Abstract
Purpose
To demonstrate the biological function of Secreted Phosphoprotein 1(SPP1) and its immune suppressive role in the progression intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC).
Methods
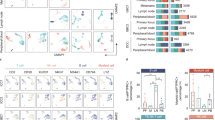
We collected 62,770 cells’ published transcriptome data of nine patients whose paired adjacent liver and tumor tissues were both available. We applied differential gene expression analysis to screen potential ICC marker genes, survival analysis to verify the prognostic value of SPP1, and correlation analysis to decipher factors that are related to SPP1 expression. The CellChat was used to distinguish interactions between cancer and T cells. CytoSig was applied to query cytokines that modulate CD44. Further, we established a proliferation score and correlated the score with inhibitory signals to determine the proliferation-suppressive function of SPP1-CD44.
Results
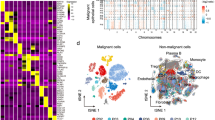
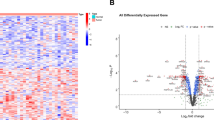
SPP1 expression is significantly upregulated in tumoral epitheliums, and patients with higher SPP1 expression have worse survival (P < 0.05). Tumor cells communicate with T cells via SPP1-CD44 interactions. The average expression of SPP1 in malignant cells (SPP1m) and CD44 in T cells (CD44t) is moderately negatively correlated with T cell proliferation score. Immunosuppressive cytokine TGFβ-3 identified as an inducer of CD44 and was significantly negatively correlated with proliferation score (R = − 0.88, P < 0.01), and the negative correlation was aggravated in samples with high CD44 expression.
Conclusion
SPP1 is a prognostic marker of ICC and is associated with the genome heterogeneity. SPP1-CD44 hinders sustained proliferation of T cells, but immunosuppressive T cells in the tumor microenvironment may evade this inhibition by reducing CD44 expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The published data used in this study were retrieved from the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus database accession code GSE1387089. The remaining data are within the article or available from the authors upon request. Analysis scripts are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- ICC:
-
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- SPP1:
-
Secreted Phosphoprotein 1
- TAM:
-
Tumor-associated macrophages
- CAFs:
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- HIFs:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factors
- IDH:
-
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- scRNA-seq:
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing
- CNV:
-
Copy number variation
- DC:
-
Dendritic cells
- ITH:
-
Intratumoral heterogeneity
- SPP1m:
-
Expression of SPP1 in malignant cells
- CD44t:
-
Expression of CD44 in T cells
References
Abou-Shady M, Baer HU, Friess H et al (1999) Transforming growth factor betas and their signaling receptors in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg 177:209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9610(99)00012-4
Argemi J, Ponz-Sarvise M, Sangro B (2022) Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: current and developing strategies. Adv Cancer Res 156:367–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acr.2022.03.002
Bang Y-J, Ueno M, Malka D et al (2019) Pembrolizumab (pembro) for advanced biliary adenocarcinoma: results from the KEYNOTE-028 (KN028) and KEYNOTE-158 (KN158) basket studies. J Clin Oncol 37:4079–4079. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.4079
Cai X, Zhang H, Li T (2022) The role of SPP1 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 51:732–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2021.07.022
Darvin P, Toor SM, Sasidharan Nair V et al (2018) Immune checkpoint inhibitors: recent progress and potential biomarkers. Exp Mol Med 50:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0191-1
Degrendele HC, Kosfiszer M, Estess P et al (1997) CD44 activation and associated primary adhesion is inducible via T cell receptor stimulation. J Immunol 159:2549–2553
English NM, Lesley JF, Hyman R (1998) Site-specific de-N-glycosylation of CD44 can activate hyaluronan binding, and CD44 activation states show distinct threshold densities for hyaluronan binding. Cancer Res 58:3736–3742
Guo X, Zhang Y, Zheng L et al (2018) Global characterization of T cells in non-small-cell lung cancer by single-cell sequencing. Nat Med 24:978–985. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0045-3
Hao Y, Hao S, Andersen-Nissen E et al (2021) Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 184:3573-3587.e3529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.048
Hornburg M, Desbois M, Lu S et al (2021) Single-cell dissection of cellular components and interactions shaping the tumor immune phenotypes in ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell 39:928-944.e926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.004
Jiang P, Zhang Y, Ru B et al (2021) Systematic investigation of cytokine signaling activity at the tissue and single-cell levels. Nat Methods 18:1181–1191. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01274-5
Jin S, Guerrero-Juarez CF, Zhang L et al (2021) Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using cell chat. Nat Commun 12:1088. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21246-9
Katagiri YU, Sleeman J, Fujii H et al (1999) CD44 Variants but not CD44s cooperate with β1-containing Integrins to permit cells to bind to osteopontin independently of arginine-glycine-aspartic acid, thereby stimulating cell motility and chemotaxis1. Cancer Res 59:219–226
Kelley RK, Bridgewater J, Gores GJ et al (2020) Systemic therapies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol 72:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.009
Kim RD, Kim DW, Alese OB et al (2019) A phase II study of nivolumab in patients with advanced refractory biliary tract cancers (BTC). J Clin Oncol 37:4097–4097. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.4097
Klement JD, Paschall AV, Redd PS et al (2018) An osteopontin/CD44 immune checkpoint controls CD8+ T cell activation and tumor immune evasion. J Clin Invest 128:5549–5560. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci123360
Korsunsky I, Millard N, Fan J et al (2019) Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat Methods 16:1289–1296. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0619-0
Lauer S, Gresham D (2019) An evolving view of copy number variants. Curr Genet 65:1287–1295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-019-00980-0
Lee KE, Spata M, Bayne LJ et al (2016) Hif1a deletion reveals pro-neoplastic function of B cells in pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Discov 6:256–269. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-15-0822
Li C, Jiang P, Wei S et al (2020) Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: new mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol Cancer 19:116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01234-1
Liu S, Galat V, Galat Y et al (2021) NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy: from basic biology to clinical development. J Hematol Oncol 14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-01014-w
Llovet JM, Castet F, Heikenwalder M et al (2022) Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 19:151–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-021-00573-2
Ma L, Hernandez MO, Zhao Y et al (2019) Tumor cell biodiversity drives microenvironmental reprogramming in liver cancer. Cancer Cell 36:418-430.e416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2019.08.007
Martin-Serrano MA, Kepecs B, Torres-Martin M et al (2022) Novel microenvironment-based classification of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with therapeutic implications. Gut. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326514
Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y et al (2018) Maftools: efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res 28:1747–1756. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.239244.118
Mcginnis CS, Murrow LM and Gartner ZJ (2019) DoubletFinder: Doublet Detection in Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data Using Artificial Nearest Neighbors. Cell Syst 8:329–337.e324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2019.03.003
Nallasamy P, Nimmakayala RK, Karmakar S et al (2021) Pancreatic tumor microenvironment factor promotes cancer stemness via SPP1–CD44 axis. Gastroenterology 161:1998-2013.e1997. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.08.023
Nguyen CT, Caruso S, Maille P et al (2022) Immune profiling of combined hepatocellular- cholangiocarcinoma reveals distinct subtypes and activation of gene signatures predictive of response to immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 28:540–551. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-21-1219
Peery AF, Crockett SD, Murphy CC et al (2019) Burden and cost of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases in the United States: update 2018. Gastroenterology 156:254-272.e211. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.063
Peng J, Sun BF, Chen CY et al (2019) Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intra-tumoral heterogeneity and malignant progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Res 29:725–738. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0195-y
Puram SV, Tirosh I, Parikh AS et al (2017) Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of primary and metastatic tumor ecosystems in head and neck cancer. Cell 171:1611-1624.e1624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.044
Reinholt FP, Hultenby K, Oldberg A et al (1990) Osteopontin—a possible anchor of osteoclasts to bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4473–4475. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.12.4473
Song G, Shi Y, Meng L et al (2022) Single-cell transcriptomic analysis suggests two molecularly distinct subtypes of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Commun 13:1642. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29164-0
Syn NL, Teng MWL, Mok TSK et al (2017) De-novo and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint targeting. Lancet Oncol 18:e731–e741. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30607-1
Tanaka A, Sakaguchi S (2017) Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res 27:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.151
Therneau TM, Grambsch PM (2000) Modeling survival data: extending the Cox model. Springer, New York
Tirosh I, Izar B, Prakadan SM et al (2016) Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 352:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad0501
Trapnell C, Cacchiarelli D, Grimsby J et al (2014) The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat Biotechnol 32:381–386. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2859
Valle JW (2010) Advances in the treatment of metastatic or unresectable biliary tract cancer. Ann Oncol 21(7):vii345-348. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdq420
Wang KX, Denhardt DT (2008) Osteopontin: role in immune regulation and stress responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 19:333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.08.001
Wang S, Wu Q, Chen T et al (2022) Blocking CD47 promotes antitumour immunity through CD103(+) dendritic cell-NK cell axis in murine hepatocellular carcinoma model. J Hepatol 77:467–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2022.03.011
Weber GF, Ashkar S, Glimcher MJ et al (1996) Receptor-ligand interaction between CD44 and osteopontin (Eta-1). Science 271:509–512. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.271.5248.509
Wherry EJ, Kurachi M (2015) Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol 15:486–499. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3862
Wu S-Y, Fu T, Jiang Y-Z et al (2020) Natural killer cells in cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer 19:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01238-x
Wu F, Fan J, He Y et al (2021) Single-cell profiling of tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun 12:2540. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22801-0
Xiang X, Liu Z, Zhang C et al (2021) IDH mutation subgroup status associates with intratumor heterogeneity and the tumor microenvironment in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Adv Sci (Weinh) 8:e2101230. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202101230
Xue R, Chen L, Zhang C et al (2019) Genomic and transcriptomic profiling of combined hepatocellular and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma reveals distinct molecular subtypes. Cancer Cell 35:932-947.e938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2019.04.007
Yang L, He YT, Dong S et al (2022) Single-cell transcriptome analysis revealed a suppressive tumor immune microenvironment in EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2021-003534
Zhang Y, Du W, Chen Z et al (2017) Upregulation of PD-L1 by SPP1 mediates macrophage polarization and facilitates immune escape in lung adenocarcinoma. Exp Cell Res 359:449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.08.028
Zhang Q, He Y, Luo N et al (2019) Landscape and dynamics of single immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell 179(829–845):e820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.003
Zhang M, Yang H, Wan L et al (2020) Single-cell transcriptomic architecture and intercellular crosstalk of human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol 73:1118–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.039
Zheng C, Zheng L, Yoo J-K et al (2017a) Landscape of infiltrating T cells in liver cancer revealed by single-cell sequencing. Cell 169:1342-1356.e1316
Zheng GXY, Terry JM, Belgrader P et al (2017b) Massively parallel digital transcriptional profiling of single cells. Nat Commun 8:14049. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14049
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L et al (2019) Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 10:1523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge TCGA and GEO database for providing their platforms and contributors for uploading their meaningful datasets. We thank Dr. Xiaona Lin and Dr. Qihui Sun (both are from South China University of Technology) for generously sharing their experience and codes.
Funding
This work was supported by China postdoctoral science foundation (No. 2022M710838).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and MLC designed the outline and drafted the manuscript. MLC analyzed the data, performed the research, and designed the figures and tables. XNL and QHS offered professional suggestions to the manuscript. GDL and ZYY provided the language editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Published data is involved in this paper. The patients involved in these data have obtained ethical approval. Users can download relevant data for free for research and publish relevant articles. Our study is based on open-source data, so there are no ethical issues and no conflict of interest.
Consent to publish
All the authors consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, M., Liang, G., Yin, Z. et al. Immunosuppressive role of SPP1-CD44 in the tumor microenvironment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma assessed by single-cell RNA sequencing. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 5497–5512 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04498-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04498-w