Abstract
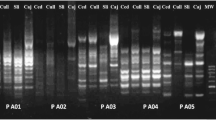
The present communication focuses on molecular characterization of Fasciola gigantica isolates derived from cattle, buffalo, and goat using random-amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD)–polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis to elucidate genetic variability between the three isolates. Seventeen random oligonucleotide primers of 10–11 bases with GC content varying from 50–81.8% were used in the study. Depending upon the F. gigantica isolate–primer combination, one to five fragments in the range of 327–1,973 bp were amplified. It was significant to observe that, out of the 17 primers directing amplification of DNA fingerprints, only two designated as AP9 and AP14 were found to be of potential interest in the generation of polymorphic DNA. On the basis of similarity coefficient data, it may be suggested that cattle and buffalo isolates of F. gigantica show 100% homogeneity against 92.68% similarity coefficient observed between goat and cattle/buffalo isolates. In other words, 7.32% divergence was observed between goat and cattle/buffalo isolates while the primers AP1, AP4, AP10, AP13, and AP17 were able to generate monomorphic DNA fingerprints. Primers AP9 and AP14 are potentially informative in terms of the polymorphic nature of the fingerprints generated in RAPD assays. The finding of the absence of 626-bp DNA fragment in the goat and the uniqueness of the AP14 in generating a single RAPD-PCR product of 1,211 bp as against the product size of 1,162 bp in cattle/buffalo seem to be significant. This is the first report of elucidation of RAPD-PCR based molecular variability in the DNA fingerprinting pattern of F. gigantica isolated from cattle, buffalo, and goat.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldemir OS (2006) Differentiation of cattle and sheep originated Fasciola hepatica by RAPD-PCR. Rev Med Vet 157:65–67
Basagoudanavar SH, Rao JR, Singh RK, Butchaiah G (1999) Random amplification of polymorphic DNA fingerprinting of Trypanaosoma evansi. Vet Res Commun 243:249–255
Bowditch BM, Albright DG, Williams JG, Braun MJ (1993) Use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers in comparative genome studies. Methods Enzymol 224:294–309
Elsh J, McClelland M (1991) Genomic fingerprinting using arbitrarily primed PCR and a matrix of pairwise combinations of primers. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5275–5279
Epe C, Bienioschek S, Rehbein S, Schnieder T (1995) Comparative RAPD-PCR analysis of lung worms (Dictyocaulidae) from fallow deer, cattle, sheep and horses. J Vet Med Series B 42:187–191
Gasser RB (1999) PCR-based technology in veterinary parasitology. Vet Parasitol 84:229–258
Kaplan RH, Dame JB, Reddy GR, Courtney CH (1995) A repetitive DNA profile for the sensitive detection of Fasciola hepatica infected snails. Int J Parasitol 25:601–610
Krammer F, Schnieder T (1998) Sequence heterogeneity in a repetitive DNA element of Fasciola. Int J Parasitol 28:1923–1929
Loxdale HD, Lushai G (1998) Molecular markers in entomology. Bull Entomol Res 88:577–600
MacPherson JM, Gajadhar AA (1993) Differentiation of seven Eimeria species by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Vet Parasitol 45:257–266
McManus DP, Bowles J (1996) Molecular genetic approaches to parasitic identification: their value in diagnostic parasitology and systematics. Int J Parasitol 26:687–704
Nadler SA (1990) Molecular approaches to studying helminth population genetics and phylogeny. Int J Parasitol 20:11–29
Neto ED, Steindel M, Passos LKF (1993) The use of RAPD’s for the study of the genetic diversity of Schistosoma mansoni and Trypanosoma cruzi. In: Pena SDJ, Chakraborty R, Epplen JT, Jeffreys AJ (eds) DNA fingerprinting: state of science. Birkhäuser-Verlag, Basel, pp 339–345
Omanwar S, Rao JR, Singh RK, Butchaiah G (2001) DNA polymorphism in Trypanosoma evansi isolates defined by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA-PCR. Vet Rec 148:244–246
Petrie JL, Burg EF, Cain GD (1996) Molecular characterization of Echinostoma caproni and E. paraensei by random amplification of polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. J Parasitol 82:360–362
Prichard R (1997) Application of molecular biology in veterinary parasitology. Vet Parasitol 71:155–175
Reddy YA, Rao JR, Butchaiah G, Sharma B (1998) Random amplified polymorphic DNA for the specific detection of bubaline Echinococcus granulosus by hybridization assay. Vet Parasitol 79:315–323
Romanova EA, Semenova SK, Benediktov II, Ryskov AP (1997) Use of polymerase chain reaction for identifying the DNA of helminths from the genera Trichinella, Fasciola, Echinococcus, Nematodirus and Taenia. Parazitologiya 31:53–65
Saike RK, Gefland DH, Staffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sandoval H, Manga-Gonzalez Y, Campo R, Garca P, Castro JM, Perez de la Vega M (1999) Preliminary study on genetic variability of Dicrocoelium dendriticum determined by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Parasitol Int 48:21–26
Semenova SK, Romanova EA, Benediktov II, Ryskov AP (1995) Analysis of genetic variability of Fasciola hepatica using the polymerase chain reaction with random primers. Genetika-Moskova 31:273–275
Semenova SK, Romanova EA, Ryskov AP (1996) Genetic differentiation of helminths on the basis of data of polymerase chain reaction using random primers. Genetika 32:304–309
Siles-Lucas M, Cuesta-Bandera C, Cesar-Benito M (1993) Random amplified polymorphic DNA technique for speciation studies of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitol Res 79:343–345
Thompson RCA, Lymbery AJ, Constantine CC (1995) Variation in Echinococcus: towards a taxonomic revision of the genus. Adv Parasitol 35:146–176
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Wu Z, Nagano I, Takashashi Y (1998) The detection of Trichinella with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers constructed using sequences of complimentary DNA encoding excretory-secretory (E-S) glycoproteins. Parasitology 117:173–183
Yu JR, Chung JS, Chai JY (1997) Different RAPD patterns between Metagonimus yokogawai and Metagonimus type. Kor J Parasitol 35:295–298
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Director of the Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Izatnagar for the facilities provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunasekar, K.R., Tewari, A.K., Sreekumar, C. et al. Elucidation of genetic variability among different isolates of Fasciola gigantica (giant liver fluke) using random-amplified polymorphic DNA polymerase chain reaction. Parasitol Res 103, 1075–1081 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1095-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1095-0