Abstract
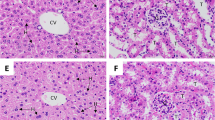
Malaria is still one of the most common infectious diseases and leads to various public health problems worldwide. Medicinal plants are promising sources for identifying novel agents with potential antimalarial activity. This study aimed to investigate the antimalarial and the antioxidant activities of Indigofera oblongifolia on Plasmodium chabaudi-induced spleen tissue injury in mice. Mice were divided into five groups. The first group served as a vehicle control; the second, third, fourth, and fifth groups were infected with 1 × 106 P. chabaudi-parasitized erythrocytes. Mice of the last three groups were gavaged with 100 μl of I. oblongifolia leave extract (IOLE) at a dose of 100, 200, and 300 mg IOLE/kg, respectively, once daily for 7 days. IOLE was significantly able to lower the percentage of parasitemia. The most effective dose was the 100 mg IOLE/kg, which could reduce the parasitemia from about 38 to 12 %. The infection induced spleen injury. This was evidenced by disorganization of spleen white and red pulps, appearance of hemozoin granules and parasitized erythrocytes. These changes in spleen led to the increased histological score. Also, the infection increased the spleen oxidative damage where the levels of nitrite/nitrate, malondialdehyde, and catalase were significantly altered. All these infection-induced parameters were significantly improved during IOLE treatment. In addition, the mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha were upregulated after infection with P. chabaudi, whereas IOLE significantly reduced the expression of these genes. Our results indicate that I. oblongifolia leaves extract exhibits a significant antimalarial and antioxidant effects, and protects host spleen tissue from injuries induced by P. chabaudi.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtman AH, Khan M, MacLennan ICM, Langhorne J (2003) Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi infection in mice induces strong B cell responses and striking but temporary changes in splenic cell distribution. J Immunol 171:317–324
Aebi HU (ed) (1984) Methods in enzymatic analysis. Academic, New York, pp 276–286
Al-Adhroey AH, Nor ZM, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Amran AA, Mahmud R (2010) Antimalarial activity of methanolic leaf extract of Piper betle L. Molecules 16:107–118
Ali NA, Julich WD, Kusnick C, Lindequist U (2001) Screening of Yemeni medicinal plants for antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. J Ethanopharmacol 74:173–179
Berkels R, Purol-Schnabel S, Roesen R (2004) Measurement of nitric oxide by reconversion of nitrate/nitrite to NO. J Humana Press 279:1–8
Cabrales P, Zanini GM, Meays D, Frangos JA, Carvalho LJ (2011) Nitric oxide protection against murine cerebral malaria is associated with improved cerebral microcirculatory physiology. J Infect Dis 203:1454–1463
Dahot MU (1999) Antimicrobial and antifungal activity of small protein of Indigofera oblongifolia leaves. J Ethnopharmcol 64:277–282
Day NPJ (1999) The prognostic and pathophysiologic role of pro- and antiinflammatory cytokines in severe malaria. J Infect Dis 180:1288–1297
de ACarli CB, Quilles MB, Maia DC, Lopes FC, Santos R, Pavan FR, Fujimura Leite CQ, Calvo TR, Vilegas W, Carlos IZ (2010) Antimycobacterial activity of Indigofera suffruticosa with activation potential of the innate immune system. Pharm Biol 48:878–882
Delic D, Gailus N, Vohr HW, Dkhil M, Al-Quraishy S, Wunderlich F (2010) Testosterone-induced permanent changes of hepatic gene expression in female mice sustained during Plasmodium chabaudi malaria infection. J Mol Endocrinol 45:379–390
Dkhil MA (2009) Apoptotic changes induced in mice splenic tissue due to malaria infection. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 42:13–18
Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S, Al-Shamrany A, Alazzouni AS, Lubbad MY, Al-Shaebi EM, Noory T Taib NT (2015) Protective effect of berberine chloridr on Plasmodium chabaudi-induced hepatic tissue injury in mice. Saudi J Biol Sci
Foster SD (1991) Pricing, distribution, and use of antimalarial drugs. Bull World Health Organ 69:349–363
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Tziortzioti V, Koutoukas P, Baziaka F, Raftogiannis M, Antonopoulou A, Adamis T, Sabracos L, Giamarellou H (2006) Clarithromycin is an effective immunomodulator in experimental pyelonephritis caused by panresistant Klebsiella pneumonia. J Antimicrob Chemother 57:937–944
Guha M, Kumar S, Choubey V, Maity P, Bandyopadhyay U (2006) Apoptosis in liver during malaria: role of oxidative stress and implication of mitochondrial pathway. FASEB J 20:439–449
Kirtikar KR, Basu BD (1984) Indian medicinal plants, 2nd edition, Vol. 1. International Book Distributors, Dehradun, pp. 712
Krücken J, Mehnert LI, Dkhil MA, El-Kadragy M, Benten WPM, Mossmann H, Wunderlich F (2005) Massive destruction of malaria parasitized red blood cells despite spleen closure. Infect Immun 73:6390–6398
Kumar RS, Jayakar B, Rajkapoor B (2007) Antitumour activity of Indigofera trita on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma induced mice. Int J Cancer Res 3:180–185
Lopes FC, Calvo TR, Colombo LL, Vilegas W, Carlos IZ (2010) Immunostimulatory and cytotoxic activities of Indigofera suffruticosa (Fabaceae). Nat Prod Res 25:1796–1806
Lyke KE, Burges R, Cissoko Y, Sangare L, Dao M, Diarra I, Kone A, Harley R, Plowe CV, Doumbo OK, Sztein MB (2004) Serum levels of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 beta (IL-1ß), IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and IL-12 (p70) in Malian children with severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria and matched uncomplicated malaria or healthy controls. Infect Immunol 72:5630–5637
Malaguarnera L, Musumeci S (2002) The immune response to Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet Infect Dis 2:472–478
Mau JL, Lin HC, Chen CC (2002) Antioxidant properties of several medicinal mushrooms. J Agric Food Chem 50:6072–6077
Mehlhorn H (ed) (2008) Encyclopedic reference of parasitology, vol 1, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin
Mohd Abd Razak MR, Afzan A, Ali R, Amir Jalaluddin NF, Wasiman MI, Shiekh Zahari SH, Abdullah NR, Ismail Z (2014) Effect of selected local medicinal plants on the asexual blood stage of chloroquine resistant Plasmodium falciparum. BMC Complement Altern Med 14(1):492
Mubaraki MA, Dkhil MA, Al-Shaebi EM, Lubbad MY, Ibrahim KE, Al-Quraishy S (2014) The protective effect of pomegranate, Punica granatum, on murine malaria. Pak J Zool 46:1345–1350
Odediran SA, Elujoba AA, Adebajo AC (2014) Influence of formulation ratio of the plant components on the antimalarial properties of MAMA decoction. Parasitol Res 113(5):1977–1984
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Pabón A, Carmona J, Burgos LC, Blair S (2002) Oxidative stress in patients with non-complicated malaria. Clin Biochem 36:71–78
Pagola S, Stephens PW, Bohle DS, Kosar AD, Madsen SK (2000) The structure of malaria pigment beta-haematin. Nature 404:307–310
Pichyangkul S, Saengkrai P, Webster HK (1994) Plasmodium falciparum pigment induces monocytes to release high levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta. Am J Trop Med Hyg 51:430–435
Ridley RG (2002) Medical need, scientific opportunity and the drive for antimalarial drugs. Nature 415:686–693
Sasidharan S, Chen Y, Saravanan D, Sundram KM, Yoga Latha L (2011) Extraction, isolation and characterization of bioactive compounds from plants’ extracts. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 8:1–10
Shahjahan M, Vani G, Shyamala Devi CS (2005) Protective effect of Indigofera oblongifolia in CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity. J Med Food 8:261–265
Sohail M, Kaul A, Raziuddin M, Adak T (2007) Decreased glutathione-S-transferase activity: diagnostic and protective role in vivax malaria. Clin Biochem 40:377–382
Stevenson MM, Riley EM (2004) Innate immunity to malaria. Nat Rev Immunol 4:169–180
Taherkhani M, Rustaiyan A, Nahrevanian H, Naeimi S, Taherkhani T (2013) Comparison of antimalarial activity of Artemisia turanica extract with current drugs in vivo. J Vector Borne Dis 50:51–g6
Toma A, Deyno S, Fikru A, Eyado A, Beale A (2015) In vivo antiplasmodial and toxicological effect of crude ethanol extract of Echinops kebericho traditionally used in treatment of malaria in Ethiopia. Malar J 14:196
Tsakiris S, Schulpis KH, Marinou K, Behrakis P (2004) Protective effect of L-cysteine and glutathione on the modulated suckling rat brain Na+, K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities induced by the in vitro galactosaemia. Pharmacol Res 49:475–479
Vale VV, Vilhena TC, Trindade RC, Ferreira MR, Percário S, Soares LF, Pereira WL, Brandão GC, Oliveira AB, Dolabela MF, De Vasconcelos F (2015) Anti-malarial activity and toxicity assessment of Himatanthus articulatus, a plant used to treat malaria in the Brazilian Amazon. Malar J 14:132
Worrall E, Basu S, Hanson K (2005) Is malaria a disease of poverty? A review of the literature. Trop Health Med 10:1047–1059
Wunderlich F, Stübig H, Königk E (1982) Development of Plasmodium chabaudi in mouse red blood cells: structural properties of the host and parasite membranes. J Protozool 29:60–66
Wunderlich F, Dkhil MA, Mehnert LI, Braun JV, El-Khadragy M, Borsch E, Hermsen D, Benten WPM, Pfeffer K, Mossmann H, Krücken J (2005) Testosterone-responsiveness of spleen and liver in female lymphotoxin-beta receptor-deficient mice resistant to blood stage malaria. Microbes Infect 7:399–409
Wunderlich F, Al-Quraishy S, Steinbrenner H, Sies H, Dkhil MA (2014) Towards identifying novel anti-Eimeria agents: trace elements, vitamins, and plant-based natural products. Parasitol Res 113:3547–3556
Zhang J, Krugliak M, Ginsburg H (1999) The fate of ferriprotorphyrin IX in malaria infected erythrocytes in conjunction with the mode of action of antimalarial drugs. Mol Biochem Parasitol 99:129–141
Zhang XG, Li GX, Zhao SS, Xu FL, Wang YH, Wang W (2014) A review of dihydroartemisinin as another gift from traditional Chinese medicine not only for malaria control but also for schistosomiasis control. Parasitol Res 113(5):1769–1773
Acknowledgments
The authors extend appreciations to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding the work through the research group project number PRG-1436-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. S1
Indigofera oblongifolia leaves. (JPEG 210 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lubbad, M.Y., Al-Quraishy, S. & Dkhil, M.A. Antimalarial and antioxidant activities of Indigofera oblongifolia on Plasmodium chabaudi-induced spleen tissue injury in mice. Parasitol Res 114, 3431–3438 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4568-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4568-y