Abstract
Purpose
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common liver malignancy. Early vascular invasion (VI) has been associated with poor prognosis in HCC patients. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a significant role in the emergence and development of many tumor types.
Methods
Differential expression analysis of miRNAs related to VI was performed based on data from the TCGA database, and survival-associated miRNAs identified. We identified miR-9-5p as a survival-related miRNA and verified its expression in 61 clinical samples using quantitative real-time PCR. We further performed functional enrichment analysis, protein-protein interaction analysis, univariate and multivariate analysis of the survival-related miRNAs, and cell function assays.
Results
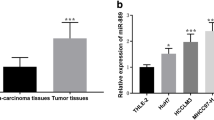
In this study, we identified miR-9-5p that could predict VI and prognosis in HCC patients. Cellular experiments demonstrated that downregulation of miR‑9‑5p inhibits migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of HCC cells. Further, we explored and verified the possible mechanism through which miR-9-5p is involved in HCC progression. Univariate and multivariate analysis revealed that miR-9-5p was an independent risk factor for HCC. Finally, the nomogram based on miR-9-5p showed a good predictive value of HCC survival.
Conclusions
MiR-9-5p is associated with VI in HCC, and higher expression of miR-9-5p indicates poor prognosis in HCC.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Online data are available at the TCGA database (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/). The clinical patient data used during this study can be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- VI:
-
Vascular invasion
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- mRNAs:
-
Messenger RNAs
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- DEMs:
-
Differentially expressed miRNAs
- RT-qPCR:
-
Quantitative real‑time PCR
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- PPI:
-
Protein–protein interaction
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- ROC:
-
Receiver operator characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area under curve
References
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW et al (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 4
Bandini E, Fanini F, Vannini I et al (2020) miR-9-5p as a regulator of the androgen receptor pathway in breast cancer cell lines. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:579160
Cai K, Li T, Guo L et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA LINC00467 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by modulating miR-9-5p/PPARA expression. Open Biol 9(9):190074
Chen L, Hu W, Li G et al (2019) Inhibition of miR-9-5p suppresses prostate cancer progress by targeting StarD13. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:20
Chen L, Liu DM, Yi XF et al (2020) The novel miR-1269b-regulated protein SVEP1 induces hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis likely through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Death Dis 11(5)
Chen Y, Wang G, Xu H et al (2021) Identification of a novel metastasis-related miRNAs-based signature for predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Oncol 2021:6629633
Dong X, Wang F, Xue Y et al (2019) MicroRNA95p downregulates Klf4 and influences the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the AKT signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 43(3):1417–1429
Ertl IE, Brettner R, Kronabitter H et al (2022) The SMARCD family of SWI/SNF accessory proteins is involved in the transcriptional regulation of androgen receptor-driven genes and plays a role in various essential processes of prostate cancer. Cells 12(1):124
Fan F, Chen K, Lu X et al (2021) Dual targeting of PD-L1 and PD-L2 by PCED1B-AS1 via sponging hsa-miR-194-5p induces immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int 15(2):444–458
Frankish A, Diekhans M, Ferreira AM et al (2019) GENCODE reference annotation for the human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D766–D773
Guo CM, Liu SQ, Sun MZ (2020) miR-429 as biomarker for diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of cancers and its potential action mechanisms: a systematic literature review. Neoplasma 67(2):215–228
Hassanipour S, Vali M, Gaffari-Fam S et al (2020) The survival rate of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asian countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EXCLI J 19:108–130
Hayes CN, Chayama K (2016) MicroRNAs as biomarkers for liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 17(3):280
Kim E, Viatour P (2020) Hepatocellular carcinoma: old friends and new tricks. Exp Mol Med 52(12):1898–1907
Komoll RM, Hu QL, Olarewaju O et al (2021) MicroRNA-342-3p is a potent tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 74(1):122–134
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S (2019) miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D155–D162
Krishnan MS, Rajan KdA, Park J et al (2021) Genomic analysis of vascular invasion in HCC reveals molecular drivers and predictive biomarkers. Hepatology 73(6):2342–2360
Leijssen LGJ, Dinaux AM, Amri R et al (2019) Impact of intramural and extramural vascular invasion on stage II–III colon cancer outcomes. J Surg Oncol 119(6):749–757
Li J, Huang C, Zou Y et al (2020a) CircTLK1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by sponging miR-136-5p. Mol Cancer 19(1):103
Li W, Chen QF, Huang T et al (2020b) Identification and validation of a prognostic lncRNA signature for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 10:780
Lin YL, Li Y (2020) Study on the hepatocellular carcinoma model with metastasis. Genes Dis 7(3):336–350
Liu AG, Pang YY, Chen G et al (2020) Downregulation of miR-199a-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma and its relevant molecular mechanism via GEO, TCGA database and in silico analyses. Technol Cancer Res Treat 19:1533033820979670
Mazumder S, Datta S, Ray JG et al (2019) Liquid biopsy: miRNA as a potential biomarker in oral cancer. Cancer Epidemiol 58:137–145
Menyhart O, Nagy A, Gyorffy B (2018) Determining consistent prognostic biomarkers of overall survival and vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. R Soc Open Sci 5(12):181006
Mi S, Du J, Liu J et al (2020) FtMt promotes glioma tumorigenesis and angiogenesis via lncRNA SNHG1/miR-9-5p axis. Cell Signal 75:109749
Oura K, Morishita A, Masaki T (2020) Molecular and functional roles of MicroRNAs in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma—a review. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):8362
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G, Kostoulas N et al (2013) DIANA-microT web server v5.0: service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Web Server issue):W169-173
Rodriguez-Peralvarez M, Luong TV, Andreana L et al (2013) A systematic review of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnostic and prognostic variability. Ann Surg Oncol 20(1):325–339
Sun QY, Li J, Jin BX et al (2020) Evaluation of miR-331-3p and miR-23b-3p as serum biomarkers for hepatitis c virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma at early stage. Clin Res Hepatol Gas 44(1):21–28
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Tang A, Hallouch O, Chernyak V et al (2018) Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: target population for surveillance and diagnosis. Abdom Radiol (n Y) 43(1):13–25
Tonellotto F, Bergmann A, Abrahao K et al (2020) Lymphatic/vascular invasion has a negative impact on overall survival and disease-free survival in patients with breast cancer and positive axillary lymph nodes. Breast J 26(9):1867–1868
Vejnar CE, Zdobnov EM (2012) MiRmap: comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength. Nucleic Acids Res 40(22):11673–11683
Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ (2012) Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent among samples. Theor Biosci 131(4):281–285
Wang M, Gao Q, Chen Y et al (2019) PAK4, a target of miR-9-5p, promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:58
Wang XL, He Y, Mackowiak B et al (2021a) MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut 70(4):784–795
Wang L, Cui M, Cheng D et al (2021b) miR-9-5p facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting ESR1. Mol Cell Biochem 476(2):575–583
Wei YQ, Jiao XL, Zhang SY et al (2019) MiR-9-5p could promote angiogenesis and radiosensitivity in cervical cancer by targeting SOCS5. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol 23(17):7314–7326
Wu M, Huang Y, Chen T et al (2019) LncRNA MEG3 inhibits the progression of prostate cancer by modulating miR-9-5p/QKI-5 axis. J Cell Mol Med 23(1):29–38
Wu XL, Li JH, Gassa A et al (2020a) Circulating tumor DNA as an emerging liquid biopsy biomarker for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci 16(9):1551–1562
Wu F, Jiang X, Wang Q et al (2020b) The impact of miR-9 in osteosarcoma: a study based on meta-analysis, TCGA data, and bioinformatics analysis. Medicine (baltimore) 99(35):e21902
Xie Y, Wang Y, Gong R et al (2020) SNHG7 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence by sequestering miR-9-5p to upregulate CNNM1 expression. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 35(10):731–740
Xing S, Tian Z, Zheng WY et al (2021) Hypoxia downregulated miR-4521 suppresses gastric carcinoma progression through regulation of IGF2 and FOXM1. Mol Cancer 20(1)
Ye Y, Guo J, Xiao P et al (2020) Macrophages-induced long noncoding RNA H19 up-regulation triggers and activates the miR-193b/MAPK1 axis and promotes cell aggressiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 469:310–322
Zeng Z, Dong J, Li Y et al (2020) The expression level and diagnostic value of microRNA-22 in HCC patients. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 48(1):683–686
Zhang Y, Wei C, Guo CC et al (2017) Prognostic value of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 8(63):107237–107257
Zhou Z, Zhou X, Jiang Y et al (2020) Clinical significance of miR-1180-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma: a study based on bioinformatics analysis and RT-qPCR validation. Sci Rep 10(1):11573
Zhu K, Lin J, Chen S et al (2021) miR-9-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting ID4. Technol Cancer Res Treat 20:15330338211048592
Zuo L, Li X, Tan Y et al (2021) Prospective pathway signaling and prognostic values of microRNA-9 in ovarian cancer based on gene expression omnibus (GEO): a bioinformatics analysis. J Ovarian Res 14(1):29
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the workers who participated in the construction of TCGA database and the patients who donated samples. The authors thank the Department of Biobank, Subei People’s Hospital of Jiangsu province for collecting, storing, and classifying patient specimens used in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant number 81871909; “13th five-year Plan” Science and Education strong Health Project leading personnel of Yangzhou under Grant number YZCXTD201801; and Provincial-level discipline leader of the NJPH under Grant number DTRC201809.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC conceived and designed the experiment, collected experimental data, wrote the manuscript draft, and finally approved the manuscript. HX collected and analyzed the experimental data and reviewed the manuscript. HT and HL assisted in the experiments and collected patient data. CZ and SJ reviewed the manuscript. DB reviewed the manuscript and provided financial support.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study complied with the principles set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki. The data obtained from the TCGA database are all open access data, which conforms to the database usage specification. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to the study, and this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital (approval number: 2020ky-067).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Xu, H., Tang, H. et al. miR-9-5p expression is associated with vascular invasion and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma, and in vitro verification. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 14657–14671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05257-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05257-1