Abstract
Purpose
The aim of the present study was to evaluate CD105 tissue marker in the bone marrow (BM) of multiple myeloma (MM) patients. CD105 was evaluated using immunohistochemical method. An effort was made to correlate this marker with BM microvascular density (MVD) along with other known markers of angiogenesis in order to evaluate its clinical significance.
Methods
BM MVD was estimated by CD31. CD105 in BM was estimated by immunohistochemical method in 54 newly diagnosed patients with MM. Circulating levels of known angiogenic factors such as basic fibroblast growth factor (b-FGF) and soluble CD105 (sCD105) were measured by ELISA in the same group of patients. All these factors were also measured in 20 age- and sex-matched healthy controls.
Results
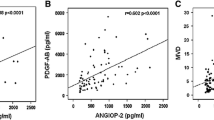
We found that CD105 MVD, along with the expected CD31 MVD, and serum levels of sCD105 and bFGF were increased, also in parallel with disease stage, and all were decreased after effective treatment. Moreover, CD105 MVD correlated with all the aforementioned markers of angiogenesis.
Conclusions
Our results indicated that CD105 MVD is following the behavior of CD31 MVD in MM, suggesting being a valid marker of BM neoangiogenesis in MM. Its prognostic impact remains to be proven.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrakis MG, Tsirakis G (2014) Circulating levels of soluble angiogenic factors in multiple myeloma: correlation with parameters of disease activity and prognosis. Curr Angiogenesis. doi:10.2174/22115528113026660012
Alexandrakis MG, Passam FH, Dambaki C, Pappa CA, Stathopoulos EN (2004a) The relation between bone marrow angiogenesis and the proliferation index Ki-67 in multiple myeloma. J Clin Pathol 57(8):856–860
Alexandrakis MG, Passam FJ, Ganotakis E, Dafnis E, Dambaki C, Konsolas J et al (2004b) Bone marrow microvascular density and angiogenic growth factors in multiple myeloma. Clin Chem Lab Med 42(10):1122–1126
Alexandrakis MG, Passam FH, Pappa CA, Dambaki C, Sfakiotaki G, Alegakis AK et al (2004c) Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in multiple myeloma: its relationship to bone marrow microvessel density and other factors of disease activity. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 17(1):49–56
Bernabeu C, Lopez-Novoa JM, Quintanilla M (2009) The emerging role of TGF-beta superfamily coreceptors in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792(10):954–973
Bhatti SS, Kumar L, Dinda AK, Dawar R (2006) Prognostic value of bone marrow angiogenesis in multiple myeloma: use of light microscopy as well as computerized image analyzer in the assessment of microvessel density and total vascular area in multiple myeloma and its correlation with various clinical, histological, and laboratory parameters. Am J Hematol 81:649–656
Duff SE, Li C, Garland JM, Kumar S (2003) CD105 is important for angiogenesis: evidence and potential applications. FASEB J 17:984–992
Hatjiharissi E, Terpos E, Papaioannou M, Hatjileontis C, Kaloutsi V, Galaktidou G et al (2004) The combination of intermediate doses of thalidomide and dexamethasone reduces bone marrow micro-vessel density but not serum levels of angiogenic cytokines in patients with refractory/relapsed multiple myeloma. Hematol Oncol 22:159–168
Henry LA, Johnson DA, Sarrio D, Lee S, Quinlan PR, Crook T et al (2011) Endoglin expression in breast tumor cells suppresses invasion and metastasis and correlates with improved clinical outcome. Oncogene 30:1046–1058
Hillengass J, Wasser K, Delorme S, Kiessling F, Zechmann C, Benner A, Kauczor HU, Ho AD, Goldschmidt H, Moehler TM (2007) Lumbar bone marrow microcirculation measurements from dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging is a predictor of event-free survival in progressive multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 13:475–481
Kumar S, Fonseca R, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Lust JA, Witzig TE et al (2002) Bone marrow angiogenesis in multiple myeloma: effect of therapy. Br J Haematol 119:665–671
Kumar S, Gertz MA, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Wellik LA, Fonseca R (2004a) Prognostic value of bone marrow angiogenesis in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing high-dose therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant 34:235–239
Kumar S, Witzig TE, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Wellik LE, Fonseca R et al (2004b) Effect of thalidomide therapy on bone marrow angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 18:624–627
Lakshman M, Huang X, Ananthanarayanan V, Jovanovic B, Liu Y, Craft CS (2011) Endoglin suppresses human prostate cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 28:39–53
Menzel T, Rahman Z, Calleja E, White K, Wilson EL, Wieder R et al (1996) Elevated intracellular level of basic fibroblast growth factor correlates with stage of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is associated with resistance to fludarabine. Blood 87:1056–1063
Moulopoulos LA, Dimopoulos MA, Christoulas D, Kastritis E, Anagnostou D, Koureas A et al (2010) Diffuse MRI marrow pattern correlates with increased angiogenesis, advanced disease features and poor prognosis in newly diagnosed myeloma treated with novel agents. Leukemia 24:1206–1212
Munshi NC, Wilson C (2001) Increased bone marrow microvessel density in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma carries a poor prognosis. Semin Oncol 28:565–569
Nassiri F, Cusimano MD, Scheithauer BW, Rotondo F, Fazio A, Yousef GM et al (2011) Endoglin (CD105): a review of its role in angiogenesis and tumor diagnosis, progression and therapy. Anticancer Res 31:2283–2290
Otjacques E, Binsfeld M, Noel A, Beguin Y, Cataldo D, Caers J (2011) Biological aspects of angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Int J Hematol 94:505–518
Pappa C, Alexandrakis M, Boula A, Psarakis F, Kolovou A, Bantouna V et al (2013) Emerging roles of endoglin/CD105 and angiogenic cytokines for disease development and progression in multiple myeloma patients. Hematol Oncol. doi:10.1002/hon.2044
Pruneri G, Ponzoni M, Ferreri AJ, Decarli N, Tresoldi M, Raggi F et al (2002) Microvessel density, a surrogate marker of angiogenesis, is significantly related to survival in multiple myeloma patients. Br J Haematol 118:817–820
Rajkumar SV, Mesa RA, Fonseca R, Schroeder G, Plevak MF, Dispenzieri A et al (2002) Bone marrow angiogenesis in 400 patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, multiple myeloma, and primary amyloidosis. Clin Cancer Res 8:2210–2216
Santibanez JF, Letamendia A, Perez-Barriocanal F, Silvestri C, Saura M, Vary CP et al (2007) Endoglin increases eNOS expression by modulating Smad2 protein levels and Smad2-dependent TGF-beta signaling. J Cell Physiol 210:456–468
Sezer O, Niemöller K, Jakob C, Zavrski I, Heider U, Eucker J et al (2001a) Relationship between bone marrow angiogenesis and plasma cell infiltration and serum beta2-microglobulin levels in patients with multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol 80:598–601
Sezer O, Niemöller K, Kaufmann O, Eucker J, Jakob C, Zavrski I et al (2001b) Decrease of bone marrow angiogenesis in myeloma patients achieving a remission after chemotherapy. Eur J Haematol 66:238–244
Tsirakis G, Pappa CA, Kanellou P, Stratinaki MA, Xekalou A, Psarakis FE et al (2012a) Role of platelet-derived growth factor-AB in tumour growth and angiogenesis in relation with other angiogenic cytokines in multiple myeloma. Hematol Oncol 30:131–136
Tsirakis G, Pappa CA, Spanoudakis M, Chochlakis D, Alegakis A, Psarakis FE et al (2012b) Clinical significance of sCD105 in angiogenesis and disease activity in multiple myeloma. Eur J Intern Med 23:368–373
Vacca A, Ribatti D, Roncali L, Ranieri G, Serio G, Silvestris F et al (1994) marrow angiogenesis and progression in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 87:503–508
Wong VC, Chan PL, Bernabeu C, Law S, Wang LD, Li JL et al (2008) Identification of an invasion and tumor-suppressing gene, Endoglin (ENG), silenced by both epigenetic inactivation and allelic loss in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 123:2816–2823
Zheng W, Liu D, Fan X, Powers L, Goswami M, Hu Y et al (2013) Potential therapeutic biomarkers in plasma cell myeloma: a flow cytometry study. Cytom B Clin Cytom 84:222–228
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The study was performed according to the guidelines of the local ethics committee. Informed consent for the study was obtained from all subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandrakis, M.G., Neonakis, I.K., Pappa, C.A. et al. Immunohistochemical expression of endoglin offers a reliable estimation of bone marrow neoangiogenesis in multiple myeloma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 1503–1509 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1952-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1952-z