Abstract
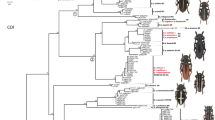
The complete internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1), 5.8S rDNA, and ITS2 region of the ribosomal DNA and a 390-bp region of the 16S rDNA gene from five taxa belonging to Rhinonyssus (Rhinonyssus vanellus, Rhinonyssus tringae, Rhinonyssus neglectus, Rhinonyssus echinipes from Kentish plover, and Rhinonyssus echinipes from grey plover) were sequenced to examine the level of sequence variation and the taxonomic levels to show utility in phylogeny estimation. Our data show that these molecular markers can help to discriminate between species and populations included in the Rhinonyssus coniventris complex (R. tringae, R. neglectus, R. echinipes), which are morphologically very close and difficult to separate by classic methods. A comparative study with sequences from other rhinonyssid mites previously published was also carried out. The resulting phylogenetic tree inferred from ITS1–5.8S–ITS2 region sequences obtained in this paper, together with those from other 11 taxa of rhinonyssid, shows slight differences from the current taxonomy of the Rhinonyssidae. This study appeals for the revision of the taxonomic status of the R. coniventris complex, as well as for the species included within it.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black WC IV, Piesman J (1994) Phylogeny of hard- and soft-tick taxa (Acari: Ixodida) based on mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:10034–10038
Butenko OM (1984) Ácaros rinonísidos de aves no paseriformes de la URSS. Leninskie Gory. Publicación especial. Moscú, pp 1–186 (en ruso)
Caporale DA, Rich SM, Spielman A, Telford SR, Kocher TD (1995) Discriminating between Ixodes ticks by means of mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 4:361–365
Dabert J, Dabert M, Mironov SV (2001) Phylogeny of feather mite subfamily Avenzoariinae (Acari: Analgoidea: Avenzoariidae) inferred from combined analyses of molecular and morphological data. Mol Phylogenet Evol 20:124–135
de Rojas M, Mora MD, Ubeda JM, Cutillas C, Navajas M, Guevara DC (2001) Phylogenetic relationships in rhinonyssid mites (Acari: Rhinonyssidae) based on mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences. Exp Appl Acarol 25:957–967
de Rojas M, Mora MD, Ubeda JM, Cutillas C, Navajas M, Guevara DC (2002) Phylogenetic relationships in rhinonyssid mites (Acari: Rhinonyssidae) based on ribosomal DNA sequences: insights for the discrimination of closely related species. Parasitol Res 88:675–681
Domrow R (1969) The nasal mites of Queensland birds (Acari: Dermanyssidae, Ereynetidae and Epidermoptidae). Proc Linn Soc N S W 93:297–426
Fain A (1957) Essai de classification des Rhinonyssidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) avec description de deux genres nouveaux. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 31:145–157
Fain A (1960) Morphologie comparée des Rhinonyssidae. Bull Ann Soc R Entomolog Belg 96:303–313
Fain A (1962) Les rhinonyssides parasites des Pigeons (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Rev Zool Bot Afr LXV(3–4):305–324
Fain A (1963) Le complexe “Rhinonyssus coniventris” (Rhinonyssidae: Mesostigmata). Bull Ann Soc R Entomolog Belg 99:86–100
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package), Version 3.5p edition. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Fukunaga M, Yabuki M, Hamase A, Oliver JH Jr, Nakao M (2000) Molecular phylogenetic analysis of ixodid ticks based on the ribosomal DNA spacer, internal transcribed spacer 2, sequences. J Parasitol 86:38–43
Hirst S (1921) On some new parasite mites. Proc Zool Soc Lond 2:769–803
Mangold AJ, Bargues MD, Mas-Coma S (1998) Mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences and phylogenetic relationships of species of Rhipicephalus and other tick genera among Metastriata (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 84:478–484
Navajas M, Fenton B (2000) The application of molecular markers in the study of diversity in acarology: a review. Exp Appl Acarol 24:751–774
Navajas M, Lagnel J, Gutierrez J, Boursot P (1998) Species-wide homogeneity of nuclear ribosomal ITS2 sequences in the spider mite Tetranychus urticae contrasts with extensive mitochondrial COI polymorphism. Heredity 80:742–752
Navajas M, Lagnel J, Fauvel G, De Moraes G (1999) Sequence variation of ribosomal internal transcribed spacers (ITS) in comercially important Phytoseiidae mites. Exp Appl Acarol 23:851–859
Noge K, Mori M, Tanaka C, Nishida R, Tsuda M, Kuwahara Y (2005) Identification of astigmatid mites using the second internal transcribed spacer (ITS2) region and its application for phylogenetic study. Exp Appl Acarol 35:29–46
Norris DE, Klompen JSH, Keirans JE, Black WC IV (1996) Population genetics of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) based on mitochondrial 16S and 12S genes. J Med Entomol 33:78–89
Pence DB (1975) Keys, species and host list, and bibliography for nasal mites of North American birds (Acarina: Rhinonyssinae, Turbinoptinae, Speleognathinae and Cytoditidae). Spec Publ Mus Tex Tech Univ 8:1–148
Pence DB, Casto SD (1976) Studies on the variation and morphology of the Ptilonyssus “sairae” complex (Acarina: Rhinonyssidae) from North American Passeriform birds. J Med Entomol 13:71–95
Rich SM, Caporale DA, Telford SR III, Kocher TD, Kartl DL, Spielman A (1995) Distribution of Ixodes ricinus-like ticks of eastern North America. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6284–6288
Simon C, Frat F, Beckenbach A, Crespi B, Liu H, Flook P (1994) Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann Entomol Soc Am 87:651–701
Strandtmann RW (1951) The Mesostigmatic nasal mites of birds. II. New and poorly known species of Rhinonyssidae. J Parasitol 37:129–140
Strandtmann RW (1956) The mesostigmatic nasal mites of birds. IV. The species and hosts of genus Rhinonyssus. (Acarina: Rhinonyssidae). Proc Entomol Soc Wash 58:129–142
Vargas M, García Varela M, Laclette J, Pérez TM (2005) Application of ITS-2 sequences as markers for identification and phylogenetic inference within the genus Geomylichus (Acari: Listrophoridae). Exp Appl Acarol 35:223–238
Whitfield JB, Cameron SA (1998) Hierarchical analysis of variation in the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene among Hymenoptera. Mol Biol Evol 15:1728–1743
Zahler M, Gothe R, Rinder H (1995) Genetic evidence against a morphologically suggestive conspecificity of Dermacentor reticulatus and D. marginatus (Acari: Ixodidae). Int J Parasitol 25:1413–1419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Rojas, M., Úbeda, J.M., Cutillas, C. et al. Utility of ITS1–5.8S–ITS2 and 16S mitochondrial DNA sequences for species identification and phylogenetic inference within the Rhinonyssus coniventris species complex (Acari: Rhinonyssidae). Parasitol Res 100, 1041–1046 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0356-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0356-z