Abstract
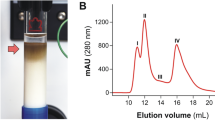
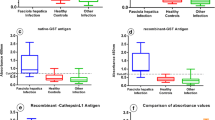
In several studies, different antigenic preparations and diverse immunological tests were applied for serodiagnosis of Fasciola hepatica infections. Most of these preparations showed cross-reactivity with proteins of other parasites. Application of purified antigens might reduce these cross-reactivities. Here, we used fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC)-fractionated extracts of F. hepatica excretory/secretory antigens (E/S Ags) for serodiagnosis of human and sheep fasciolosis. To develop an improved diagnostic method, we fractionated F. hepatica E/S Ags by anion exchange chromatography on a Sepharose CL-6B column and then tested the serodiagnostic values of the fractions. We used sera from F. hepatica-infected human and sheep as positive controls. Sera from patients with hydatidosis and strongyloidiasis were used for cross-reactivity studies. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) of the second FPLC peak, containing 20, 25, and 70 kDa proteins, discriminated between F. hepatica-infected and uninfected human and sheep samples. Fractionation of F. hepatica E/S Ags by FPLC is a fast and reproducible way of obtaining antigens useful for serodiagnosis of human and sheep fasciolosis with acceptable sensitivity and specificity.

ᅟ







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abath FG, Werkhauser RC (1996) The tegument of Schistosoma mansoni: functional and immunological features. Parasite Immunol 18:15–20
Allam AF, El-Agamy E-SI, Helmy MH (2002) Molecular and immunological characterization of Fasciola species. Br J Biomed Sci 59:191–195
Ashrafi K, Valero MA, Panova M, Periago MV, Massoud J, Mas-Coma S (2006) Phenotypic analysis of adults of Fasciola hepatica, Fasciola gigantica and intermediate forms from the endemic region of Gilan, Iran. Parasitol Int 55(4):249–260
Bossaert K, Farnir F, Leclipteux T, Protz M, Lonneux JF, Losson B (2000) Humoral immune response in calves to single-dose, trickle and challenge infections with Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol 87:103–123
Carnevale S, Rodriguez MI, Santillan G, Labbe JH, Cabrera MG, Bellegarde EJ, Velasquez JN, Trgovcic JE, Guarnera EA (2001) Immunodiagnosis of human fascioliasis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and a micro-ELISA. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 8:174–177
Cornelissen JB, Gaasenbeek CP, Boersma W, Borgsteede FH, van Milligen FJ (1999) Use of a pre-selected epitope of cathepsin-L1 in a highly specific peptide-based immunoassay for the diagnosis of Fasciola hepatica infections in cattle. Int J Parasitol 29:685–696
Cornelissen JB, Gaasenbeek CP, Borgsteede FH, Holland WG, Harmsen MM, Boersma WJ (2001) Early immunodiagnosis of fasciolosis in ruminants using recombinant Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L-like protease. Int J Parasitol 31:728–737
Demerdash ZA, Diab TM, Aly IR, Mohamed SH, Mahmoud FS, Zoheiry MK, Mansour WA, Attia ME, El-Bassiouny AE (2011) Diagnostic efficacy of monoclonal antibody based sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of Fasciola gigantica excretory/secretory antigens in both serum and stool. Parasit Vectors 4:176
Espino AM, Hillyer GV (2001) Identification of fatty acid molecules in a Fasciola hepatica immunoprophylactic fatty acid-binding protein. J Parasitol 87:426–428
Falak R, Sankian M, Noorbakhsh R, Tehrani M, Assarehzadegan MA, Jabbari Azad F, Abojhasani A, Varasteh AR (2013) Identification and characterisation of main allergic proteins in Vitis vinifera vitis. Food Agric Immunol 24:255–268
Farghaly AM, Nada SM, Emam WA, Mattar MA, Mohamed SM, Sharaf EM, Gamal RE (2009) Role of Fast-ELISA and Western blot in diagnosis of human fasciolosis using crude adult worm and excretory/secretory fasciola antigens. PUJ 2:55–65
Gonenc B, Sarimehmetoglu HO, Kara M, Kircali F (2004) Comparison of crude and excretory/secretory antigens for the diagnosis of Fasciola hepatica in sheep by Western blotting. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 28:943–949
Hacariz O, Sayers G, Mulcahy G (2011) A preliminary study to understand the effect of Fasciola hepatica tegument on naive macrophages and humoral responses in an ovine model. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 139:245–249
Hillyer GV (1999) Immunodiagnosis of human and animal fasciolosis. In: Dalton JP (ed) Fasciolosis. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp 435–447
Mas-Coma S, Bargues MD, Valero MA (2005) Fascioliasis and other plant-borne trematode zoonoses. Int J Parasitol 35:1255–1278
McGonigle S, Dalton JP (1995) Isolation of Fasciola hepatica haemoglobin. Parasitology 111:209–215
Meshgi B, Eslami A, Hemmatzadeh F (2008) Determination of somatic and excretory-secretory antigens of Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica using SDS-PAGE. Iranian J Vet Res 9:77–80
Mezo M, Gonzalez-Warleta M, Ubeira FM (2003) Optimized serodiagnosis of sheep fascioliasis by Fast-D protein liquid chromatography fractionation of Fasciola hepatica excretory-secretory antigens. J Parasitol 89:843–849
Mohamed MM, Al-Sherbiny MM, Sharaf AA, Elmamlouk TH (2004) Immunological identification of Fasciola hepatica antigens containing major human T-cell and B-cell epitopes. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 34:751–766
Morales A, Espino AM (2012) Evaluation and characterization of Fasciola hepatica tegument protein extract for serodiagnosis of human fascioliasis. Clin Vaccine Immunol 19:1870–1878
Rivera-Marrero CA, Santiago N, Hillyer GV (1988) Evaluation of immunodiagnostic antigens in the excretory-secretory products of Fasciola hepatica. J Parasitol 74:646–652
Robinson MW, Menon R, Donnelly SM, Dalton JP, Ranganathan S (2009) An integrated transcriptomics and proteomics analysis of the secretome of the helminth pathogen Fasciola hepatica: proteins associated with invasion and infection of the mammalian host. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:1891–1907
Rokni MB, Massoud J, O’Neill SM, Parkinson M, Dalton JP (2002) Diagnosis of human fasciolosis in the Gilan province of Northern Iran: application of cathepsin L-ELISA. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 44:175–179
Rokni MB, Baghernejhad A, Mohebali M, Kia EB (2004) Enzyme linked immunotransfer blot analysis of somatic and excretory-secretory antigens of Fasciola hepatica in diagnosis of human fasciolosis. Iran J Publ Health 33:8–13
Rokni MB, Mirhendi H, Behnia M, Fasihi Harandi M, Jalalizand N (2010) Molecular characterization of Fasciola hepatica isolates by RAPD-PCR and ribosomal ITS1 sequencing. Iranian Red Crescent Med J 12:27–32
Sampaio-Silva ML, Da Costa JM, Da Costa AM, Pires MA, Lopes SA, Castro AM, Monjour L (1996) Antigenic components of excretory-secretory products of adult Fasciola hepatica recognized in human infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg 54:146–148
Sarkari B, Ghobakhloo N, Moshfea A, Eilami O (2012) Seroprevalence of human fasciolosis in a new-emerging focus of fasciolosis in Yasuj District, Southwest of Iran. Iran J Parasitol 7:15–20
Spithill TW, Smooker PM, Sexton JL, Bozas E, Morrison CA, Creaney J, Parsons JCJP (1999) Development of vaccines against Fasciola hepatica. In: Dalton JP (ed) Fasciolosis. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp 377–401
Upadhyay AK, Kumar M (2002) SDS-PAGE analysis of Fasciola gigantica antigen. J Immunol Immunopathol 4:91–92
Valero MA, Periago MV, Perez-Crespo I, Rodriguez E, Perteguer MJ, Garate T, Gonzalez-Barbera EM, Mas-Coma S (2012) Assessing the validity of an ELISA test for the serological diagnosis of human fascioliasis in different epidemiological situations. Trop Med Int Health 17:630–636
Yamano K, Goto A, Nakamura-Uchiyama F, Nawa Y, Hada N, Takeda T (2009) Galbeta1-6Gal, antigenic epitope which accounts for serological cross-reaction in diagnosis of Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Parasite Immunol 31:481–487
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant 24488 from the Iran University of Medical Sciences (IUMS), Tehran, Iran. We thank Professor Eshrat beigom Kia from the School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Tehran, Iran) for providing strongyloidiasis sera and Professor AbdolFatah Sarafinejhad from the Noor Referral Laboratory (Tehran, Iran) for providing us with fasciolosis patients’ sera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Highlights
• Fasciola hepatica antigens were fractionated by FPLC anion exchange chromatography.
• Fractions containing the 17-, 48-, and 50-kDa proteins cross-reacted with sera from hydatidosis patients.
• The 12-, 14-, and 25-kDa proteins discriminate fasciolosis with high sensitivity and specificity.
• FPLC is a fast, simple, and reproducible way to purify F. hepatica immunogens.
• FPLC-fractionated antigens are useful for serodiagnosis of human and sheep fasciolosis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtarian, K., Akhlaghi, L., Meamar, A.R. et al. Serodiagnosis of fasciolosis by fast protein liquid chromatography-fractionated excretory/secretory antigens. Parasitol Res 115, 2957–2965 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5049-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5049-7