Abstract.
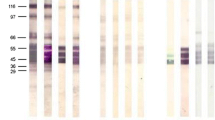
Immunoglobulin G subclass antibody (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4) responses to the rat lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, were analyzed using the immunoblotting technique in an attempt to further improve the sensitivity and specificity for the serodiagnosis of human angiostrongyliasis. Serum samples from patients with proven angiostrongyliasis and from clinically suspected cases of angiostrongyliasis with eosinophilic meningitis were tested. Sera from patients with other parasitic illnesses and from healthy volunteers were also analyzed. The results indicate that the immunoblotting used to detect IgG4 antibodies to the antigenic band of an approximate molecular mass of 29 kDa from young adult somatic extract of A. cantonensis is the most reliable test. It gives accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of 89.2%, 75%, 95%, 85.7% and 90.4%, respectively. More importantly, the test can discriminate between human angiostrongyliasis, gnathostomiasis and cysticercosis, three diseases that produce eosinophilic meningitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Intapan, P.M., Maleewong, W., Sawanyawisuth, K. et al. Evaluation of human IgG subclass antibodies in the serodiagnosis of angiostrongyliasis. Parasitol Res 89, 425–429 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-002-0781-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-002-0781-6