Abstract
Purpose
RAS mutational status in colorectal cancer (CRC) represents a predictive biomarker of response to anti-EGFR therapy, but to date it cannot be considered an appropriate biomarker of response to anti-VEGF therapy. To elucidate the function of K-Ras in promoting angiogenesis, the effect of conditioned media from KRAS mutated and wild type colon cancer cell lines on HUVECs tubule formation ability and the correspondent production of pro-angiogenic factors have been evaluated by a specific ELISA assay.
Methods
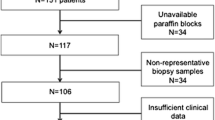
Ras-activated signaling pathways were compared by western blot analysis and RTq-PCR. In addition, VEGF, IL-8, bFGF and HIF-1α expression was determined in K-RAS silenced cells. Furthermore, we conducted an observational study in a cohort of RAS mutated metastatic CRC patients, treated with first-line bevacizumab-based regimens, evaluating VEGF-A and IL-8 plasma levels at baseline, and during treatment.
Results
K-RAS promotes VEGF production by cancer cell lines. At the transcriptional level, this is reflected to a K-RAS dependent HIF-1α over-expression. Moreover, the HIF-1α, VEGF and FGF expression inhibition in KRAS knocked cells confirmed these results. Within the clinical part, no statistically significant correlation has been found between progression-free survival (PFS) and VEGF-A/IL-8 levels, but we cannot exclude that these biomarkers could be further investigated as predictive or prognostic biomarkers in this setting.
Conclusion
Our study confirmed the direct involvement of K-Ras in promoting angiogenesis into colon cancer cell lines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abajo A et al (2012) Identification of predictive circulating biomarkers of bevacizumab-containing regimen efficacy in pre-treated metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer 107:287–290. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.242
Alamo P et al (2015) Higher metastatic efficiency of KRas G12V than KRas G13D in a colorectal cancer model. FASEB J 29:464–476. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-262303
Angelucci A, Delle Monache S, Cortellini A, Di Padova M, Ficorella C (2018) "Vessels in the Storm": searching for prognostic and predictive angiogenic factors in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010299
Aoyagi Y, Iinuma H, Horiuchi A, Shimada R, Watanabe T (2010) Association of plasma VEGF-A, soluble VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 levels and clinical response and survival in advanced colorectal cancer patients receiving bevacizumab with modified FOLFOX6. Oncol Lett 1:253–259. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol_00000045
Bernaards C et al (2010) Circulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a biomarker for bevacizumab-based therapy in metastatic colorectal, non-small cell lung, and renal cell cancers: analysis of phase III studies. DOI, J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.28.15_suppl.10519
Bruns AF, Bao L, Walker JH, Ponnambalam S (2009) VEGF-A-stimulated signalling in endothelial cells via a dual receptor tyrosine kinase system is dependent on coordinated trafficking and proteolysis. Biochem Soc Trans 37:1193–1197. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0371193
Catanzaro JM et al (2014) Oncogenic Ras induces inflammatory cytokine production by upregulating the squamous cell carcinoma antigens SerpinB3/B4. Nat Commun 5:3729. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4729
Cidon EU, Alonso P, Masters B (2016) Markers of response to antiangiogenic therapies in colorectal cancer: where are we now and what should be next? Clin Med Insights Oncol 10:41–55. https://doi.org/10.4137/CMO.S34542
Di Salvatore M et al (2017) IL-8 and eNOS polymorphisms predict bevacizumab-based first line treatment outcomes in RAS mutant metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget 8:16887–16898. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14810
Eisenhauer EA et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Engin H, Ustundag Y, Tekin IO, Gokmen A, Ertop S, Ilikhan SU (2012) Plasma concentrations of angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2 and Tie-2 in colon cancer. Eur Cytokine Netw 23:68–71. https://doi.org/10.1684/ecn.2012.0308
Figueras A, Arbos MA, Quiles MT, Vinals F, Germa JR, Capella G (2013) The impact of KRAS mutations on VEGF-A production and tumour vascular network. BMC Cancer 13:125. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-125
Fleming JB, Shen GL, Holloway SE, Davis M, Brekken RA (2005) Molecular consequences of silencing mutant K-ras in pancreatic cancer cells: justification for K-ras-directed therapy. Mol Cancer Res: MCR 3:413–423. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-04-0206
Fukuda R, Hirota K, Fan F, Jung YD, Ellis LM, Semenza GL (2002) Insulin-like growth factor 1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression, which is dependent on MAP kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem 277:38205–38211. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M203781200
Ge H, Luo H (2018) Overview of advances in vasculogenic mimicry—a potential target for tumor therapy. Cancer Manag Res 10:2429–2437. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S164675
Gong J, Zhou S, Yang S (2019) Vanillic acid suppresses HIF-1alpha expression via inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1 and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in human colon cancer HCT116 cells. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030465
Hara M, Nagasaki T, Shiga K, Takahashi H, Takeyama H (2017) High serum levels of interleukin-6 in patients with advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer: the effect on the outcome and the response to chemotherapy plus bevacizumab. Surg Today 47:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-016-1404-7
Harada Y, Egi Y, Honda Y, Shirota T, Hayashi T (2001) Multiple myeloma with Sweet disease developing from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and Sjogren syndrome] [Rinsho ketsueki]. Jpn J Clin Hematol 42:1176–1180
Hegde PS et al (2013) Predictive impact of circulating vascular endothelial growth factor in four phase III trials evaluating bevacizumab Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for. Cancer Res 19:929–937. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2535
Honda T, Yamamoto I, Inagawa H (2013) Angiogenesis-, metastasis- and signaling pathway-related factor dynamics in human colon cancer cells following interaction with monocytes. Anticancer Res 33:2895–2900
Ihle NT et al (2012) Effect of KRAS oncogene substitutions on protein behavior: implications for signaling and clinical outcome. J Natl Cancer Inst 104:228–239. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djr523
Jiang BH, Jiang G, Zheng JZ, Lu Z, Hunter T, Vogt PK (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell Growth Diff 12:363–369
Khan S et al (2014) Differential gene expression of chemokines in KRAS and BRAF mutated colorectal cell lines: role of cytokines. World J Gastroenterol 20:2979–2994. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.2979
Kikuchi H, Pino MS, Zeng M, Shirasawa S, Chung DC (2009) Oncogenic KRAS and BRAF differentially regulate hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in colon cancer. Cancer Res 69:8499–8506. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2213
Kopetz S et al (2010) Phase II trial of infusional fluorouracil, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer: efficacy and circulating angiogenic biomarkers associated with therapeutic resistance. J Clin Oncol 28:453–459. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.24.8252
Krajnovic M et al (2016) Locally advanced rectal cancers with simultaneous occurrence of KRAS mutation and high VEGF expression show invasive characteristics. Pathol Res pract 212:598–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2016.02.018
Lambrechts D, Lenz HJ, de Haas S, Carmeliet P, Scherer SJ (2013) Markers of response for the antiangiogenic agent bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 31:1219–1230. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.46.2762
Li L et al (2008) Local RAS and inflammatory factors are involved in cardiovascular hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacol Res 58:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2008.06.009
Liotta LA (2001) An attractive force in metastasis. Nature 410:24–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/35065180
Low HB, Zhang Y (2016) Regulatory roles of MAPK phosphatases in cancer. Immune Netw 16:85–98. https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2016.16.2.85
Luppi F, Longo AM, de Boer WI, Rabe KF, Hiemstra PS (2007) Interleukin-8 stimulates cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer through epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Lung Cancer 56:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.11.014
Marisi G et al (2018) IL-8 and thrombospondin-1 as prognostic markers in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer receiving bevacizumab. Cancer Manage Res 10:5659–5666. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S181570
Masoud GN, Li W (2015) HIF-1alpha pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta pharm Sin B 5:378–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2015.05.007
Mousa L, Salem ME, Mikhail S (2015) Biomarkers of angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Biomark Cancer 7:13–19. https://doi.org/10.4137/BIC.S25250
Nastase A et al (2014) Expression of interleukine-8 as an independent prognostic factor for sporadic colon cancer dissemination. J Med Life 7:215–219
Petrova V, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Melino G, Amelio I (2018) The hypoxic tumour microenvironment. Oncogenesis 7:10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-017-0011-9
Schimanski CC et al (2010) K-ras mutation status correlates with the expression of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and PDGFRalpha in colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 25:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-009-0843-7
Setrerrahmane S, Xu H (2017) Tumor-related interleukins: old validated targets for new anti-cancer drug development. Mol Cancer 16:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0721-9
Sparmann A, Bar-Sagi D (2004) Ras-induced interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 6:447–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.028
Stephens RM, Yi M, Kessing B, Nissley DV, McCormick F (2017) Tumor RAS gene expression levels are influenced by the mutational status of RAS genes and both upstream and downstream RAS pathway genes. Cancer Inform 16:1176935117711944. https://doi.org/10.1177/1176935117711944
Sunaga N et al (2012) Oncogenic KRAS-induced interleukin-8 overexpression promotes cell growth and migration and contributes to aggressive phenotypes of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 130:1733–1744. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.26164
Tang N et al (2004) Loss of HIF-1alpha in endothelial cells disrupts a hypoxia-driven VEGF autocrine loop necessary for tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 6:485–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.026
Van Cutsem E et al (2016) ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for. Med Oncol 27:1386–1422. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw235
Vauthey JN et al (2013) RAS mutation status predicts survival and patterns of recurrence in patients undergoing hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg 258:619–626. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182a5025a (Discussion 626–617)
Wang Y, Lei F, Rong W, Zeng Q, Sun W (2015) Positive feedback between oncogenic KRAS and HIF-1alpha confers drug resistance in colorectal cancer. OncoTarg Ther 8:1229–1237. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S80017
Willaert W, Van Der Speeten K, Liberale G, Ceelen W (2015) BEV-IP: perioperative chemotherapy with bevacizumab in patients undergoing cytoreduction and intraperitoneal chemoperfusion for colorectal carcinomatosis. BMC Cancer 15:980. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1954-x
Wu Y, Jin M, Xu H, Shimin Z, He S, Wang L, Zhang Y (2010) Clinicopathologic significance of HIF-1alpha, CXCR4, and VEGF expression in colon cancer. Clin Dev Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/537531
Xu L, Pathak PS, Fukumura D (2004) Hypoxia-induced activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase signaling pathways contributes to expression of interleukin 8 in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 10:701–707
Yoshikawa Y, Takano O, Kato I, Takahashi Y, Shima F, Kataoka T (2017) Ras inhibitors display an anti-metastatic effect by downregulation of lysyl oxidase through inhibition of the Ras-PI3K-Akt-HIF-1alpha pathway. Cancer Lett 410:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.017
Zeng M, Kikuchi H, Pino MS, Chung DC (2010) Hypoxia activates the K-ras proto-oncogene to stimulate angiogenesis and inhibit apoptosis in colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 5:e10966. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010966
Zhang X, Gaspard JP, Chung DC (2001) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by the Wnt and K-ras pathways in colonic neoplasia. Cancer Res 61:6050–6054
Zhu Y, Denhardt DT, Cao H, Sutphin PD, Koong AC, Giaccia AJ, Le QT (2005) Hypoxia upregulates osteopontin expression in NIH-3T3 cells via a Ras-activated enhancer. Oncogene 24:6555–6563. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208800
Zimmitti G et al (2015) RAS mutations predict radiologic and pathologic response in patients treated with chemotherapy before resection of colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol 22:834–842. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-4042-6
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the MIUR ALCLI “Giorgio e Silvia” no profit Association for the financial support.
Funding
Roche contribution; ALCLI “Giorgio e Silvia” no profit Association; RFO MIUR Ex-60%; FFABR 2017 MIUR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SDM, CF and AA organized and concept the manuscript; AC and AP have been involved in the enrolling of patients and angiogenic factors plasma levels analysis; SDM and FP have conducted in vitro experiments and analyzed and interpreted data; SDM, AP and AC wrote the manuscript; VM, SM, CM and MED supervisioned and proofread the manuscript; SDM, VM and CF provided financial support. All the authors have contributed in its realization and have approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Alessio Cortellini received grants as speaker by MSD and Astra-Zeneca, grant consultancies by MSD, BMS, Roche, Novartis, Istituto Gentili, Astellas and Ipsen. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All patients provided written, informed consent to the proposed treatment option. The procedures followed were in accordance with the precepts of Good Clinical Practice. Being an observational study with no intervention a notification was sent to the local responsible committee on human experimentation (Comitato Etico per le province di L’Aquila e Teramo) (normative ref: Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana n. 76 of 31-3-2008).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2020_3186_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary file 1 Inhibition exerted by Bevacizumab on tube formation ability of CM derived from colon cancer cell lines. a representative images of tube formation ability of HUVEC treated with Conditioned Media (CM) from K-RAS mutant cell lines in the presence or in the absence of Bevacizumab (0.1 mg/ml). b Histograms show that HUVECs tube formation stimulated with CM of SW48, SW480 and LS174T was significantly inhibited in the presence of Bevacizumab as determined by quantitative analysis of branching index. *p < 0.05 The inhibitory effect of Bevacizumab on HUVEC treated with CM of SW480 was significantly higher than in HUVEC treated with CM of LS174T. #p < 0.05 (JPG 55 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delle Monache, S., Cortellini, A., Parisi, A. et al. Expression of pro-angiogenic factors as potential biomarkers in experimental models of colon cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 1427–1440 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03186-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03186-x