Abstract
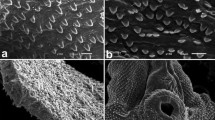
The effects of the novel benzimidazole, triclabendazole (Fasinex, Ciba-Geigy), in its active sulphoxide metabolite form (TCBZ-SX), on the tegumental surface ofFasciola hepatica has been examined in vitro. The tegument of adult flukes incubated in TCBZ-SX (50 μg/ml) appeared swollen and blebbed after only 6 h. In addition, progressive spine loss at the oral cone was evident following 12 h treatment. After 24 h, the tegumental syncytium and spines had completely sloughed away, leaving an exposed basal lamina and empty spine sockets. Juvenile flukes (3 weeks old) also demonstrated tegumental alterations after treatment with TCBZ-SX (20 μg/ml). The syncytium became extremely roughened and corrugated on both dorsal and ventral surfaces after only 3 h. Following 6- and 9-h incubations, there were many deep furrows, which were especially pronounced on the ventral surface, and by 18 h, the juvenile tegument was severely disrupted, especially on the ventral surface. In all cases, the effects were more marked than in the previous incubation periods. The results confirm the potent activity of triclabendazole againstF. hepatica and suggest that the tegument of adult and juvenile flukes may be a target organ for this important fasciolicide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson HR, Fairweather I (1988)Fasciola hepatica: scanning electron microscopic observations of juvenile flukes following treatment in vitro with the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide (DAMD) Int J Parasitol 18:827–837
Atkinson C, Newsam RJ, Gull K (1980) Influence of the antimicrotubule agent, mebendazole, on the secretory activity of intestinal cells ofAscaridia galli. Protoplasma 105:69–76
Becker B, Mehlhorn H, Andrews P, Thomas H, Eckert J (1980) Light and electron microscopic studies on the effect of praziquantel onSchistosoma mansoni, Dicrocoelium dendriticum, andFasciola hepatica (Trematoda) in vitro. Z Parasitenkd 63:113–128
Becker B, Mehlhorn H, Andrews P, Thomas H (1981) Ultrastructural investigations on the effect of praziquantel on the tegument of five species of cestodes. Z Parasitenkd 64:257–267
Bennett JL, Köhler P (1987)Fasciola hepatica: action in vitro of triclabendazole on immature and adult stages. Exp Parasitol 63:49–57
Boray JC (1982) Chemotherapy of fasciolosis. N S W Vet Proc 1982:42–47
Boray JC, Crowfoot PD, Strong MB, Allison JR, Schellenbaum M, Von Orelli M, Sarasin G (1983) Treatment of immature and matureFasciola hepatica infections in sheep with triclabendazole. Vet Rec 113:315–317
Borgers M, De Nollin S (1975) Ultrastructural changes inAscaris suum intestine after mebendazole treatment in vivo. J Parasitol 61:110–122
Borgers M, De Nollin S, De Brabander M, Thienpont D (1975a) Influence of the anthelmintic mebendazole on microtubules and intracellular organelle movement in nematode intestinal cells. Am J Vet Res 36:1153–1166
Borgers M, De Nollin S, Verheyen A, Vanparijs O, Thienpont D (1975b) Morphological changes in cysticerci ofTaenia taeniaeformis after mebendazole treatment. J Parasitol 61:830–843
Bricker CS, Depenbusch JW, Bennett JL, Thompson DP (1983) The relationship between tegumental disruption and muscle contraction inSchistosoma mansoni exposed to various compounds. Z Parasitenkd 69:61–71
Campbell WC (1990) Benzimidazoles: veterinary uses. Parasitol Today 6:130–133
Coles GC (1986) Anthelmintic activity of triclabendazole. J Helminthol 60:210–212
Conder GA, Marchiondo AA, Anderson FL (1981) Effect of praziquantel on adultEchinococcus granulosus in vitro: scanning electron microscopy. Z Parasitenkd 66:191–199
Craig TM, Huey RL (1984) Efficacy of triclabendazole againstFasciola hepatica andFascioloides magna in naturally infected calves. Am J Vet Res 45:1644–1645
Fairweather I, Holmes SD, Threadgold LT (1984)Fasciola hepatica: motility responses to fasciolicides in vitro. Exp Parasitol 57:209–224
Fairweather I, Anderson HR, Baldwin TMA (1987)Fasciola hepatica: tegumental surface alterations following treatment in vitro with the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide. Parasitol Res 73:99–106
Fetterer RH (1986) The effect of albendazole and triclabendazole on colchicine binding in the liver flukeFasciola hepatica. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 9:49–54
Friedman PA, Platzer EG (1978) Interaction of anthelmintic benzimidazoles and benzimidazole derivatives with bovine brain tubulin. Biochim Biophys Acta 544:605–614
Güralp N, Tinar R (1984) Trematodiasis in Turkey: comparative efficacy of triclabendazole and niclofolan against natural infections ofFasciola hepatica andF. gigantica in sheep. J Helminthol 58:113–116
Gull K, Dawson PJ, Davis C (1987) Microtubules as target organelles for benzimidazole anthelmintic chemotherapy. Biochem Soc Trans 15:59–60
Gusel'nikova LM (1975) The effect of certain fasciolicides on the tegument ofFasciola hepatica implanted under the skin on the back of white rats. Med Parazitol (Mask) 43:214–217
Ibarra OF, Jenkins DC (1984) An in vitro screen for new fasciolicidal agents. Z Parasitenkd 70:655–661
Ireland CM, Gull K, Gutteridge WE, Pogson CI (1979) The interaction of benzimidazole carbamates with mammalian microtubule protein. Biochem Pharmacol 28:2680–2682
Kelly RB (1990) Microtubules, membrane traffic and cell organization. Cell 61:5–7
Kendall SB, Parfitt JW (1973) The effect of diamphenethide onFasciola hepatica at different stages of development. Res Vet Sci 15:37–40
Köhler P, Bachman R (1981) Intestinal tubulin as a possible target for the chemotherapeutic action of mebendazole in parasitic nematodes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 4:325–336
Lacey E (1988) The role of the cytoskeletal protein, tubulin, in the mode of action and mechanism of drug resistance to benzimidazoles. Int J Parasitol 18:885–936
Laclette JP, Guerra G, Zetina C (1980) Inhibition of tubulin polymerisation by mebendazole. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 92:417–423
Lipkowitz KB, McCracken RO (1991) A molecular modeling approach to in vivo efficacy of triclabendazole. J Parasitol 77:998–1005
Lubega GW, Prichard RK (1990) Specific interaction of benzimidazole anthelmintics with tubulin: high-affinity binding and benzimidazole resistance inHaemonchus contortus. Mol Biochem Parasitol 38:221–232
Lubega GW, Prichard RK (1991) Interaction of benzimidazole anthelmintics withHaemonchus contortus tubulin: binding affinity and anthelmintic efficacy. Exp Parasitol 73:203–213
Rowlands D, ap T (1973) Diamphenethide — a drug offering a fresh approach to the treatment of liver fluke disease in sheep. Pestic Sci 4:883–889
Shaw MK, Erasmus DA (1983)Schistosoma mansoni: dose-related tegumental surface changes after in vivo treatment with praziquantel. Z Parasitenkd 69:643–653
Skuce PJ, Fairweather I (1990) The effect of the hydrogen ionophore closantel upon the pharmacology and ultrastructure of the adult liver flukeFasciola hepatica Parasitol Res 76:241–250
Skuce PJ, Anderson HR, Fairweather I (1987) The interaction between the deacetylated (amine) metabolite of diamphenethide (DAMD) and cytochemically demonstrable Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the tegument ofFasciola hepatica. Parasitol Res 74:161–167
Smeal MG, Hall CA (1983) The activity of triclabendazole against immature and adultFasciola hepatica infections in sheep. Aust Vet J 60:329–331
Stitt AW, Fairweather I (1992) Spermatogenesis inFasciola hepatica: an ultrastructural comparison of the effects of the anthelmintic, triclabendazole (Fasinex), and the microtubule inhibitor, tubulozole. Invertebr Reprod Dev 22:139–150
Stitt AW, Fairweather I (1993)Fasciola hepatica: the effect of the microtubule inhibitors colchicine and tubulozole-C on the ultrastructure of the adult fluke. Parasitology (in press)
Stitt AW, Fairweather I, Trudgett AG, Johnston CF (1992)Fasciola hepatica: localization and partial characterization of tubulin. Parasitol Res 78:103–107
Threadgold LT (1984) Parasitic platyhelminths. In: Bereiter-Hahn J, Matoltsy AG, Richards KS (eds) Biology of the integument, vol 1. Invertebrates. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 132–191
Turner K, Armour J, Richards RJ (1984) Anthelmintic efficacy of triclabendazole againstFasciola hepatica in sheep. Vet Rec 114:41–42
Vale RD (1987) Intracellular transport using microtubule-based motors. Annu Rev Cell Biol 3:347–378
Vale RD (1992) Microtubule motors: many new models off the assembly line. TIBS 17:300–304
Van den Bossche H, Rochette F, Hörig C (1982) Mebendazole and related anthelmintics. Adv Pharmacol Chemother 19:67–128
Verheyen A, Borgers M, Vanparijs O, Thienpont D (1976) The effects of mebendazole on the ultrastructure of cestodes. In: Van den Bossche H (ed) Biochemistry of parasites and hostparasite relationships. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 605–618
Verheyen A, Vanparijs O, Borgers M, Thienpont D (1978) Scanning electron microscopic observations ofCysticercus fasciolaris (=Taenia taeniaeformis) after treatment of mice with mebendazole. J Parasitol 64:411–425
Verheyen A, Vanparijs O, Lauwers H, Thienpont D (1980) The influence of closantel administration to sheep on the ultrastructure of the adult liver flukeFasciola hepatica L. In: Van den Bossche H (ed) The host-invader interplay. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam New York Oxford, pp 705–708
Voge M, Bueding E (1980)Schistosoma mansoni: tegumental surface alterations induced by subcurative doses of the schistosomicide amoscanate. Exp Parasitol 50:251–259
Wolff K, Eckert J, Schneiter G, Lutz H (1983) Efficacy of triclabendazole againstFasciola hepatica in sheep and goats. Vet Parasitol 13:145–150
Xiao S, Friedman PA, Catto BA, Webster LT Jr. (1984) Praziquantel-induced vesicle formation in the tegument of maleSchistosoma mansoni is calcium-dependent. J Parasitol 70:177–179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stitt, A.W., Fairweather, I. Fasciola hepatica: Tegumental surface changes in adult and juvenile flukes following treatment in vitro with the sulphoxide metabolite of triclabendazole (Fasinex). Parasitol Res 79, 529–536 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932235
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932235