Abstract
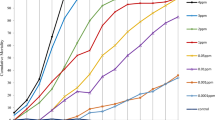
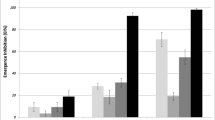
Pyriproxyfen, a juvenile hormone analogue, diflubenzuron, a chitin synthesis inhibitor, and azadirachtin, an ecdysone agonist, are three insect growth regulators (IGRs) considered as selective and effective insecticides for mosquitoes. Romanomermis iyengari (Welch) is a mosquito-parasitic mermithid that can provide biological control against many medically important mosquito species. The compatibility of these two control tactics was tested by evaluating the sublethal effects of exposure to IGR on nematode developmental stages (preparasitic, parasitic, and preparasitic + parasitic) using Culex pipiens larvae as the host. Sublethal concentrations of IGRs were 90 % emergence inhibition of host mosquito. Preparasitic exposure to pyriproxyfen, azadirachtin, and diflurbenzuron had no effect on infectivity, parasite load, sex ratio, or male size but reduced nematode female length and increased male sex ratio at one parasite/larva. When IGRs treatments were made against the parasitic and preparasitic + parasitic stages, pyriproxyfen and azadirachtin reduced R. iyengari infectivity, parasite load, and male nematode length, whereas pyriproxyfen exposure increased male sex ratio and reduced the female R. iyengari length. Thus, IGRs have significant negative impacts on different stages of mosquito mermithid that can destabilize the balance of host–parasite population interaction. Therefore, IGRs should be used with caution in mosquito habitats where these parasites have established.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charnov EL, Bull JJ (1977) When is sex environmentally determined? Nature 266:828–830
Dennis RD (1976) Insect morphogenetic hormones and developmental mechanisms in the nematode, Nematospiroides dubius. Comp Biochem Physiol A 53:53–56
Dobson AP (1986) Inequalities in the individual reproductive success of parasites. Parasitology 92:675–682
Finney JR, Gordon R, Condon WJ, Rusted TN (1977) Laboratory studies on the feasibility of integrated mosquito control using an insect growth regulator and a mermithid nematode. Mosq News 37:6–11
Giblin RM, Platzer EG (1985) Romanomermis culicivorax parasitism and the development, growth, and feeding rates of two mosquito species. J Invertebr Pathol 46:11–19
Gordon R (1981) Mermithid nematodes: physiological relationship with their insect hosts. J Nematol 13:266–274
Gordon R, Squires JM, Babie SJ, Buford IR (1981) Effects of host diet on Romanomermis culicivorax, a mermithid parasite of mosquitoes. J Nematol 13:285–290
Gordon R, Chippett J, Tilley J (1996) Effects of two carbamates on infective juveniles of Steinernema carpocapsae all strain and Steinernema feltiae Uumea strain. J Nematol 28:310–317
Kerwin JL, Zurakowaski KA, Washino RK (1990) Carbohydrate-mediated recognition of larval mosquito hosts by Romanomermis culicivorax. J Nematol 22:119–126
Korpelainen H (1990) Sex ratios and conditions required for environmental sex determination in animals. Biol Rev 65:147–184
Kumar J, Parmar BS (1998) Neem oil—chemistry and bioactivity. Pestic Res J 10:14–43
Leonardi MG, Cappellozza S, Ianne P, Cappellozza L, Parenti P, Giordana B (1996) Effects of the topical application of an insect growth regulator (fenoxycarb) on some physiological parameters in the fifth instar larvae of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Comp Biochem Physiol B 113:361–365
Levy R, Miller TW Jr (1977) Susceptibility of the mosquito nematode Romanomermis culicivorax (Mermithidae) to pesticides and growth regulators. Environ Entomol 6:447–448
May RM, Anderson RM (1978) Regulation and stability of host–parasite population interactions. II. Destabilizing processes. J Anim Ecol 47:249–267
Mulla MS, Darwazeh HA, Ede L, Kennedy B, Dawson DM (1986) Evaluation of new insect growth regulators against mosquitoes with notes on nontarget organisms. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 2:314–320
Paily KP, Balaraman K (1994) Effect of temperature on different stages of Romanomermis iyengari, a mermithid nematode parasite of mosquitoes. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz Rio de Janeiro 89: 635–642
Petersen JJ (1972) Factors affecting sex ratios of a mermithid parasite of mosquitoes. J Nematol 4:82–87
Petersen JJ (1977) Effects of host size and parasite burden on sex ratio in the mosquito parasite Octomyomermis muspratti. J Nematol 9:343–346
Petersen JJ, Willis OR (1970) Some factors affecting parasitism by mermithid nematodes in southern house mosquito larvae. J Econ Entomol 63:175–178
Petersen JJ, Willis OR (1972) Procedure for the mass rearing of a mermithid parasite of mosquitoes. Mosq News 32:226–230
Platzer EG (2007) Mermithid nematodes. Biorational Control of Mosquitoes. Bulletin No. 7. J Am Mosq Control Assoc (Suppl) 23:58–64
Poulin R (1998) Evolutionary ecology of parasites: from individuals to communities. Chapman & Hall, London
Poulin R, Latham ADM (2002) Inequalities in size and intensity-dependent growth in a mermithid nematode parasitic in beach hoppers. J Helminthol 76:65–70
Santamarina AM, Garcia AI, Gonzalez RB (1993) Valoracion de la capacidad infectiva de nematodo parasito Romanomermis iyengari (Nematoda: Mermithidae) en criaderos naturales de larvas de mosquitoes. Rev Cubana Med Trop 45:128–131
Santamarina AM, Pacheco RP, Martinez SHT, Canton LE, Ambrosio GF (1999) The Romanomermis iyengari parasite for Anopheles psuedopunctipennis suppression in natural habitats in Oaxaca State, Mexico. Rev Panam Salud Publica/Pan Am J Publ Hlth 5:23–28
Suman DS, Parashar BD, Prakash S (2010) Efficacy of various insect growth regulators on organophosphate resistant immature of Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) from different geographical areas of India. J Entomol 7:33–43
Tingley GA, Anderson RM (1986) Environmental sex determination and density-dependent population regulation in the entomogenous nematode Romanomermis culicivorax. Parasitology 92:431–449
WHO [World Health Organization] (2006) Pesticides and their application for the control of vectors and pests of public health importance (6th edn). WHO/CTD/NTD/WHOPES/GCDPP, Geneva
Acknowledgments
We thank Don Hanson for providing IGR samples, and Linda McCuiston and Jennifer Sunn for assistance in culture maintenance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suman, D.S., Brey, C.W., Wang, Y. et al. Effects of insect growth regulators on the mosquito-parasitic nematode Romanomermis iyengari . Parasitol Res 112, 817–824 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3201-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3201-6