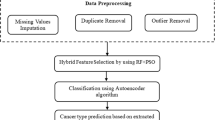
Abstract
Purpose
Early identification of lung cancer (LC) will considerably facilitate the intervention and prevention of LC. The human proteome micro-arrays approach can be used as a “liquid biopsy” to diagnose LC to complement conventional diagnosis, which needs advanced bioinformatics methods such as feature selection (FS) and refined machine learning models.
Methods
A two-stage FS methodology by infusing Pearson’s Correlation (PC) with a univariate filter (SBF) or recursive feature elimination (RFE) was used to reduce the redundancy of the original dataset. The Stochastic Gradient Boosting (SGB), Random Forest (RF), and Support Vector Machine (SVM) techniques were applied to build ensemble classifiers based on four subsets. The synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) was used in the preprocessing of imbalanced data.
Results
FS approach with SBF and RFE extracted 25 and 55 features, respectively, with 14 overlapped ones. All three ensemble models demonstrate superior accuracy (ranging from 0.867 to 0.967) and sensitivity (0.917 to 1.00) in the test datasets with SGB of SBF subset outperforming others. The SMOTE technique has improved the model performance in the training process. Three of the top selected candidate biomarkers (LGR4, CDC34, and GHRHR) were highly suggested to play a role in lung tumorigenesis.
Conclusion
A novel hybrid FS method with classical ensemble machine learning algorithms was first used in the classification of protein microarray data. The parsimony model constructed by the SGB algorithm with the appropriate FS and SMOTE approach performs well in the classification task with higher sensitivity and specificity. Standardization and innovation of bioinformatics approach for protein microarray analysis need further exploration and validation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and code supporting the results or analysis presented in this study were available upon reasonable request from Jianbo Pan and Yazhou Wu.
References
Abdulla M, Khasawneh MT (2020) G-Forest: An ensemble method for cost-sensitive feature selection in gene expression microarrays. Artif Intell Med 108:101941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101941
Assawamakin A, Prueksaaroon S, Kulawonganunchai S, Shaw PJ, Varavithya V, Ruangrajitpakorn T, Tongsima S (2013) Biomarker selection and classification of “-omics” data using a two-step bayes classification framework. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/148014
Azadifar S, Rostami M, Berahmand K, Moradi P, Oussalah M (2022) Graph-based relevancy-redundancy gene selection method for cancer diagnosis. Comput Biol Med 147:105766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105766
Cai Z, Xu D, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Ngai SM, Shao J (2015) Classification of lung cancer using ensemble-based feature selection and machine learning methods. Mol Biosyst 11(3):791–800. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mb00659c
Desmetz C, Mange A, Maudelonde T, Solassol J (2011) Autoantibody signatures: progress and perspectives for early cancer detection. J Cell Mol Med 15(10):2013–2024. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01355.x
Doseeva V, Colpitts T, Gao G, Woodcock J, Knezevic V (2015) Performance of a multiplexed dual analyte immunoassay for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med 13:55–69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0419-y
Duarte JG, Blackburn JM (2017) Advances in the development of human protein microarrays. Expert Rev Proteomics 14(7):627–641. https://doi.org/10.1080/14789450.2017.1347042
Friedman JH (2002) Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput Stat Data Anal 38(4):367–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-9473(01)00065-2
Gicić A, Subasi A (2018) Credit scoring for a microcredit data set using the synthetic minority oversampling technique and ensemble classifiers. Exp Syst 36(2):e12363. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12363
Gupta S, Manubhai KP, Mukherjee S, Srivastava S (2017) Serum profiling for identification of autoantibody signatures in diseases using protein microarrays. Methods Mol Biol 1619:303–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7057-5_21
Hijazi H, Wu M, Nath A, Chan C (2012) Ensemble Classification of cancer types and biomarker identification. Drug Dev Res 73(7):414–419. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21032
Hu CA, Chen CM, Fang YC, Liang SJ, Wang HC, Fang WF, Sheu CC, Perng WC, Yang KY, Kao KC, Wu CL et al (2020). Using a machine learning approach to predict mortality in critically ill influenza patients: a cross- sectional retrospective multicentre study in Taiwan. BMJ Open, 10(2), e033898. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033898
Jeong JS, Jiang L, Albino E, Marrero J, Rho HS, Hu J, Blackshaw S (2012) Rapid identification of monospecific monoclonal antibodies using a human proteome microarray. Mol Cell Proteomics. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.O111.016253
Jonas DE, Reuland DS, Reddy SM, Nagle M, Clark SD, Weber RP, Harris RP (2021) Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography: updated evidence report and systematic review for the us preventive services task force. JAMA 325(10):971–987. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.0377
Kečo D, Subasi A, Kevric J (2016) Cloud computing-based parallel genetic algorithm for gene selection in cancer classification. Neural Comput Appl 30(5):1601–1610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2780-z
Lastwika KJ, Kargl J, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Lo E, Shelley D, Houghton AM (2019) Tumor-derived autoantibodies identify malignant pulmonary nodules. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 199(10):1257–1266. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201804-0628OC
Li R, liu, X., Zhou, X., Chen, X., Li, J., Yin, Y., & Qu, Y. (2020) Identification and validation of the prognostic value of immune-related genes in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Transl Res 12(9):5844–5865
Li Y, Luo Y (2020) Performance-weighted-voting model: an ensemble machine learning method for cancer type classification using whole-exome sequencing mutation. Quant Biol 8(4):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40484-020-0226-1
Liu Q, Sung AH, Chen Z, Liu J, Chen L, Qiao M, Deng Y (2011) Gene selection and classification for cancer microarray data based on machine learning and similarity measures. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-S5-S1
Lopez-Rincon A, Mendoza-Maldonado L, Martinez-Archundia M, Schonhuth A, Kraneveld AD, Garssen J, Tonda A (2020) Machine learning-based ensemble recursive feature selection of circulating mirnas for cancer tumor classification. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071785
Ltd., C. P. A. (2020). About HuProt™ Arrays. Retrieved from https://cambridgeproteinarrays.com/about-huprot.php#:~:text=HuProt%20arrays%20contain%20over%2020%2C000%20individually%20printed%20proteins%2C,contexts%20of%20high%20interest%20are%20covered%20in%20depth.
Mogi A, Kuwano H (2011) TP53 mutations in nonsmall cell lung cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/583929
Ozaki T, Nakagawara A (2011) Role of p53 in cell death and human cancers. Cancers (basel) 3(1):994–1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3010994
Pan J, Song G, Chen D, Li Y, Liu S, Hu S, Huang Y (2017) Identification of serological biomarkers for early diagnosis of lung cancer using a protein array-based approach. Mol Cell Proteomics 16(12):2069–2078. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.RA117.000212
Pan J, Zheng QZ, Li Y, Yu LL, Wu QW, Zheng JY, Huang Y (2019) Discovery and validation of a serologic autoantibody panel for early diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 28(9):1454–1460. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-1269
Pan J, Yu L, Wu Q, Lin X, Liu S, Hu S, Huang Y (2020) Integration of IgA and IgG autoantigens improves performance of biomarker panels for early diagnosis of lung cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics 19(3):490–500. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.RA119.001905
Ramaswamy S, Tamayo P, Rifkin R, Mukherjee S, Yeang CH, Angelo M, Golub TR (2001) Multiclass cancer diagnosis using tumor gene expression signatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(26):15149–15154. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.211566398
Shukla AK, Tripathi D (2019) Identification of potential biomarkers on microarray data using distributed gene selection approach. Math Biosci 315:108230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mbs.2019.108230
Smith RA, Andrews KS, Brooks D, Fedewa SA, Manassaram-Baptiste D, Saslow D, Wender RC (2017) Cancer screening in the United States, 2017: a review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin 67(2):100–121. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21392
Sun L, Zhang Z, Yao Y, Li WY, Gu J (2020) Analysis of expression differences of immune genes in non-small cell lung cancer based on TCGA and ImmPort data sets and the application of a prognostic model. Ann Transl Med 8(8):550–562. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.04.38
Tan AC, Gilbert D (2003) Ensemble machine learning on gene expression data for cancer classification. Appl Bioinformatics 2(3 Suppl):S75-83
Vural H, Subaşı A (2015) Data-Mining techniques to classify microarray gene expression data using gene selection by SVD and information gain. Model Artif Intell 6(2):171–182. https://doi.org/10.13187/mai.2015.6.171
Wang Y, Tetko IV, Hall MA, Frank E, Facius A, Mayer KF, Mewes HW (2005) Gene selection from microarray data for cancer classification–a machine learning approach. Comput Biol Chem 29(1):37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2004.11.001
Wang H, Zhang X, Vidaurre I, Cai R, Sha W, Schally AV (2018) Inhibition of experimental small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancers by novel antagonists of growth hormone-releasing hormone. Int J Cancer 142(11):2394–2404. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31308
Wang X, Yu B, Ma A, Chen C, Liu B, Ma Q (2019) Protein-protein interaction sites prediction by ensemble random forests with synthetic minority oversampling technique. Bioinformatics 35(14):2395–2402. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty995
Yang L, Wang J, Li J, Zhang H, Guo S, Yan M, Tao SC (2016) Identification of serum biomarkers for gastric cancer diagnosis using a human proteome microarray. Mol Cell Proteomics 15(2):614–623. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M115.051250
Zhang S, Sun Y (2020) Targeting CDC34 E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme for lung cancer therapy. EBioMedicine 54:102718
Zhang C, Cui T, Cai R, Wangpaichitr M, Mirsaeidi M, Schally AV, Jackson RM (2020a) Growth hormone-releasing hormone in lung physiology and pulmonary disease. Cells 9(10):2331–2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102331
Zhang S, Liu Y, Chen J, Shu H, Shen S, Li Y, Gao Q (2020b) Autoantibody signature in hepatocellular carcinoma using seromics. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00918-x
Zhao XC, Wang GZ, Wen ZS, Zhou YC, Hu Q, Zhang B, Zhou GB (2020) Systematic identification of CDC34 that functions to stabilize EGFR and promote lung carcinogenesis. EBioMedicine 53:102689
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82173621, 81872716).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. NY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal Analysis, Writing-Original Draft. JP: Methodology, Resources, Writing-Original Draft. XC: Formal analysis, Editing & polishing. PL: Software, Validation, Investigation. YL: Validation, Formal analysis, Visualization. ZW: Software, Editing & polishing. TY: Methodology, Formal Analysis. LQ: Validation, Visualization. DY: Conceptualization, Validation, Methodology. YW: Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Resources, Methodology, Writing-review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The data collection procedure that involved human beings in his study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Fujian Provincial Hospital and conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration. Written informed consent was obtained from the participants of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, N., Pan, J., Chen, X. et al. Discovery of potential biomarkers for lung cancer classification based on human proteome microarrays using Stochastic Gradient Boosting approach. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 6803–6812 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04643-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04643-z