nature 401:82–85 doi:10.1038/43466
Palma PF, Baggio GL, Spada C, Silva RD, Ferreira SI, Treitinger A (2008) Evaluation of annexin V and Calcein-AM as markers of mononuclear cell apoptosis during human immunodeficiency virus infection The Brazilian journal of infectious diseases: an official publication of the Brazilian Society of Infectious Diseases 12:108–114
Rege K, Patel SJ, Megeed Z, Yarmush ML (2007) Amphipathic peptide-based fusion peptides and immunoconjugates for the targeted ablation of prostate cancer cells Cancer research 67:6368–6375 doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3658
Ruano AL, Lopez-Aban J, Gajate C, Mollinedo F, De Melo AL, Muro A (2012) Apoptotic mechanisms are involved in the death of Strongyloides venezuelensis after triggering of nitric oxide Parasite immunology 34:570–580 doi:10.1111/pim.12004
Serradell MC, Guasconi L, Masih DT (2009) Involvement of a mitochondrial pathway and key role of hydrogen peroxide during eosinophil apoptosis induced by excretory-secretory products from Fasciola hepatica Molecular and biochemical parasitology 163:95–106 doi:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2008.10.005
Shin MH (2000) Excretory-secretory product of Paragonimus westermani newly excysted metacercariae inhibits superoxide production of granulocytes stimulated with IgG The Korean journal of parasitology 38:103–106
Tato P, Fernandez AM, Solano S, Borgonio V, Garrido E, Sepulveda J, Molinari JL (2004) A cysteine protease from Taenia solium metacestodes induce apoptosis in human CD4+ T-cells Parasitology research 92:197–204 doi:10.1007/s00436-003-1008-1
Taylor RC, Cullen SP, Martin SJ (2008) Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 9:231–241 doi:10.1038/nrm2312
Van Herreweghe F, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: to break or to burst, that’s the question Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS 67:1567–1579 doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0283-0
Yan C et al. (2015) Clonorchis sinensis excretory/secretory products promote the secretion of TNF-alpha in the mouse intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells via Toll-like receptor 4 Parasites & vectors 8:559 doi:10.1186/s13071-015-1171-0
Zhu L et al. (2012) Real-time monitoring of caspase cascade activation in living cells Journal of controlled release: official journal of the Controlled Release Society 163:55–62 doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.05.044
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Research Grant from the Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Fiscal Year 2013–2014 for YM. It was also supported in part by Grant-in-Aids from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan (No. H20-Shinko-Ippan-015) to YE and from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (Kiban B, Overseas, No. 20401050) to YE. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Mahidol-Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit (MORU) for providing access to the FACSCalibur flow cytometer and CellQuest software. We thank Mr. Paul R. Adams for English proofreading and Katie E. Oakley, PhD, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a later draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SN was responsible for the collection of G. spinigerum L3 cultures and preparation of ES. YM and WD were responsible for laboratory work, PBMC culture, and sample preparation for all experiments, and they carried out the FACS analysis. NV and SB contributed to the microarray experiment study design, performed the RNA extraction, and carried out the real-time PCR assays and analyses. WD was responsible for data analysis and statistical analysis. YM and NV participated in the study design, conceived the study, participated in its design and coordination, and contributed to writing the manuscript. All authors interpreted the results and have read and approved the final manuscript. The funding was granted to YM and YE.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
Profile of gene expression and their functions in PBMC cultured with G. spinigerum L3 ES at the dose of 0.5 μg/ml for 30 min in comparison to those in medium alone. (JPG 908 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Profile of gene expression and their functions in PBMC cultured with G. spinigerum L3 ES at the dose of 0.5 μg/ml for 60 min in comparison to those in medium alone. (JPG 920 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Profile of gene expression and their functions in PBMC cultured with G. spinigerum L3 ES at the dose of 0.5 μg/ml for 90 min in comparison to those in medium alone. (JPG 935 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Profile of gene expression and their functions in PBMC cultured with G. spinigerum L3 ES at the dose of 0.1 μg/ml for 3 h in comparison to those in medium alone. (JPG 928 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
Profile of gene expression and their functions in PBMC cultured with G. spinigerum L3 ES at the dose of 0.5 μg/ml for 3 h in comparison to those in medium alone. (JPG 924 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viseshakul, N., Dechkhajorn, W., Benjathummarak, S. et al. Excretory-secretory product of third-stage Gnathostoma spinigerum larvae induces apoptosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Parasitol Res 116, 2783–2794 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5589-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5589-5