Abstract
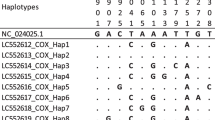
Piroplasms isolated from a farmed reindeer and elk in Wisconsin were determined to be Babesia odocoilei, based on morphology and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) analysis. Different clinical manifestations were observed in the two host species. The reindeer was parasitemic and exhibited acute babesiosis resulting in death, while the elk showed no parasites in blood smears and no overt clinical signs of babesiosis. B. odocoilei was, however, readily cultured from elk erythrocytes. Small subunit rRNA gene sequences from the two isolates were identical to that previously reported for B. odocoilei. Internal transcribed spacers 1 and 2 and 5.8S rRNA sequence analysis showed an overall identity range of 94.3–98.1% to corresponding sequences from three previously reported B. odocoilei isolates, but the Wisconsin reindeer B. odocoilei shared only 87.3% identity with a previously reported Babesia sp. isolated from a reindeer in California (RD61).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Armstrong PM, Katavolos P, Caproale DA, Smith RP, Spielman A, Telford SR III (1998) Diversity of Babesia infecting deer ticks (Ixodes dammini). Am Trop Med Hyg 58:739–742
Emerson HR (1969) A clinical, histopathological, and immunofluorescent study of Babesia spp infection in white-tailed deer. MSc thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, Tex.
Emerson HR, Wright WT (1968) The isolation of a Babesia in white-tailed deer. Bull Wildl Dis Assoc 4:142–143
Emerson HR, Wright WT (1970) Correction. J Wildl Dis 6:519
Holman PJ, Chieves L, Olson D, Wagner GG (1994a) Babesia equi erythrocytic stage continuously cultured in an enriched medium. J Parasitol 80:232–236
Holman PJ, Craig TM, Doan D, Petrini KR, Rhyan J, Wagner GG (1994b) Culture isolation and partial characterization of a Babesia sp. from a North American elk (Cervus elaphus). J Wildl Dis 30:460–465
Holman PJ, Petrini KR, Rhyan JC, Wagner GG (1994c) Culture isolation and partial characterization of a Babesia from a North American woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou). J Wildl Dis 30:195–200
Holman PJ, Becu T, Bakos E, Polledo G, Wagner GG (1998) Babesia equi field isolates cultured from horse blood using a microcentrifuge method. J Parasitol 84:696–699
Holman PJ, Madeley J, Craig TM, Allsopp BA, Petrini KR, Waghela SD, Wagner GG (2000) Antigenic, phenotypic and molecular characterization confirms Babesia odocoilei isolated from three cervine hosts. J Wildl Dis 36:518–530
Holman PJ, Swift PK, Frey RE, Bennett J, Cruz D, Wagner GG (2002) Genotypically unique Babesia spp isolated from reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) in the United States. Parasitol Res 88:405–411
Kjemtrup AM, Thomford J, Robinson T, Conrad PA (2000) Phylogenetic relationships of human and wildlife piroplasm isolates in the western United States inferred from the 18S nuclear small subunit RNA gene. Parasitology 120:487–493
Pearson WR, Wood T, Zhang Z, Miller W (1997) Comparison of DNA sequences with protein sequences. Genomics 46:24–36
Perry BD, Nichols DK, Cullom ES (1985) Babesia odocoilei Emerson and Wright, 1970, in white-tailed deer, Odocoileus virginianus (Zimmerman), in Virginia. J Wildl Dis 21:149–152
Petrini KR, Holman PJ, Rhyan JC, Jenkins SJ, Wagner GG (1995) Fatal babesiosis in a North American woodland caribou (Rangifer tarandus caribou). J Zoo Wildl Med 26:298–305
Sambrook JE, Fritsch F, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Sogin M L (1990) Amplification of ribosomal RNA genes for molecular evolution studies. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Suninsky JJ, White TH (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 307–314
Waldrup KA (1991) The involvement of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in the epidemiology of bovine Babesia bovis infection in Texas. PhD thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, Tex.
Waldrup KA, Kocan AA, Qureshi T, Davis DS, Baggett D, Wagner GG (1989) Serological prevalence and isolation of Babesia odocoilei among white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in Texas and Oklahoma. J Wildl Dis 25:194–201
Waldrup KA, Kocan AA, Barker RW, Wagner GG (1990) Transmission of Babesia odocoilei in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) by Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). J Wildl Dis 26:390–391
Waldrup KA, Moritz J, Baggett D, Magyar S, Wagner GG (1992) Monthly incidence of Theileria cervi and seroconversion to Babesia odocoilei in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in Texas. J Wildl Dis 28:457–459
Zahler M, Schein E, Rinder H, Gothe R (1998) Characteristic genotypes discriminate between Babesia canis isolates of differing vector specificity and pathogenicity to dogs. Parasitol Res 84:544–548
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Project H-6261. All experiments were conducted in compliance with the current laws of the United States.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holman, P.J., Bendele, K.G., Schoelkopf, L. et al. Ribosomal RNA analysis of Babesia odocoilei isolates from farmed reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) and elk (Cervus elaphus canadensis) in Wisconsin. Parasitol Res 91, 378–383 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0984-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0984-5