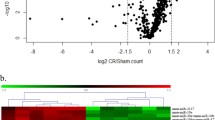
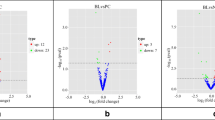
Abstract
Accumulating evidence indicates a critical role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the outcome of diseases. Here, we investigate the effect of garlic on the intestinal miRNA signature of male Balb/c mice during infections with Eimeria papillata. Garlic decreases the intracellular development as evidenced by a lowered fecal output of E. papillata oocysts from 3,150 ± 410 to approximately 1,750 ± 390 oocysts per gram feces on day 4 postinoculation. This anti-coccidial activity of garlic is associated with an inhibition of the E. papillata-induced increases of interferon gamma, inducible nitric oxide synthase, nitrite/nitrate, and malondialdehyde and decrease in glutathione. Moreover, garlic downregulates the E. papillata-induced increases in the expression of the miRNAs miR-1959, miR-203, and miR-21, and it upregulates the expression of the 11 miRNA species miR-142-5P, miR-15A, miR-10A, miR-29B, miR-1902, miR-125A-5P, let-7E, miR-148A, miR-130A, miR-10B, and miR-93, respectively, as revealed by miRXplore microarray technology. Real-time PCR confirms these effects of garlic in the jejunum of E. papillata-infected mice. Our data indicate that the anti-coccidial activity of garlic is associated with specific changes in the miRNA signature of the mouse jejunum, the target site of E. papillata. These changes may reflect an involvement of miRNAs in garlic-activated pathways to reduce and/or to repair E. papillata-induced tissue injuries.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi ΗU (ed) (1984) Catalase. In: Methods in enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 276–286
Bala S, Marcos M, Szabo G (2009) Emerging role of microRNAs in liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 15:5633–5640
Balasenthil S, Arivazhagan S, Ramachandran CR, Nagini S (1999) Effects of garlic on 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis. Cancer Detect Prev 23:534–538
Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O’Conell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD (2008) MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol 9:839–845
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bartzatt R, Blum D, Nagel D (1992) Isolation of garlic derived sulphur compounds from urine. Anal Lett 25:1217–1224
Berkels R, Purol-Schnabel S, Roesen R (2004) Measurement of nitric oxide by reconversion of nitrate/nitrite to NO. J Humana Press 279:1–8
Bezman NA, Cedars E, Steiner DF, Blelloch R, Hesslein DGT, Lanier LL (2010) Distinct requirements of miRNAs in NK cell activation, survival, and function. J Immunol 185:3835–3846
Bi Y, Liu G, Yang R (2009) MicroRNAs: novel regulators during the immune response. J Cell Physiol 218:467–472
Buege JA, Aust SD (1987) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Calzada F, Meckes M, Cedillo-Rivera R (1999) Antiamoebic and antigiardial activity of plant flavonoids. Planta Med 65:78–80
Celada A, Schreiber RD (1986) Role of protein kinase C and intracellular calcium mobilization in the induction of macrophage tumoricidal activity by interferon-gamma. J Immunol 137:2373–2379
Cho BH, Xu S (2000) Effects of allyl mercaptan and various allium-derived compounds on cholesterol synthesis and secretion in Hep-G2 cells. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 126:195–201
Chobotar B, Danforth HD, Entzeroth R (1993) Ultrastructural observations of host-cell invasion by sporozoites of Eimeria papillata in vivo. Parasitol Res 79:15–23
Danforth HD, Entzeroth R, Chobotar B (1992) Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of host cell pathology associated with penetration by Eimeria papillata sporozoites. Parasitol Res 78:570–573
Delic D, Gailus N, Vohr H-V, Dkhil M, Al-Quraishy S, Wunderlich F (2010) Testosterone-induced permanent changes of hepatic gene expression in female mice sustained during Plasmodium chabaudi malaria infection. J Mol Endocrinol 45:379–390
Dkhil M, Abdel-Baki AA, Delić D, Wunderlich F, Sies H, Al-Quraishy S (2010) Eimeria papillata: upregulation of specific miRNA-species in the mouse jejunum. Exp Parasitol (in press)
Dkhil MA, Abdel-Baki AS, Wunderlich F, Sies H, Al-Quraishi S (2011) Anticoccidial and antiinflammatory activity of garlic in murine Eimeria papillata infections. Vet Parasitol 175:66–72
Dommels YE, Butts CA, Zhu S, Davy M, Martell S, Hedderley D, Barnett MP, McNabb WC, Roy NC (2007) Characterization of intestinal inflammation and identification of related gene expression changes in mdr1a(−/−) mice. Genes Nutr 2:209–223
Drury RAB, Wallington EA (1980) Carleton’s histological technique, 5th edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford New York Toronto, pp 188–189, pp 237–240, pp 290–291
Duraka A, Ozturk HS, Olcay E, Guven C (2002) Effects of garlic extract supplementation on blood lipid and antioxidant parameters and atherosclerotic plaque formation process in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Herb Pharmacother 2:19–32
El Shenawy NS, Soliman MF, Reyad SI (2008) The effect of antioxidant properties of aquatic garlic extract and Nigella sativa as anti-schistosomiasis agent in mice. Rev Inst Med trop Sao Paulo 50:29–36
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Fenwick GR, Hanley AB (1985) The genus Allium—part 1. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 22:199–271
Ghazanfari T, Hassan ZM, Khamesipour A (2006) Enhancement of peritoneal macrophage phagocytic activity against Leishmania major by garlic (Allium sativum) treatment. J Ethnopharmacol 103:333–337
Gres V, Voza T, Chabaud A, Landau I (2003) Coccidiosis of the wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in France. Parasite 10:51–57
Hnida JA, Duszynski DW (1999) Taxonomy and phylogeny of some Eimeria (Apicomplexa:Eimeriidae) species of rodents as determined by polymerase chain reaction/restriction-fragment-length polymorphism analysis of 18S rDNA. Parasitol Res 85:887–894
Karasaki Y, Tsukamoto S, Mizusaki K, Sugiura T, Gotoh S (2001) A garlic lectin exerted an antitumor activity and induced apoptosis in human tumor cells. Food Res Int 24:3
Kiesewetter H, Jung F, Jung EM, Blume J, Mrowietz C, Birk A, Koscielny J, Wenzel E (1993) Effects of garlic coated tablets in peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Clin Investig 71:383–386
Koch HP (1996) The long pass toward “odorless garlic”. Pharm Unserer Zeit 25:186–191
Kumar VG, Surendranathan KP, Umesh KG, Gayathri Devi DR, Belwadi MR (2003) Effect of onion (Allium cepa Linn.) and garlic (AlliumSativum Linn.) on plasma triglyceride content in Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonicum). Indian J Exp Biol 41:88–90
Landgraf PM, Rusu M, Sheridan A, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M et al (2007) A mammalian miRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 129:1401–1414
Licois D, Coudert P, Bahagia S, Rossi GL (1992) Endogenous development of Eimeria intestinalis in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). J Parasitol 78:1041–1048
Liu M, Chen H (2010) The role of microRNAs in colorectal cancer. J Genet Genomics 37:347–358
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 – ŽŽ C T Method. Methods 25:402–408
Matzinger P (2007) Friendly and dangerous signals: is the tissue in control? Nat Immunol 8:11–13
Mehlhorn H (ed) (2008) Encyclopedic reference of parasitology, vol 1, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin
Milner JA (1996) Garlic: its anticarcinogenic and antitumorigenic properties. Nutr Rev 54:82–86
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Nok AJ, Williams S, Onyenekwe PC (1996) Allium sativum-induced death of African trypanosomes. Parasitol Res 82:634–637
Pakandl M (2005) Selection of a precocious line of the rabbit coccidium Eimeria flavescens Marotel and Guilhon (1941) and characterisation of its endogenous cycle. Parasitol Res 97:150–155
Peyghan R, Powell MD, Zadkarami MR (2008) In vitro effect of garlic extract and metronidazole against Neoparamoeba pemaquidensis, page 1987 and isolated amoebae from Atlantic salmon. Pak J Biol Sci 11:41–47
Ryley JF, Robinson TE (1976) Life cycle studies with Eimeria magna Perard, 1925. Parasitol Res 12:257–275
Schito ML, Barta JR (1997) Nonspecific immune responses and mechanisms of resistance to Eimeria papillata infections in mice. Infect Immun 65:3165–3170
Schito ML, Barta JR, Chobotar B (1996) Comparison of four murine Eimeria species in immune competent and immunodeficient mice. J Parasitol 82:255–262
Sharma VD, Sethi MS, Kumar A, Rarotra JR (1977) Antibacterial property of Allium sativum Linn.: in vivo & in vitro studies. Indian J Exp Biol 15:466–468
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Michalek J, Vyzula R (2009) MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: translation of molecular biology into clinical application. Mol Cancer 8:102
Sonkoly E, Ståhle M, Pivarcsi A (2008) MicroRNAs and immunity: novel players in the regulation of normal immune function and inflammation. Sem Canc Biol 18:131–140
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Gandhi V, Plunkett W, Sampath D, Calin GA (2007) miRNAs and their potential for use against cancer and other diseases. Future Oncol 3:521–537
Toulah FH, Al-Rawi MM (2007) Efficacy of garlic extract on hepatic coccidiosis in infected rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus): histological and biochemical studies. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 37:957–969
Wahba A (2003) Studies on the efficacy of garlic extract on cryptosporidiosis in experimentally infected mice. Egypt J Agric Res 81:793–803
Wu H, Neilson JR, Kumar P, Manocha M, Shankar P, Sharp PA, Manjunath N (2007) miRNA profiling of naive, effector and memory CD8 T-cells. PLoS ONE 2:e1020
Yamada Y, Azuma K (1977) Evaluation of the in vitro antifungal activity of allicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 11:743–749
Zhao X, Duszynski DW (2001) Molecular phylogenies suggests the oocyst residuum can be used to distinguish two independent lineages of Eimeria spp in rodents. Parasitol Res 87:638–643
Zhu XM, Han T, Wang XH, Li YH, Yang HG, Luo YN, Yin GW, Yao YQ (2010) Overexpression of miR-152 leads to reduced expression of human leukocyte antigen-G and increased natural killer cell mediated cytolysis in JEG-3 cells. Am J Obstet Gynecol 202(592):e1–e7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Hy5/Hy3 false-color images after scanning of miRExplore microarrays obtained after hybridization of jejuna RNA from non-infected mice vs. mice infected with E. papillata on day 4 p.i. (a) and from infected mice vs. infected and garlic-treated mice (b). The evaluation of these microarrays was done as described in Material and methods (GIF 116 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Quraishy, S., Delic, D., Sies, H. et al. Differential miRNA expression in the mouse jejunum during garlic treatment of Eimeria papillata infections. Parasitol Res 109, 387–394 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2266-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2266-y