Abstract
Purpose
CD226 (DNAM-1) is an activating receptor mainly expressed in CD8 + and NK cells. CD226 deficiency and blockade have been shown to impair tumor suppression, while enhanced CD226 expression positively correlated with the increased efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies. However, the detailed function and role of CD226 in pan-cancer are largely unknown and require further in-depth investigation. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the biological functions of CD226, its role in tumor immunity, and its potential to predict prognosis and immunotherapy response in pan-cancer.
Methods
By taking advantage of single-cell and bulk sequencing analyses, we analyzed the expression profile of CD226, its correlation with patient prognosis, immune infiltration level, immune-related genes, tumor heterogeneity, and stemness in pan-cancer. We also investigated the biological functions of CD226 using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and evaluated its predictive value in response to immunotherapy and small-molecule targeted drugs. In addition, we validated the expression of CD226 in tumor-infiltrating CD8 + and NK cells and studied its association with their functions using a murine B16F10 melanoma model.
Results
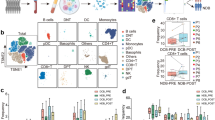
CD226 exhibited differential expression across most tumor types, and its elevated expression was associated with improved clinical outcomes in multiple cancer types. CD226 is closely correlated with numerous tumor-infiltrating immune cells, tumor stemness, and heterogeneity in most cancers. Furthermore, based on single-cell sequencing analysis, CD226 expression was found to be higher on effector CD4 + T cells than naïve CD4 + T cells, and its expression level was decreased in exhausted CD8 + T cells relative to effector CD8 + T cells in multiple cancer types. Additionally, flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that CD226 was highly correlated with the function of tumor-infiltrating NK and CD8 + T cells in murine B16F10 melanoma. Moreover, GSEA analysis revealed that CD226 was closely associated with T cell activation, natural killer cell mediated immunity, natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and T cell receptor signaling pathway. Finally, CD226 showed promising predictive potential for responsiveness to both ICB therapies and various small-molecule targeted drugs.
Conclusion
CD226 has shown great potential as an innovative biomarker for predicting patient prognosis, immune infiltration levels, and the function of tumor-infiltrating CD8 + T cells, as well as immunotherapy response. Additionally, our findings suggest that the optimal modification of CD226 expression and function, combined with current ICBs, could be a promising strategy for tumor immunotherapy.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Please contact author for data requests.
References
Banta KL, Xu X, Chitre AS et al (2022) Mechanistic convergence of the TIGIT and PD-1 inhibitory pathways necessitates co-blockade to optimize anti-tumor CD8(+) T cell responses. Immunity 55:512–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2022.02.005. (e519)
Bonneville R, Krook MA, Kautto EA et al (2017) Landscape of microsatellite instability across 39 cancer types. JCO Precis Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.17.00073
Braun M, Aguilera AR, Sundarrajan A et al (2020) CD155 on Tumor cells drives resistance to immunotherapy by inducing the degradation of the activating receptor CD226 in CD8(+) T cells. Immunity 53:805–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.09.010. (e815)
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U et al (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2:401–404. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla PK et al (2022) UALCAN: an update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 25:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2022.01.001
Charoentong P, Finotello F, Angelova M et al (2017) Pan-cancer immunogenomic analyses reveal genotype-immunophenotype relationships and predictors of response to checkpoint blockade. Cell Rep 18:248–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.019
Chiang EY, Mellman I (2022) TIGIT-CD226-PVR axis: advancing immune checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2022-004711
Conner M, Hance KW, Yadavilli S et al (2022) Emergence of the CD226 Axis in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol 13:914406. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.914406
Deng Y, Kerdiles Y, Chu J et al (2015) Transcription factor Foxo1 is a negative regulator of natural killer cell maturation and function. Immunity 42:457–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2015.02.006
Digre A, Lindskog C (2021) The Human Protein Atlas-Spatial localization of the human proteome in health and disease. Protein Sci 30:218–233. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3987
Du X, de Almeida P, Manieri N et al (2018) CD226 regulates natural killer cell antitumor responses via phosphorylation-mediated inactivation of transcription factor FOXO1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E11731–E11740. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1814052115
El-Sayes N, Vito A, Mossman K (2021) Tumor heterogeneity: a great barrier in the age of cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040806
Farkona S, Diamandis EP, Blasutig IM (2016) Cancer immunotherapy: the beginning of the end of cancer? BMC Med 14:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-016-0623-5
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Chauvin JM et al (2018) CD226 opposes TIGIT to disrupt Tregs in melanoma. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.121157
Gaud G, Roncagalli R, Chaoui K et al (2018) The costimulatory molecule CD226 signals through VAV1 to amplify TCR signals and promote IL-17 production by CD4(+) T cells. Sci Signal. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aar3083
Goodman AM, Sokol ES, Frampton GM et al (2019) Microsatellite-stable tumors with high mutational burden benefit from immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Res 7:1570–1573. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0149
Han Y, Wang Y, Dong X et al (2023) TISCH2: expanded datasets and new tools for single-cell transcriptome analyses of the tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res 51:D1425–D1431. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac959
Hassan G, Afify SM, Du J et al (2021) MEK1/2 is a bottleneck that induces cancer stem cells to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 583:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.10.047
Jiang P, Lee W, Li X et al (2018a) Genome-scale signatures of gene interaction from compound screens predict clinical efficacy of targeted cancer therapies. Cell Syst 6:343–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2018.01.009. (e345)
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D et al (2018b) Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 24:1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1
Jin HS, Ko M, Choi DS et al (2020) CD226(hi)CD8(+) T cells are a prerequisite for anti-TIGIT immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Res 8:912–925. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0877
Jochems C, Schlom J (2011) Tumor-infiltrating immune cells and prognosis: the potential link between conventional cancer therapy and immunity. Exp Biol Med (maywood) 236:567–579. https://doi.org/10.1258/ebm.2011.011007
Johnston RJ, Comps-Agrar L, Hackney J et al (2014) The immunoreceptor TIGIT regulates antitumor and antiviral CD8(+) T cell effector function. Cancer Cell 26:923–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2014.10.018
Kojima H, Kanada H, Shimizu S et al (2003) CD226 mediates platelet and megakaryocytic cell adhesion to vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 278:36748–36753. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M300702200
Lakshminarasimhan R, Liang G (2016) The role of DNA methylation in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 945:151–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-43624-1_7
Li T, Fu J, Zeng Z et al (2020) TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res 48:W509–W514. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa407
Li J, Wang J, Xie D et al (2021a) Characteristics of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways involved in the maintenance of self-renewal in lung cancer stem-like cells. Int J Biol Sci 17:1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.57871
Li Y, Zhang Y, Cao G et al (2021b) Blockade of checkpoint receptor PVRIG unleashes anti-tumor immunity of NK cells in murine and human solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol 14:100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01112-3
Man YG, Stojadinovic A, Mason J et al (2013) Tumor-infiltrating immune cells promoting tumor invasion and metastasis: existing theories. J Cancer 4:84–95. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.5482
Manes TD, Pober JS (2011) Identification of endothelial cell junctional proteins and lymphocyte receptors involved in transendothelial migration of human effector memory CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 186:1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1002835
Miranda A, Hamilton PT, Zhang AW et al (2019) Cancer stemness, intratumoral heterogeneity, and immune response across cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:9020–9029. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1818210116
Newkirk KM, Brannick EM, Kusewitt DF et al (2017) Chapter 6 - Neoplasia and Tumor Biology1[M]. Mosby. pp 286–321 (e281)
Oliver AJ, Lau PKH, Unsworth AS et al (2018) Tissue-dependent tumor microenvironments and their impact on immunotherapy responses. Front Immunol 9:70. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00070
Qi D, Wu E (2019) Cancer prognosis: considering tumor and its microenvironment as a whole. EBioMedicine 43:28–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.04.031
Ru B, Wong CN, Tong Y et al (2019) TISIDB: an integrated repository portal for tumor-immune system interactions. Bioinformatics 35:4200–4202. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz210
Sanchez-Correa B, Valhondo I, Hassouneh F et al (2019) DNAM-1 and the TIGIT/PVRIG/TACTILE axis: novel immune checkpoints for natural killer cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060877
Shi X, Liu Y, Cheng S et al (2021) Cancer stemness associated with prognosis and the efficacy of immunotherapy in adrenocortical carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:651622. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.651622
Singer M, Wang C, Cong L et al (2017) A Distinct gene module for dysfunction uncoupled from activation in tumor-infiltrating T cells. Cell 171:1221–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.006
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC et al (2021) The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D605–D612. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1074
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B et al (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Tang X, Yang J, Shi A et al (2022) CD155 cooperates with PD-1/PD-L1 to promote proliferation of esophageal squamous cancer cells via PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225610
Tie Y, Tang F, Wei YQ et al (2022) Immunosuppressive cells in cancer: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. J Hematol Oncol 15:61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-022-01282-8
Wang B, Zhang W, Jankovic V et al (2018) Combination cancer immunotherapy targeting PD-1 and GITR can rescue CD8(+) T cell dysfunction and maintain memory phenotype. Sci Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.aat7061
Wei C, Wang B, Peng D et al (2022) Pan-cancer analysis shows that ALKBH5 is a potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic biomarker for multiple cancer types including gliomas. Front Immunol 13:849592. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.849592
Weulersse M, Asrir A, Pichler AC et al (2020) Eomes-dependent loss of the co-activating receptor CD226 restrains CD8(+) T cell anti-tumor functions and limits the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Immunity 53:824–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.09.006. (e810)
Yeo J, Ko M, Lee DH et al (2021) TIGIT/CD226 axis regulates anti-tumor immunity. Pharmaceuticals (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030200
Yu Y, Sun Y, Li Z et al (2023) Systematic analysis identifies XRCC4 as a potential immunological and prognostic biomarker associated with pan-cancer. BMC Bioinformatics 24:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-023-05165-8
Zeng Z, Wong CJ, Yang L et al (2022) TISMO: syngeneic mouse tumor database to model tumor immunity and immunotherapy response. Nucleic Acids Res 50:D1391–D1397. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab804
Zhang Z, Wu N, Lu Y et al (2015) DNAM-1 controls NK cell activation via an ITT-like motif. J Exp Med 212:2165–2182. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20150792
Zhao Z, Li W, Zhang X et al (2020) Correlation between TMB and MSI in patients with solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 38:e15169–e15169. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.e15169
Zugazagoitia J, Guedes C, Ponce S et al (2016) Current challenges in cancer treatment. Clin Ther 38:1551–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.03.026
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the databases used in this study, as well as to the Cole Foundation. We also extend our appreciation to the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was designed by PM and WS, who also conducted the bioinformatics analysis and interpreted the data. WS conceived the study and wrote the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of IRCM (2019-03 HG).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, P., Sun, W. Integrated single-cell and bulk sequencing analyses with experimental validation identify the prognostic and immunological implications of CD226 in pan-cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 14597–14617 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05268-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05268-y