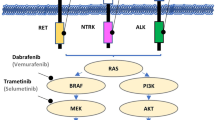
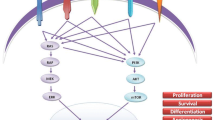
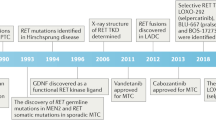
Abstract
The incidence of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), the major type of thyroid cancer, is increasing rapidly around the world, and its pathogenesis is still unclear. There is poor prognosis for PTC involved in rapidly progressive tumors and resistance to radioiodine therapy. Kinase gene fusions have been discovered to be present in a wide variety of malignant tumors, and an increasing number of novel types have been detected in PTC, especially progressive tumors. As a tumor-driving event, kinase fusions are constitutively activated or overexpress their kinase function, conferring oncogenic potential, and their frequency is second only to BRAFV600E mutation in PTC. Diverse forms of kinase fusions have been observed and are associated with specific pathological features of PTC (usually at an advanced stage), and clinical trials of therapeutic strategies targeting kinase gene fusions are feasible for radioiodine-resistant PTC. This review summarizes the roles of kinase gene fusions in PTC and the value of clinical therapy of targeting fusions in progressive or refractory PTC, and discusses the future perspectives and challenges related to kinase gene fusions in PTC patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors can confirm that all relevant data are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- PTC:
-
Papillary thyroid cancer
- DTC:
-
Differentiated thyroid cancer
- RAI:
-
Radioiodine
- RNA-seq:
-
Transcriptome level of sequencing
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- CC domain:
-
Coiled-coil domain
- LisH:
-
Lis1 homology
- SAM:
-
Sterile alpha motif
- S/TK:
-
Serine/threonine kinase
- RBD:
-
Ras-GTP binding domain
- FNAC:
-
Fine needle aspiration cytology
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- NIFTP:
-
Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- FGFR1-4:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptors1-4
- PDGFRα:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor α
- ORR:
-
Objective response rate
References
Albert C, Davis J, Federman N, Casanova M, Laetsch TW (2019) TRK fusion cancers in children: a clinical review and recommendations for screening. J Clin Oncol 37:513–524. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.18.00573
Aparicio-Gallego G, Blanco M, Figueroa A, Garcia-Campelo R, Valladares-Ayerbes M, Grande-Pulido E, Anton-Aparicio L (2011) New insights into molecular mechanisms of sunitinib-associated side effects. Mol Cancer Ther 10:2215–2223. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1124
Ardini E et al (2016) Entrectinib, a Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor with activity in multiple molecularly defined cancer indications. Mol Cancer Ther 15:628–639. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-15-0758
Bikas A et al (2016) Phase 2 clinical trial of sunitinib as adjunctive treatment in patients with advanced differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur J Endocrinol 174:373–380. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-15-0930
Bongarzone I et al (1993) Molecular characterization of a thyroid tumor-specific transforming sequence formed by the fusion of ret tyrosine kinase and the regulatory subunit RI alpha of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A. Mol Cell Biol 13:358–366. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.13.1.358
Bordeaux M et al (2000) The RET proto-oncogene induces apoptosis: a novel mechanism for Hirschsprung disease. EMBO J 19:4056–4063. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.15.4056
Borrello M et al (1994) The oncogenic versions of the Ret and Trk tyrosine kinases bind Shc and Grb2 adaptor proteins. Oncogene 9:1661–1668
Bossi D et al (2014) Functional characterization of a novel FGFR1OP-RET rearrangement in hematopoietic malignancies. Mol Oncol 8:221–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2013.11.004
Brose MS et al (2014) Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 384:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60421-9
Butti M, Bongarzone I, Ferraresi G, Mondellini P, Borrello M, Pierotti MJG (1995) A sequence analysis of the genomic regions involved in the rearrangements between TPM3 and NTRK1 genes producing TRK oncogenes in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Genomics 28:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1995.1100
Cabanillas ME et al (2015) A phase 2 trial of lenvatinib (E7080) in advanced, progressive, radioiodine-refractory, differentiated thyroid cancer: a clinical outcomes and biomarker assessment. Cancer 121:2749–2756. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29395
Cabanillas M et al (2017) Cabozantinib As salvage therapy for patients with tyrosine kinase inhibitor-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: results of a multicenter phase II international thyroid oncology group trial. J Clin Oncol 35:3315–3321. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2017.73.0226
Cantara S et al (2010) Impact of proto-oncogene mutation detection in cytological specimens from thyroid nodules improves the diagnostic accuracy of cytology. J Clin Endocr Metab 95:1365–1369. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-2103
Carlomagno F et al (2002) ZD6474, an orally available inhibitor of KDR tyrosine kinase activity, efficiently blocks oncogenic RET kinases. Cancer Res 62:7284–7290
Cell J et al (2014) Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell 159:676–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.050
Chu YH, Dias-Santagata D, Farahani AA, Boyraz B, Faquin WC, Nose V, Sadow PM (2020) Clinicopathologic and molecular characterization of NTRK-rearranged thyroid carcinoma (NRTC). Mod Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41379-020-0574-4
Ciampi R et al (2005) Oncogenic AKAP9-BRAF fusion is a novel mechanism of MAPK pathway activation in thyroid cancer. J Clin Invest 115:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI23237
Ciampi R, Giordano TJ, Wikenheiser-Brokamp K, Koenig RJ, Nikiforov YE (2007) HOOK3-RET: a novel type of RET/PTC rearrangement in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer 14:445–452. https://doi.org/10.1677/ERC-07-0039
Cocco E, Scaltriti M, Drilon A (2018) NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:731–747. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-018-0113-0
Cooper D et al (2009) Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 19:1167–1214. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2009.0110
Cordioli MI et al (2016) AGK-BRAF gene fusion is a recurrent event in sporadic pediatric thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Med 5:1535–1541. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.698
Corvi R, Berger N, Balczon R, Romeo GJO (2000) RET/PCM-1: a novel fusion gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncogene 19:4236–4242. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203772
Coulier F, Martin-Zanca D, Ernst M, Barbacid M (1989) Mechanism of activation of the human trk oncogene. Mol Cell Biol 9:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.9.1.15
Dai X, Theobard R, Cheng H, Xing M, Zhang J (2018) Fusion genes: a promising tool combating against cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1869:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.12.003
Demeure MJ, Aziz M, Rosenberg R, Gurley SD, Bussey KJ, Carpten JD (2014) Whole-genome sequencing of an aggressive BRAF wild-type papillary thyroid cancer identified EML4-ALK translocation as a therapeutic target. World J Surg 38:1296–1305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2485-3
Doebele RC et al (2020) Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol 21:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30691-6
Drilon A, Hu ZI, Lai GGY, Tan DSW (2017a) Targeting RET-driven cancers: lessons from evolving preclinical and clinical landscapes. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:151–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.175
Drilon A et al (2017b) Safety and antitumor activity of the multitargeted Pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor entrectinib: combined results from two phase i trials (ALKA-372–001 and STARTRK-1). Cancer Discov 7:400–409. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-16-1237
Drilon A et al (2018a) Efficacy of larotrectinib in TRK fusion-positive cancers in adults and children. N Engl J Med 378:731–739. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1714448
Drilon AE et al (2018b) A phase 1 study of LOXO-292, a potent and highly selective RET inhibitor, in patients with RET-altered cancers. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.102
DuBois SG et al (2018) The use of neoadjuvant larotrectinib in the management of children with locally advanced TRK fusion sarcomas. Cancer 124:4241–4247. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31701
DuBois SG et al (2019) A phase I study of LOXO-292, a highly selective RET inhibitor, in pediatric patients with RET-altered cancers. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.TPS10066
Ducray SP, Natarajan K, Garland GD, Turner SD, Egger G (2019) The transcriptional roles of ALK fusion proteins in tumorigenesis. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11081074
Efanov AA et al (2018) Investigation of the relationship between radiation dose and gene mutations and fusions in post-Chernobyl thyroid cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 110:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djx209
Fenton C, Lukes Y, Nicholson D, Dinauer C, Francis G, Tuttle RM (2000) The ret/PTC mutations are common in sporadic papillary thyroid carcinoma of children and young adults. J Clin Endocrinol Med 85:1170–1175. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.85.3.6472
Fugazzola L, Pierotti MA, Vigano E, Pacini F, Vorontsova TV, Bongarzone I (1996) Molecular and biochemical analysis of RET/PTC4, a novel oncogenic rearrangement between RET and ELE1 genes, in a post-Chernobyl papillary thyroid cancer. Oncogene 13:1093–1097
Fusco A et al (1987) A new oncogene in human thyroid papillary carcinomas and their lymph-nodal metastases. Nature 328:170–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/328170a0
Fusco A, Viglietto G, Santoro M (2005) A new mechanism of BRAF activation in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. J Clin Invest 115:20–23. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci23987
Fusco A, Viglietto G, Santoro M (2005) A new mechanism of BRAF activation in human thyro.id papillary carcinomas. J Clin Investig 115:20–23
Gatalica Z, Xiu J, Swensen J, Vranic S (2018) Molecular characterization of cancers with NTRK gene fusions. Mod Pathol 32:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41379-018-0118-3
Greco A, Pierotti M, Bongarzone I, Pagliardini S, Lanzi C, Della Porta GJO (1992) TRK-T1 is a novel oncogene formed by the fusion of TPR and TRK genes in human papillary thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene 7:237–242
Greco A et al (1995) The DNA rearrangement that generates the TRK-T3 oncogene involves a novel gene on chromosome 3 whose product has a potential coiled-coil domain. Mol Cell Biol 15:6118–6127. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.15.11.6118
Greco A, Miranda C, Pierotti MA (2010) Rearrangements of NTRK1 gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mol Cell Endocrinol 321:44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2009.10.009
Grieco M et al (1990) PTC is a novel rearranged form of the ret proto-oncogene and is frequently detected in vivo in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Cell 60:557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90659-3
Gupta-Abramson V et al (2008) Phase II trial of sorafenib in advanced thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:4714–4719. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.16.3279
Hamatani K et al (2008) RET/PTC rearrangements preferentially occurred in papillary thyroid cancer among atomic bomb survivors exposed to high radiation dose. Cancer Res 68:7176–7182. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-08-0293
Hamatani K, Eguchi H, Koyama K, Mukai M, Nakachi K, Kusunoki Y (2014) A novel RET rearrangement (ACBD5/RET) by pericentric inversion, inv(10)(p12.1;q11.2), in papillary thyroid cancer from an atomic bomb survivor exposed to high-dose radiation. Oncol Rep 32:1809–1814. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2014.3449
He H et al (2018) Identification of a recurrent LMO7-BRAF fusion in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 28:748–754. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2017.0258
Henderson YC, Ahn SH, Kang Y, Clayman GL (2008) Sorafenib potently inhibits papillary thyroid carcinomas harboring RET/PTC1 rearrangement. Clin Cancer Res 14:4908–4914. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1772
Ibrahimpasic T et al (2017) Genomic alterations in fatal forms of non-anaplastic thyroid cancer: identification of MED12 and RBM10 as novel thyroid cancer genes associated with tumor virulence. Clin Cancer Res 23:5970–5980. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1183
Ito T et al (1994) Activated RET oncogene in thyroid cancers of children from areas contaminated by Chernobyl accident. Lancet 344:259. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(94)93024-4
Iyama K et al (2017) Identification of three novel fusion oncogenes, SQSTM1-NTRK3, AFAP1L2-RET, and PPFIBP2-RET, in thyroid cancers of young patients in Fukushima. Thyroid 27:811–818. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0673
Kato S, Subbiah V, Marchlik E, Elkin SK, Carter JL Kurzrock R (2017) RET aberrations in diverse cancers: next-generation sequencing of 4,871 patients. Clin Cancer Res 23:1988–1997. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-16-1679
Kelly LM et al (2014) Identification of the transforming STRN-ALK fusion as a potential therapeutic target in the aggressive forms of thyroid cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:4233–4238. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1321937111
Khan MS et al (2020) RET/PTC gene rearrangements in thyroid carcinogenesis: assessment and clinico-pathological correlations. Pathol Oncol Res 26:507–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0540-3
Kim DW et al (2006) An orally administered multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, SU11248, is a novel potent inhibitor of thyroid oncogenic RET/papillary thyroid cancer kinases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4070–4076. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-2845
Kim H et al (2017) Oncogenic BRAF fusions in mucosal melanomas activate the MAPK pathway and are sensitive to MEK/PI3K inhibition or MEK/CDK4/6 inhibition. Oncogene 36:3334–3345. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.486
Klugbauer S, Rabes HJO (1999) The transcription coactivator HTIF1 and a related protein are fused to the RET receptor tyrosine kinase in childhood papillary thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene 18:4388–4393. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202824
Klugbauer S, Demidchik E, Lengfelder E, Rabes HM (1998) Detection of a novel type of RET rearrangement (PTC5) in thyroid carcinomas after Chernobyl and analysis of the involved RET-fused gene RFG5. Cancer Res 58:198–203
Klugbauer S, Jauch A, Lengfelder E, Demidchik E, Rabes HM (2000) A novel type of RET rearrangement (PTC8) in childhood papillary thyroid carcinomas and characterization of the involved gene (RFG8). Cancer Res 60:7028–7032
Knezevich S, McFadden D, Tao W, Lim J, Sorensen PHB (1998) A novel ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion in congenital fibrosarcoma. Nat Genet 18:184–187. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0298-184
Kohno T et al (2012) KIF5B-RET fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Med 18:375–377. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2644
Lan X et al (2020) Genomic landscape of metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma and novel biomarkers for predicting distant metastasis. Cancer Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14389
Lassen U (2020) Entrectinib for ROS1 fusion-positive NSCLC and NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours. Lancet Oncol 21:193–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30789-2
Lavoie H et al (2018) MEK drives BRAF activation through allosteric control of KSR proteins. Nature 554:549–553. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25478
Leboulleux S et al (2012) Vandetanib in locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 13:897–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(12)70335-2
Leeman-Neill R et al (2013) RET/PTC and PAX8/PPARγ chromosomal rearrangements in post-Chernobyl thyroid cancer and their association with iodine-131 radiation dose and other characteristics. Cancer 119:1792–1799. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.27893
Liang J et al (2018) Genetic landscape of papillary thyroid carcinoma in the Chinese population. J Pathol 244:215–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5005
Lim SM et al (2015) An open label, multicenter, phase II study of dovitinib in advanced thyroid cancer. Eur J Cancer 51:1588–1595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2015.05.020
Lim H, Devesa S, Sosa J, Check D, Kitahara CJJ (2017) Trends in thyroid cancer incidence and mortality in the United States. JAMA 1974–2013(317):1338–1348. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.2719
Lu H et al (2017a) Engineering and functional characterization of fusion genes identifies novel oncogenic drivers of cancer. Cancer Res 77:3502–3512. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2745
Lu Z, Zhang Y, Feng D, Sheng J, Yang W, Liu BJO (2017b) Targeted next generation sequencing identifies somatic mutations and gene fusions in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget 8:45784–45792. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17412
Mao WF et al (2012) The important roles of RET, VEGFR2 and the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in cancer treatment with sorafenib. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.76
Martin-Zanca D, Hughes SH, Barbacid M (1986) A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. Nature 319:743–748. https://doi.org/10.1038/319743a0
Martin-Zanca D, Oskam R, Mitra G, Copeland T, Barbacid M (1989) Molecular and biochemical characterization of the human trk proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol 9:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.9.1.24
Matsui J, Funahashi Y, Uenaka T, Watanabe T, Tsuruoka A (2008a) Multi-kinase inhibitor E7080 suppresses lymph node and lung metastases of human mammary breast tumor MDA-MB-231 via inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor (VEGF-R) 2 and VEGF-R3 kinase. Clin Cancer Res 14:5459–5465. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-07-5270
Matsui J et al (2008b) E7080, a novel inhibitor that targets multiple kinases, has potent antitumor activities against stem cell factor producing human small cell lung cancer H146, based on angiogenesis inhibition. Int J Cancer 122:664–671. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23131
Mehlen P, Bredesen DE (2011) Dependence receptors: from basic research to drug development. Sci Signal 4:mr2. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2001521
Mercalli E et al (2001) Key role of Shc signaling in the transforming pathway triggered by Ret/ptc2 oncoprotein. Oncogene 20:3475–3485. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204462
Miranda C, Greco A, Miele C, Pierotti M, Van Obberghen E (2001) IRS-1 and IRS-2 are recruited by TrkA receptor and oncogenic TRK-T1. J Cell Physiol 186:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4652(200101)186:1%3c35::Aid-jcp1003%3e3.0.Co;2-x
Möckelmann N, Betz C (2019) New aspects in thyroid cancer treatment: highlights of the 2019 ASCO Annual Meeting. HNO 67:925–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00106-019-00764-5
Nakata T et al (1999) Fusion of a novel gene, ELKS, to RET due to translocation t(10;12)(q11;p13) in a papillary thyroid carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 25:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-2264(199906)25:2%3c97::aid-gcc4%3e3.0.co;2-l
Nikiforov YE (2006) RET/PTC Rearrangement—a link between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and thyroid cancer...or not. J Clin Endoct Metab 91:2040–2042. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-0791
Nikiforov Y, Rowland J, Bove K, Monforte-Munoz H, Fagin JA (1997) Distinct pattern of ret oncogene rearrangements in morphological variants of radiation-induced and sporadic thyroid papillary carcinomas in children. Cancer Res 57:1690–1694
Nikiforov YE et al (2015) Impact of the multi-gene thyroseq next-generation sequencing assay on cancer diagnosis in thyroid nodules with atypia of undetermined significance/follicular lesion of undetermined significance cytology. Thyroid 25:1217–1223. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2015.0305
Okamoto K, Kodama K, Takase K, Sugi NH, Yamamoto Y, Iwata M, Tsuruoka A (2013) Antitumor activities of the targeted multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib (E7080) against RET gene fusion-driven tumor models. Cancer Lett 340:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.07.007
Panebianco F et al (2019) Characterization of thyroid cancer driven by known and novel ALK fusions. Endocr Relat Cancer 26:803–814. https://doi.org/10.1530/erc-19-0325
Pfeifer A et al (2019) Novel TG-FGFR1 and TRIM33-NTRK1 transcript fusions in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 58:558–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22737
Prasad ML et al (2016) NTRK fusion oncogenes in pediatric papillary thyroid carcinoma in northeast United States. Cancer 122:1097–1107. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29887
Ricarte-Filho JC et al (2013) Identification of kinase fusion oncogenes in post-Chernobyl radiation-induced thyroid cancers. J Clin Invest 123:4935–4944. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI69766
Ritterhouse LL, Wirth LJ, Randolph GW, Sadow PM, Ross DS, Liddy W, Lennerz JK (2016) ROS1 Rearrangement in thyroid cancer. Thyroid 26:794–797. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0101
Romei C, Elisei R (2012) RET/PTC translocations and clinico-pathological features in human papillary thyroid carcinoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 3:54. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2012.00054
Romei C et al (2012) Modifications in the papillary thyroid cancer gene profile over the last 15 years. J Clin Endrocrinol 97:E1758–1765. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-1269
Romei C, Ciampi R, Elisei R (2016) A comprehensive overview of the role of the RET proto-oncogene in thyroid carcinoma. Nat Rev Endocr 12:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.11
Ross JS et al (2016) The distribution ofBRAFgene fusions in solid tumors and response to targeted therapy. Int J Cancer 138:881–890. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29825
Saenko V et al (2003) Novel tumorigenic rearrangement, Δrfp/ret, in a papillary thyroid carcinoma from externally irradiated patient. Mut Res 527:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0027-5107(03)00056-3
Saito M, Ishigame T, Tsuta K, Kumamoto K, Imai T, Kohno TJC (2014) A mouse model of KIF5B-RET fusion-dependent lung tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis 35:2452–2456. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgu158
Salassidis K, Bruch J, Zitzelsberger H, Lengfelder E, Kellerer A, Bauchinger M (2000) Translocation t(10;14)(q11.2:q22.1) fusing the kinetin to the RET gene creates a novel rearranged form (PTC8) of the RET proto-oncogene in radiation-induced childhood papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Res 60:2786–2789
Santoro M, Carlomagno F (2013) Central role of RET in thyroid cancer. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 5:a009233. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009233
Santoro M et al (1994) Molecular characterization of RET/PTC3; a novel rearranged version of the RETproto-oncogene in a human thyroid papillary carcinoma. Oncogene 9:509–516
Santoro M et al (1996) Development of thyroid papillary carcinomas secondary to tissue-specific expression of the RET/PTC1 oncogene in transgenic mice. Oncogene 12:1821–1826
Santoro M, Melillo R, Fusco A (2006) RET/PTC activation in papillary thyroid carcinoma: European Journal of Endocrinology Prize Lecture. Eur J Endocrinol 155:645–653. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.1.02289
Schlumberger M et al (2015) Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 372:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1406470
Schram A, Chang M, Jonsson P, Drilon A (2017) Fusions in solid tumours: diagnostic strategies, targeted therapy, and acquired resistance. Nat Rev Oncol 14:735–748. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.127
Sciuto R, Romano L, Rea S, Marandino F, Sperduti I, Maini CL (2009) Natural history and clinical outcome of differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 1503 patients treated at a single institution. Ann Oncol 20:1728–1735. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp050
Shaw AT, Hsu PP, Awad MM, Engelman JA (2013) Tyrosine kinase gene rearrangements in epithelial malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 13:772–787. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3612
Sherman SJL (2003) Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet 361:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)12488-9
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics. CA-Cancer J Clin 69:7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Sisdelli L et al (2019) AGK-BRAF is associated with distant metastasis and younger age in pediatric papillary thyroid carcinoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 66:e27707. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.27707
Soda M et al (2007) Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 448:561–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05945
Staubitz JI et al (2019a) ANKRD26-RET—A novel gene fusion involving RET in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Genet 238:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cancergen.2019.07.002
Staubitz JI et al (2019b) Novel rearrangements involving the RET gene in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Genet 230:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cancergen.2018.11.002
Stransky N, Cerami E, Schalm S, Kim J, Lengauer C (2014) The landscape of kinase fusions in cancer. Nat Commun 5:4846. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5846
Subbiah V et al (2018) Selective RET kinase inhibition for patients with RET-altered cancers. Ann Oncol 29:1869–1876. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy137
Subbiah V et al (2018) Precision targeted therapy with BLU-667 for RET-driven cancers. Cancer Discov 8:836–849. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0338
Taylor MH et al (2019) Activity and tolerability of BLU-667, a highly potent and selective RET inhibitor, in patients with advanced RET-altered thyroid cancers. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.6018
Thomas G et al (1999) High prevalence of RET/PTC rearrangements in Ukrainian and Belarussian post-Chernobyl thyroid papillary carcinomas: a strong correlation between RET/PTC3 and the solid-follicular variant. J Clin Endocr 84:4232–4238. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.11.6129
Turner JA et al (2019) BRAF fusions identified in melanomas have variable treatment responses and phenotypes. Oncogene 38:1296–1308. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0514-7
van Velsen E, Stegenga M, van Kemenade F, Kam B, van Ginhoven T, Visser W, Peeters RP (2019) Evaluating the 2015 American thyroid association risk stratification system in high-risk papillary and follicular thyroid cancer patients. Thyroid 29:1073–1079. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2019.0053
Viola D et al (2017) KIF5B/RET rearrangement in a carcinoma of the thyroid gland: a case report of a fatal disease. J Clin Endocr Metab 102:3091–3096. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-00304
Wedge SR et al (2002) ZD6474 inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor signaling, angiogenesis, and tumor growth following oral administration. Cancer Res 62:4645–4655
Wells SA et al (2012) Vandetanib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer: a randomized, double-blind phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 30:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2011.35.5040
White C et al (2020) Is less more? A microsimulation model comparing cost-effectiveness of the revised american thyroid association’s 2015 to guidelines for the management of patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Ann Surg 271:765–773. https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000003074
Wilhelm SM et al (2004) BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:7099–7109. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-04-1443
Wirth L et al (2019) Registrational results of LOXO-292 in patients with RET-altered thyroid cancers. Ann Oncol 30:933–933
Wirtschafter A et al (1997) Expression of the RET/PTC fusion gene as a marker for papillary carcinoma in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Laryngoscope 107:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199701000-00019
Wolf J (2020) Registrational results of Libretto-001: a phase 1/2 trial of LOXO-292 in patients with RET-fusion-positive lung cancer. Oncol Res Treat 43:117–117
Xi H, Wu X, Wei B, Chen L (2012) Eph receptors and ephrins as targets for cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med 16:2894–2909. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01612.x
Xing M (2013) Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 13:184–199. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3431
Yip L et al (2015) Tumor genotype determines phenotype and disease-related outcomes in thyroid cancer: a study of 1510 patients. Ann Surg 262:519–525. https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000001420
Yoo SK et al (2016) Comprehensive analysis of the transcriptional and mutational landscape of follicular and papillary thyroid cancers. PLoS Genet 12:e1006239. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006239
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81974423, 81902729), the Key Research and Development Programme of Hunan Province (2019SK2031), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (2020JJ5904) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M672517).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, P.H. and S.C.; Resources, M.L., P.C., H.H., D.O., R.K., and H.T.; Data Curation, P.C., H.H., D.O., R.K., and H.T.; Writing, M.L. and P.H.; Supervision, P.H. and S.C.; Funding Acquisition, P.H. and S.C.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Chen, P., Hu, HY. et al. Kinase gene fusions: roles and therapeutic value in progressive and refractory papillary thyroid cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 323–337 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03491-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03491-5