Abstract
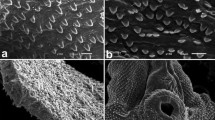
Sheep infected with the triclabendazole-susceptible Cullompton isolate of Fasciola hepatica were dosed with 15 mg/kg of compound alpha at 12 weeks postinfection. Adult flukes were recovered from the bile ducts at 24, 48, and 72 h post-treatment (p.t.). Changes to the surface morphology of the flukes were assessed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Flukes were still active at 24 h p.t. and displayed limited areas of disruption, which were restricted to the oral cone region. At 48 h p.t., a reduced level of motility was observed in ~50% of the flukes recovered. Swelling of the tegument was more widespread and was accompanied by blebbing and partial loss of the tegumental covering of the spines. By 72 h p.t., the reduction in motility was greater, and approximately one quarter of the flukes recovered were inactive. In the majority of the flukes examined, the midbody region was marked by a discoloration of the flukes’ tissues. This was seen to be due to the loss of the tegumental syncytium. Sloughing extended into the tail region in some specimens and, in the more badly-affected specimens, the basal lamina was breached to expose the underlying musculature. Elsewhere on the body, the tegument that remained was relatively normal, although areas of swelling and blebbing were present. Overall, the results provided information on the time-scale of changes to the surface morphology of the fluke that underpin the efficacy of compound alpha.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Madyan AA, Morsy TA, Motawea SM, Morsy AT (2004) Clinical trial of Mirazid in treatment of human fascioliasis, Ezbet El-Bakly (Tamyia Center) Al-Fayoum Governate. J Egyptian Soc Parasitol 34:807–818
Anderson HR, Fairweather I (1995) Fasciola hepatica: ultrastructural changes to the tegument of juvenile flukes following incubation in vitro with the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide. Int J Parasitol 25:319–333
Bennett CE (1975) Scanning electron microscopy of Fasciola hepatica L. during growth and maturation in the mouse. J Parasitol 61:892–898
Boray JC, Crowfoot PD, Strong MB, Allison JR, Schellenbaum M, Von Orelli M, Sarasin G (1983) Treatment of immature and mature Fasciola hepatica infections in sheep with triclabendazole. Vet Rec 113:315–317
Buchanan JF, Fairweather I, Brennan G, Trudgett A, Hoey EM (2003) Fasciola hepatica: surface and internal tegumental changes induced by treatment in vitro with the sulphoxide metabolite of albendazole (“Valbazen”). Parasitology 126:141–153
Fairweather I (2005) Triclabendazole: new skills to unravel an old(ish) enigma. J Helminthol 79:227–234
Fairweather I (2009) Triclabendazole progress report, 2005–2009: an advancement of learning? J Helminthol 83:139–150
Fairweather I, Anderson HR, Baldwin TMA (1987) Fasciola hepatica: tegumental surface alterations following treatment in vitro with the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide. Parasitol Res 73:99–106
Fairweather I, Threadgold LT, Hanna REB (1999) Development of Fasciola hepatica in the mammalian host. In: Dalton JP (ed) Fasciolosis. CAB International Publishing, Wallingford, Oxon, UK, pp 47–111
Favennec L, Jave-Ortiz J, Gargala G, Lopez-Chegne N, Ayoub A, Rossignol JF (2003) Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of nitazoxanide in the treatment of fascioliasis in adults and children from northern Peru. Aliment Pharm Therap 17:265–270
Halferty L, Brennan GP, Trudgett A, Hoey E, Fairweather I (2009) Relative activity of triclabendazole metabolites against the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol 159:126–138
Halferty L, Brennan GP, Hanna REB, Edgar HW, Meaney M, McConville M, Trudgett A, Hoey L, Fairweather I (2008) Tegumental surface changes in juvenile Fasciola hepatica in response to treatment in vivo with triclabendazole. Vet Parasitol 155:49–58
Hanna REB (1980) Fasciola hepatica: glycocalyx replacement in the juvenile as a possible mechanism for protection against host immunity. Exp Parasitol 50:103–114
Haridy FM, El Garhy MF, Morsy TA (2003) Efficacy of Mirazid (Commiphora molmol) against fascioliasis in Egyptian sheep. J Egyptian Soc Parasitol 33:917–924
Hernández-Campos A, Ibarra-Velarde F, Vera-Montenegro Y, Rivera-Fernandez N, Castillo R (2002) Synthesis and fasciolicidal activity of 5-chloro-2-methylthio-6-(1-naphthyloxy)-1H-benzimidazole. Chem Pharm Bull 50:649–652
Ibarra VF, Vera MY, Hernández CA, Castillo BR (1997a) Eficacia fasciolicida del compuesto “alfa” contra estadios juveniles y adultos en ovinos. Vet Méx 28:297–301
Ibarra VF, Montenegro CN, Flores CJ, Hernández CA, Castillo BR (2000) Evaluación de cuatro vehículos para formular un fasciolicida experimental. Vet Méx 31:47–51
Ibarra VF, García SE, Fernández RM, Vera MY, Castillo BR, Hernández CA (1997b) Eficacia fasciolicida de dos compuestos de síntesis química in vitro e in vivo en ovinos. Vet Méx 28:291–296
Keiser J, Shu-Hua X, Tanner M, Utzinger J (2006a) Artesunate and artemether are effective fasciolicides in the rat model and in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother 57:1139–1145
Keiser J, Utzinger J, Tanner M, Dong Y, Vennerstrom JL (2006b) The synthetic peroxide OZ78 is effective against Echinostoma caproni and Fasciola hepatica. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:1193–1197
Keiser J, Utzinger J, Vennerstrom JL, Dong Y, Brennan G, Fairweather I (2007) Activity of artemether and OZ78 against triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 101:1219–1222
Mas-Coma S, Bargues MD, Valero MA (2005) Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses. Int J Parasitol 35:1255–1278
McConville M, Brennan GP, McCoy M, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Ibarra F, Fairweather I (2006) Adult triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: surface and subsurface tegumental responses to in vitro treatment with the sulphoxide metabolite of the experimental fasciolicide compound alpha. Parasitology 133:195–208
McConville M, Brennan GP, Flanagan A, Edgar HWJ, Hanna REB, McCoy M, Gordon AW, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Fairweather I (2009a) An evaluation of the efficacy of compound alpha and triclabendazole against two isolates of Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol 162:75–88
McConville M, Brennan GP, Flanagan A, Edgar HWJ, McCoy M, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Fairweather I (2008) Surface and internal tegumental changes in juvenile Fasciola hepatica following treatment in vivo with the experimental fasciolicide, compound alpha. Vet Parasitol 153:52–64
McConville M, Brennan GP, Flanagan A, Edgar HWJ, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Fairweather I (2009b) Ultrastructural changes to the tegumental system and the gastrodermal cells in adult Fasciola hepatica following in vivo treatment with the experimental fasciolicide, compound alpha. Parasitology 136:655–680
McCoy MA, Fairweather I, Brennan GP, Kenny JM, Ellison S, Forbes AF (2005) The efficacy of nitroxynil and triclabendazole administered synchronously against juvenile triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica in sheep. Res Vet Sci 78:33
McKinstry B, Fairweather I, Brennan GP, Forbes AB (2003) Fasciola hepatica: tegumental surface alterations following treatment in vivo and in vitro with nitroxynil (Trodax). Parasitol Res 91:251–263
McKinstry B, Brennan GP, Halferty L, Forbes AB, Fairweather I (2007) Ultrastructural changes induced in the tegument and gut of Fasciola hepatica following in vivo and in vitro drug treatment with nitroxynil (Trodax). Parasitol Res 101:929–941
Meaney M, Haughey S, Brennan GP, Fairweather I (2005) A scanning electron microscope study on the route of entry of clorsulon into the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 95:117–128 and 96:189–198
Meaney M, Fairweather I, Brennan GP, McDowell LSL, Forbes AB (2003) Fasciola hepatica: effects of the fasciolicide clorsulon in vitro and in vivo on the tegumental surface, and a comparison of the effects on young- and old- mature flukes. Parasitol Res 91:238–250
Meaney M, Allister J, McKinstry B, McLaughlin K, Brennan GP, Forbes AB, Fairweather I (2006) Fasciola hepatica: morphological effects of a combination of triclabendazole and clorsulon against mature fluke. Parasitol Res 99:609–621
Meaney M, Allister J, McKinstry B, McLaughlin K, Brennan GP, Forbes AB, Fairweather I (2007) Fasciola hepatica: ultrastructural effects of a combination of triclabendazole and clorsulon against mature fluke. Parasitol Res 100:1091–1104
Mottier L, Alvarez L, Ceballos L, Lanusse C (2006) Drug transport mechanisms in helminth parasites: passive diffusion of benzimidazole anthelmintics. Exp Parasitol 113:49–57
O’Neill JF, Johnston RC, Halferty L, Brennan GP, Keiser J, Fairweather I (2009) Adult triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: morphological changes in the tegument and gut following in vivo treatment with artemether in the rat model. J Helminthol 83:151–163
Ramírez N, Mayet L, Del Rivero L, Ibarra-Velarde F, Castillo R, Hernández-Campos A, Jung-Cook H (2009) Pharmacokinetic behaviour in sheep and cattle of 5-Chloro-2-(methylthio)-6-(1-naphthyloxy)-1H-benzimidazole, a new fasciolicide agent. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 32:154–159
Rivera FN, Ibarra VF, Olazaràn JS, Vera MY, Castillo BR, Hernández CA (2002) Efficacy of 5-chloro-2-methylthio-6-(1-naftiloxi)-ih-benzimidazole against different stages of Fasciola hepatica in Pelibuey sheep. Vet Méx 33:55–61
Robinson MW, Trudgett A, Hoey EM, Fairweather I (2002) Triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica: β-tubulin and response to in vitro treatment with triclabendazole. Parasitology 124:325–338
Robinson MW, Lawson J, Trudgett A, Hoey E, Fairweather I (2004) The comparative metabolism of triclabendazole sulphoxide by triclabendazole-susceptible and triclabendazole-resistant Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 92:205–210
Skuce PJ, Fairweather I (1990) The effect of the hydrogen ionophore closantel upon the pharmacology and ultrastructure of the adult liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 76:241–250
Stitt AW, Fairweather I (1993) Fasciola hepatica: tegumental surface changes in adult and juvenile flukes following treatment in vitro with the sulphoxide metabolite of triclabendazole (‘Fasinex’). Parasitol Res 79:529–536
Toner E, McConvery F, Meaney M, Brennan GP, Fairweather I (2009) A scanning electron microscope study on the route of entry of triclabendazole into the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 136:523–535
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a postgraduate studentship given by the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development Northern Ireland (DARDNI) to Maeve McConville.
The authors would like to thank the technical staff at the Agri-Food Biosciences Institute (AFBI), Veterinary Sciences Division (VSD), Stormont, Belfast, for the provision and care of the animals involved in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McConville, M., Brennan, G.P., Flanagan, A. et al. Surface changes in adult Fasciola hepatica following treatment in vivo with the experimental fasciolicide, compound alpha. Parasitol Res 105, 757–767 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1453-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1453-6