Abstract
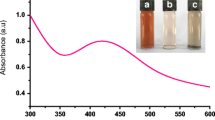
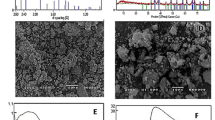
The present study was based on assessments of the anti-parasitic activities to determine the efficacies of synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) prepared by wet chemical method using zinc nitrate and sodium hydroxide as precursors and soluble starch as stabilizing agent against the larvae of cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, Canestrini (Acari: Ixodidae); head louse Pediculus humanus capitis, De Geer (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae); larvae of malaria vector, Anopheles subpictus, Grassi; and filariasis vector, Culex quinquefasciatus, Say (Diptera: Culicidae). R. microplus larvae were exposed to filter paper envelopes impregnated with different ZnO NP concentrations. Direct contact method was conducted to determine the potential of pediculocidal activity. Parasite larvae were exposed to varying concentrations of synthesized ZnO NPs for 24 h. The results suggested that the mortality effects of synthesized ZnO NPs were 43% at 1 h, 64% at 3 h, 78% at 6 h, and 100% after 12 h against R. microplus activity. In pediculocidal activity, the results showed that the optimal times for measuring mortality effects of synthesized ZnO NPs were 38% at 10 min, 71% at 30 min, 83% at 1 h, and 100% after 6 h against P. humanus capitis. One hundred percent lice mortality was observed at 10 mg/L treated for 6 h. The mortality was confirmed after 24 h of observation period. The larval mortality effects of synthesized ZnO NPs were 37%, 72%, 100% and 43%, 78% and 100% at 6, 12, and 24 h against A. subpictus and C. quinquefasciatus, respectively. It is apparent that the small size and corresponding large specific surface area of small nanometer-scale ZnO particles impose several effects that govern its parasitic action, which are size dependent. ZnO NPs were synthesized by wet chemical process, and it was characterized with the UV showing peak at 361 nm. X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra clearly shows that the diffraction peaks in the pattern indexed as the zinc oxide with lattice constants a = 3.249 and c = 5.206 Å. The FTIR spectrum showed the range of 400–4,000 cm−1. The band at 899.56 cm−1; 1,151.87 cm−1; 1,396 cm−1; and these bands showed the complete composition of ZnO NPs. SEM micrograph showed 60–120-nm size and aggregates of spherical shape nanoparticles. EDX showed the complete chemical composition of the synthesized nanoparticles of zinc oxide. The maximum efficacy was observed in zinc oxide against the R. microplus, P. humanus capitis, and the larvae of A. subpictus, C. quinquefasciatus with LC50 values of 29.14, 11.80, 11.14, and 12.39 mg/L; r 2 = 0.805, 0.876, 0.894, and 0.904, respectively. The synthesized ZnO NPs showed the LC50 and r 2 values against the R. microplus (13.41 mg/L; 0.982), P. humanus capitis (11.80 mg/L; 0.966), and the larvae of A. subpictus (3.19; 0.945 mg/L), against C. quinquefasciatus (4.87 mg/L; 0.970), respectively. The control (distilled water) showed nil mortality in the concurrent assay. This is the first report on anti-parasitic activity of the synthesized ZnO NPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Semmler M, Al-Rasheid K, Klimpel S, Mehlhorn H (2010a) Efficacy of a grapefruit extract on head lice: a clinical trial. Parasitol Res 106(2):445–449
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Semmler M, Al-Rasheid K, Mehlhorn H (2010b) Comparative in vitro tests on the efficacy and safety of 13 anti-head-lice products. Parasitol Res 106:423–429
Aruoja V, Dubourguier HC, Kasemets K, Kahru A (2009) Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci Total Environ 407:1461–1468
Aspöck H, Walochnik J (2007) Die Parasiten des Menschen aus der Sicht der Ko-Evolution. Denisia 20(60):149–254
Bai W, Zhang Z, Tian W, He X, Ma Y, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2009) Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to zebrafish embryo: a physicochemical study of toxicity mechanism. J Nanopart Res 12(5):1645–1654
Barrios S, Zerba E, Picollo MI, Audino PG (2010) Activity of increased specific and non-specific esterases and glutathione transferases associated with resistance to permethrin in Pediculus humanus capitis (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae) from Argentina. Parasitol Res 106:415–421
Baun A, Hartmann NB, Grieger K, Kusk KO (2008) Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: a brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology 17:387–395
Berardis BD, Civitelli G, Condello M, Lista P, Pozzi R, Arancia G, Meschini S (2010) Exposure to ZnO nanoparticles induces oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 246(3):116–127
Beyer WN, Anderson AI (1985) Toxicity to woodlice of zinc and lead oxides added to soil litter. Ambio 3:173–174
Brayner R, Ferrari-Iliou R, Brivois N, Djedia S, Benedetti MF, Fievet F (2006) Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultra ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett 6:866
Brown AWA, Pal R (1971) Insecticide resistance in arthropods. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 491
Brunner TJ, Wick P, Manser P, Spohn P, Grass RN, Limbach LK, Bruinink A, Stark WJ (2006) In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: comparison to asbestos, silica, and the effect of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 40:4374–4381
Burgess IF (2004) Human lice and their control. Annu Rev Entomol 49:457–481
Carpinella MC, Miranda M, Almirón WR, Ferrayoli CG, Almeida FL (2007) In vitro pediculicidal and ovicidal activity of an extract and oil from fruits of Melia azedarach L. J Am Acad Dermatol 56(2):250–256
Chand SK, Tripathy NK, Das CC (1988) Some environmental factors affecting Culex quinquefasciatus population in a coastal town. Gopalpur-on-sea. Orissa Geobios 15:53–56
Chatterjee SN, Chandra G (2000) Role of Anopheles subpictus as a primary vector of malaria in an area in India. Jpn J Trop Med Hyg 28(3):177–181
Choopun S, Tubtimtae A, Santhaveesuk T, Nilphai S, Wongrat E, Hongsith N (2009) Zinc oxide nanostructures for applications as ethanol sensors and dye sensitized solar cells. Appl Surf Sci 256:998–1002
Das NG, Goswami D, Rabha B (2007) Preliminary evaluation of mosquito larvicidal efficacy of plant extracts. J Vect Borne Dis 44:145–148
Dolianitis C, Sinclair R (2002) Optimal treatment of head lice: is a no-nit policy justified? Clin Dermatol 20:94–96
Everts M, Saini V, Leddon JL, Kok RJ, Stoff-Khalili M, Preuss MA, Millican CL, Guy Perkins G, Brown JM, Bagaria H, Nikles DE, Johnson DT, Zharov VP, Curiel DT (2006) Covalently linked Au nanoparticles to a viral vector: potential for combined photothermal and gene cancer therapy. Nano Lett 6:587
FAO (2004) Ticks: acaricide resistance: diagnosis management and prevention in: guidelines resistance management and integrated parasite control in ruminants. FAO Animal Production and Health Division, Rome
Fernandes FF (2001) Toxicological effects and resistance to pyretroids in Boophilus microplus from Goiás Brasil. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 53:548–552
Fernandes FF, Freitas EPS (2007) Acaricidal activity of an oleoresinous extract from Copaifera reticulata (Leguminosae: Caesalpinioideae) against larvae of the southern cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Vet Parasitol 147:150–154
Fernandes FF, Freitas EPS, Costa AC, Silva IG (2005) Larvicidal potential of Sapindus saponaria to control the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 40:1243–1245
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3 rdth edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, ISBN 052108041X. OCLC 174198382
Franklin NM, Rogers NJ, Apte SC, Batley GE, Gadd GE, Casey PS (2007) Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): the importance of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 41(24):8484–8490
Ghosh S, Sharma AK, Kumar S, Tiwari SS, Rastogi S, Srivastava S, Singh M, Kumar R, Paul S, Ray DD, Rawat AK (2010) In vitro and in vivo efficacy of Acorus calamus extract against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Parasitol Res. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-2070-0
Graf JF, Gogolewski R, Leach BN (2004) Tick control: an industry point of view. Parasitology 129:S247–S442
Gratz NG (1997) Human lice: their prevalence, control and resistance to insecticides—a review 1985Ð1997. World Health Organization, Geneva, WHO/CTD/WHOPES/97.8
Grisi L, Massard CL, Borja GEM, Pereira JB (2002) Impacto economic das principais ectoparasitoses em bovinos no Brasil. Hora Vet 125:23–28
Gupta K, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26:1565
Gutiérrez LA, Naranjo N, Jaramillo LM, Muskus C, Luckhart S, Conn JE, Correa MM (2008) Natural infectivity of Anopheles species from the Pacific and Atlantic Regions of Colombia. Acta Tropica 107:99–105
Heinlaan M, Ivask A, Blinova I, Dubourguier HC, Kahru A (2008) Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 71:1308–1316
Heng BC, Zhao X, Xiong S, Woei Ng K, Yin-Chiang Boey F, Say-Chye Loo J (2010) Toxicity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) is accentuated by oxidative stress. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1762–1766
Hu CW, Li M, Cui YB, Li DS, Chen J, Yang LY (2010) Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol Biochem 42:586–591
Kamaraj C, Bagavan A, Rahuman AA, Zahir AA, Elango G, Pandiyan G (2009) Larvicidal potential of medicinal plant extracts against Anopheles subpictus Grassi and Culex tritaeniorhynchus Giles (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol Res 104(5):1163–1171
Kamat PV, Meisel D (2003) Nanoscience opportunities in environmental remediation. CR Chim 6:999–1007
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim JH, Park SJ, Lee HJ (2007) Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3:95–101
Klabunde KJ, StarkJ KoperO, MohsC ParkD, Decker S (1996) Nanocrystals as stoichiometric reagents with unique surface chemistry. J Phys Chem 100:12142–12153
Kocbek P, Teskač K, Kreft ME, Kristl J (2010) Toxicological aspects of long-term treatment of keratinocytes with ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles. Small 6(17):1908–1917
Kulkarni SM (1983) Detection of sporozoites in Anopheles subpictus in Baster district, Madhya Pradesh. Indian J Malariol 20:159–160
Kwong-Chung T, Feng-Pang C, Cheng-Hung L, Kai-Sung W, Jiunn-Shiow W, Wei-Ming L (2004) Demonstration of vector competence of Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) for Setaria digitata. Vet Parasitol 123:279–284
Lin DH, Xing BS (2007) Phytotoxicity of nanoparticles: inhibition of seed germination and root growth. Environ Pollut 150(2):243–250
Lock K, Janssen CR (2001) Modelling zinc toxicity for terrestrial invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1901–1908
Magrez S, Kasas V, Salicio N, Pasquier J, Seo W, Celio M, Catsicas S, Schwaller B, Forro L (2006) Cellular toxicity of carbon-based nanomaterials. Nano Lett 6:1121
Manusadžianas L, Grigutyt R, Jurkonien S, Karitonas R, Sadauskas K, Férard JF, Cotelle S, Foucaud L (2009) Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticle suspensions to aquatic biota. METZ ISTA14: VIII 30 – IX 04
Manzo S, Rocco A, Carotenuto R, De Luca PF, Miglietta ML, Rametta G, Di Francia G (2010) Investigation of ZnO nanoparticles’ ecotoxicological effects towards different soil organisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0421-0
Marimuthu S, Rahuman AA, Rajakumar G, Santhoshkumar T, Kirthi AV, Jayaseelan C, Bagavan A, Zahir AA, Elango G, Kamaraj C (2010) Evaluation of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against parasites. Parasitol Res. doi:org/10.1007/s00436-010-2212-4
Martinez-Velazquez M, Castillo-Herrera GA, Rosario-Cruz R, Flores-Fernandez JM, Lopez-Ramirez J, Hernandez-Gutierrez R, Del Carmen Lugo-Cervantes E (2010) Acaricidal effect and chemical composition of essential oils extracted from Cuminum cyminum, Pimenta dioica and Ocimum basilicum against the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-2069-6
Mayo MJ (1996) Processing on nanocrystalline ceramics from ultra fine particles. Int Mater Rev 3:95
Mehlhorn B, Mehlhorn H (2009) Louse alarm. Düsseldorf University Press, Düsseldorf
Mehlhorn H, Eichenlaub D, Löscher T, Peters W (1995) Diagnosis and therapy of human parasites, 2nd edn. Fischer, Stuttgart
Michael E, Bundy DA, Grenfell BT (1996) Re-assessing the global prevalence and distribution of lymphatic filariasis. Parasitology 112(4):409–428
Moos PJ, Chung K, Woessner D, Honeggar M, Cutler NS, Veranth JM (2010) ZnO particulate matter requires cell contact for toxicity in human colon cancer cells. Chem Res Toxicol 23(19):733–739
Nagpal BN, Sharma VP (1995) Indian Anophelines. Oxford & IBH Pub Co. Pvt. Ltd., London, pp 189–190
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao A, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg L (2008) Environmental behaviour and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17:372–386
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622
Nel AE, Madler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EM, Somasundaran P (2009) Understanding bio-physicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat Matters 8:543–557
Nowack B, Bucheli TD (2007) Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150:5–22
Oberdörster G, Oberdörster E, Oberdörster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113:823–839
Oladimeji FA, Orafidiya OO, Ogunniyi TA, Adewunmi TA (2000) Pediculocidal and scabicidal properties of Lippia multiflora essential oil. J Ethnopharmacol 72(2):305–311
Padmavathy N, Vijayaraghavan R (2008) Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles-an antimicrobial study. Sci Technol Adv Mater 9:1–7
Panicker KN, GeethaBai M, Bheema Rao US, Viswam K, Suryanarayanamurthy U (1981) An. subpictus vector of malaria in coastal villages of South-East India. Curr Sci 50:694–695
Picollo MI, Vassena C, Casadio A, Massimo J, Zerba E (1998) Laboratory studies of susceptibility and resistance to insecticides in Pediculus capitis (Anoplura: Pediculidae). J Med Entomol 35:814–817
Picollo MI, Vassena C, Mougabure Cueto G, Vernetti M, Zerba E (2000) Resistance to insecticides and effect of synergists on permethrin toxicity in Pediculus capitis (Anoplura: Pediculidae) from Buenos Aires. J Med Entomol 37:721–725
Rao TR (1984) The anophelines of India. Malaria Research Centre (ICMR), Delhi, p 518
Rekha K, Nirmala M, Nair MG, Anukaliani A (2010) Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide and manganese doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Phys B Condens Matter 405:3180–3185
Rhee GY, Thomson PA (1992) Sorption of hydrophobic organic contaminants and trace metals on phytoplankton and implications for toxicity assessment. J Aquat Ecosyst Health 1:175–191
Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Alonso-Díaz MA, Rodríguez-Arevalo F, Fragoso-Sanchez H, Santamaría VM, Rosario-Cruz R (2006a) Prevalence and potential risk factors for organophosphate and pyrethroid resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks on cattle ranches from the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Vet Parasitol 136:335–342
Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Rodríguez-Arevalo F, Alonso-Díaz MA, Fragoso-Sanchez H, Santamaría VM, Rosario-Cruz R (2006b) Prevalence and potential risk factors for amitraz resistance in Boophilus microplus ticks in cattle farms in the State of Yucatan, Mexico. Prev Vet Med 75:280–286
Rosario-Cruz R, Guerrero FD, Miller RJ, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Domínguez-García DI, Cornel AJ, Hernandez-Ortiz R, George JE (2005) Roles played by esterase activity and by a sodium channel mutation involved in pyrethroid resistance in populations of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from Yucatan. Mexico J Med Entomol 42:1020–1025
Sandifer RD, Hopkin SP (1997) Effects of temperature on the relative toxicities of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn to Folsomia candida (Collembola). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 37:125–130
Santhoshkumar T, Rahuman AA, Rajakumar G, Marimuthu S, Bagavan A, Jayaseelan C, Zahir AA, Elango G, Kamaraj C (2010) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Nelumbo nucifera leaf extract and its larvicidal activity against malaria and filariasis vectors. Parasitol Res. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-2115-4
Santilli CV, Pulcinelli SH, Tokumoto MS, Briois V (2007) In situ UV-vis and EXAFS studies of ZnO quantum-sized nanocrystals and Zn-HDS formations from sol-gel route. J Eur Ceram Soc 27:3691–3695
Sawai J, Yoshikawa T (2004) Quantitative evaluation of anti-fungal activity of metallic coxide powders (MgO, CaO and ZnO) by an indirect conductimetric assay. J Appl Microbiol 96(4):803–809
Smit CE, Gestel CAMV (1998) Effects of soil type, prepercolation, and ageing on bioaccumulation and toxicity of zinc for the springtail Folsomia candida. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1132–1141
SPSS (2007) SPSS for Windows, version 16.0. Release 16.0.0 Chicago, IL, USA
Sunilson JSAJ, Suraj R, Rejitha G, Anandarajagopal K, Vimala AG, Husain HA (2009) In vitro screening of anti-lice activity of Pongamia pinnata leaves. Korean J Parasitol 47(4):377–380
Thenmozhi V, Rajendran R, Ayanar K, Manavalan R, Tyagi BK (2006) Long-term study of Japanese encephalitis virus infection in Anopheles subpictus in Cuddalore district, Tamilnadu, South India. Trop Med Int Health 11(3):288–293
Thill A, Zeyons O, Spalla O, Chauvat F, Rose J, Auffan M, Flank AM (2006) Cytotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles for Escherichia coli. Physico-chemical insight of the cytotoxicity mechanism. Environ Sci Technol 40:6151
Thuenemann AF, Ruland W (2000) Microvoids in polyacrylonitrile fibers: a small-angle X-ray scattering study. Macromol 33:1848–1852
Toloza AC, Lucía A, Zerba E, Masuh H, Picollo MI (2010a) Eucalyptus essential oil toxicity against permethrin-resistant Pediculus humanus capitis (Phthiraptera: Pediculidae). Parasitol Res 106(2):409–414
Toloza AC, Zygadlo J, Biurrun F, Rotman A, Picollo MI (2010b) Bioactivity of Argentinean essential oils against permethrin-resistant head lice. Pediculus humanus capitis. J Insect Sci 10:185
Van de Pol FCM (1990) Thin-film ZnO-properties and applications. Ceram Bull 69:1959
Wahab R, Ansari SG, Kim YS, Seo HK, Kim GS, Khang G, Shin HS (2007a) Low temperature solution synthesis and characterization of ZnO nano-flowers. Mater Res Bull 42:1640–1648
Wahab R, Ansari SG, Kim YS, Seo HK, Shin HS (2007b) Room temperature synthesis of needle-shaped ZnO nanorods via sonochemical method. Appl Surf Sci 253:7622–7626
Wahab R, Ansari SG, Kim YS, Khang G, Shin HS (2008) Effect of hydroxylamine hydrochloride on the floral decoration of zinc oxide synthesized by solution method. Appl Surf Sci 254:2037–2042
Wang ZL (2004) Zinc oxide nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J Phys Condens Matter 16:829–858
Wang B, Feng WY, Wang M, Wang TC, Gu YQ, Zhu MT, Ouyang H, Shi JW, Zhang F, Zhao YL, Chai ZF, Wang HF, Wang J (2008) Acute toxicological impact of nano and submicro-scaled zinc oxide powder on healthy adult mice. J Nanopart Res 10(2):263–276
Waxman MF (1998) Agrochemical and pesticide safety hand-book. Lewis Publishers, Florida, p 616
Yadav A, Prasad V, Kathe A, Sheela R, Yadav D, Sundaramoorthy C, Vigneshwaran N (2006) Functional finishing in cotton fabrics using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bull Mater Sci 29:641–645
Yamamoto O (2001) Influence of particle size on the antibacterial activity of zincoxide. Int J Inorg Mater 3(7):643–646
Zhang L, Jiang Y, Ding Y, Povey M, York D (2007) Investigation into the antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO nanofluids). J Nanoparticle Res 9:479–489
Zhu X, Zhu L, Duan Z, Qi R, Li Y, Lang Y (2008) Comparative toxicity of several metal oxide nanoparticle aqueous suspensions to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) early developmental stage. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 43(3):278–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirthi, A.V., Rahuman, A.A., Rajakumar, G. et al. Acaricidal, pediculocidal and larvicidal activity of synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using wet chemical route against blood feeding parasites. Parasitol Res 109, 461–472 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2277-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2277-8