Abstract
Purpose
This study investigated the antineoplastic effect of the membrane active alkylphosphocholine erufosine in breast carcinoma models in vitro and in vivo and determined its influence on the PI3K/Akt and Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathways.
Methods
The antiproliferative effect of erufosine in vitro was determined by the MTT dye reduction assay, and the antineoplastic efficacy on tumor growth was investigated by relating the mean total tumor volumes of treated and control rats. Immunoblot analysis was used for detecting changes in the expression level of the signal molecules p-PI3K (p-p85), p-Akt at Thr 308 and p-cRaf.
Results
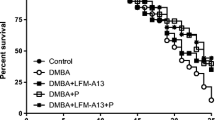
Based on their IC50 (40 μM, respectively), the breast carcinoma cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB 231, which are estrogen receptor positive and negative, respectively, were equally sensitive to erufosine. In addition, erufosine caused dose-dependent decreases in the phosphorylation of PI3K (p85), Akt (PKB) at Thr 308 and cRaf in both cell lines. Moreover, administration of erufosine to rats bearing autochthonous methylnitrosourea-induced rat mammary carcinomas caused a significant dose-related tumor remission by more than 85 % (p < 0.05), which was well tolerated, as evidenced by a body weight loss of maximally 7 % and reduced tumor-related mortality (2 of 35 instead of 6 of 18 controls, p < 0.002).
Conclusions
The results clearly indicate that erufosine possesses high antineoplastic activity not only in human breast cancer cell lines in vitro but also in rat mammary carcinoma in vivo. In addition, it can be derived that the mechanism of action of erufosine involves influence on both, PI3K/Akt and Ras/Raf/MAPK signaling pathways.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagley RG, Kurtzberg L, Rouleau C, Yao M, Teicher BA (2011) Erufosine, an alkylphosphocholine, with differential toxicity to human cancer cells and bone marrow cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68(6):1537–1546. doi:10.1007/s00280-011-1658-0
Basu A (2008) Molecular targets of breast cancer: AKTing in concert. Breast Cancer (Auckl) 2:11–16
Bauerle T, Peterschmitt J, Hilbig H, Kiessling F, Armbruster FP, Berger MR (2006) Treatment of bone metastasis induced by MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells with an antibody against bone sialoprotein. Int J Oncol 28(3):573–583
Bendell JC, Nemunaitis J, Vukelja SJ, Hagenstad C, Campos LT, Hermann RC, Sportelli P, Gardner L, Richards DA (2011) Randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial of perifosine plus capecitabine as second- or third-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(33):4394–4400. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.36.1980
Berger M, Habs M, Schmahl D (1983) Noncarcinogenic chemotherapy with a combination of vincristine, methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil (VMF) in rats. Int J Cancer 32(2):231–236
Berger MR, Muschiol C, Schmahl D, Eibl HJ (1987) New cytostatics with experimentally different toxic profiles. Cancer Treat Rev 14(3–4):307–317
Berger MR, Yanapirut P, Reinhardt M, Klenner T, Scherf HR, Schmeiser HH, Eibl H (1992) Antitumor activity of alkylphosphocholines and analogues in methylnitrosourea-induced rat mammary carcinomas. Prog Exp Tumor Res 34:98–115
Berger MR, Betsch B, Gebelein M, Amtmann E, Heyl P, Scherf HR (1993) Hexadecylphosphocholine differs from conventional cytostatic agents. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 119(9):541–548
Berger MR, Sobottka S, Konstantinov SM, Eibl H (1998) Erucylphosphocholine is the prototype of i.v. injectable alkylphosphocholines. Drugs Today 34:73–81
Bos JL (1989) Ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res 49(17):4682–4689
Calabretta B, Perrotti D (2004) The biology of CML blast crisis. Blood 103(11):4010–4022. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-12-4111
Eibl H, Engel J (1992) Synthesis of hexadecylphosphocholine (miltefosine). Prog Exp Tumor Res 34:1–5
Engelman JA (2009) Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):550–562. doi:10.1038/nrc2664
Ergezinger K, Vehmeyer K, Unger C (1999) Stimulation of human hematopoietic progenitor cells by the alkylphosphocholines hexadecylphosphocholine and hexadecyl-N,N,N-trimethyl-hexanolamine. Anticancer Res 19 (4B):3213–3219
Geilen CC, Haase R, Buchner K, Wieder T, Hucho F, Reutter W (1991) The phospholipid analogue, hexadecylphosphocholine, inhibits protein kinase C in vitro and antagonises phorbol ester-stimulated cell proliferation. Eur J Cancer 27(12):1650–1653
Georgieva MC, Konstantinov SM, Topashka-Ancheva M, Berger MR (2002) Combination effects of alkylphosphocholines and gemcitabine in malignant and normal hematopoietic cells. Cancer Lett 182(2):163–174
Grant S (2008) Cotargeting survival signaling pathways in cancer. J Clin Invest 118(9):3003–3006. doi:10.1172/JCI36898
Hilgard P, Stekar J, Voegeli R, Harleman JH (1992) Experimental therapeutic studies with miltefosine in rats and mice. Prog Exp Tumor Res 34:116–130
Hilgard P, Klenner T, Stekar J, Unger C (1993) Alkylphosphocholines: a new class of membrane-active anticancer agents. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 32(2):90–95
Hilgard P, Pohl J, Engel J (1997) The development of alkylphosphocholines as signal transduction inhibitors: experimental and clinical challenges. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 123(5):286–287
Jendrossek V, Hammersen K, Erdlenbruch B, Kugler W, Krugener R, Eibl H, Lakomek M (2002) Structure-activity relationships of alkylphosphocholine derivatives: antineoplastic action on brain tumor cell lines in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 50(1):71–79. doi:10.1007/s00280-002-0440-8
Kapoor V, Zaharieva MM, Das SN, Berger MR (2012) Erufosine simultaneously induces apoptosis and autophagy by modulating the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 319(1):39–48. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.12.032
Konigs SK, Pallasch CP, Lindner LH, Schwamb J, Schulz A, Brinker R, Claasen J, Veldurthy A, Eibl H, Hallek M, Wendtner CM (2010) Erufosine, a novel alkylphosphocholine, induces apoptosis in CLL through a caspase-dependent pathway. Leuk Res 34(8):1064–1069. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2009.12.003
Konstantinov SM, Berger MR (1999) Human urinary bladder carcinoma cell lines respond to treatment with alkylphosphocholines. Cancer Lett 144(2):153–160
Konstantinov SM, Kaminsky R, Brun R, Berger MR, Zillmann U (1997) Efficacy of anticancer alkylphosphocholines in Trypanosoma brucei subspecies. Acta Trop 64(3–4):145–154
Konstantinov SM, Eibl H, Berger MR (1998a) Alkylphosphocholines induce apoptosis in HL-60 and U-937 leukemic cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 41(3):210–216
Konstantinov SM, Topashka-Ancheva M, Benner A, Berger MR (1998b) Alkylphosphocholines: effects on human leukemic cell lines and normal bone marrow cells. Int J Cancer 77(5):778–786
Konstantinov SM, Eibl H, Berger MR (1999) BCR-ABL influences the antileukaemic efficacy of alkylphosphocholines. Br J Haematol 107(2):365–380
Kotting J, Berger MR, Unger C, Eibl H (1992) Alkylphosphocholines: influence of structural variation on biodistribution at antineoplastically active concentrations. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 30(2):105–112
Koziol JA, Maxwell DA, Fukushima M, Colmerauer ME, Pilch YH (1981) A distribution-free test for tumor-growth curve analyses with application to an animal tumor immunotherapy experiment. Biometrics 37(2):383–390
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M, Tafuri A, Stivala F, Libra M, Basecke J, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM, Franklin RA (2007) Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773(8):1263–1284. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001
Mendelsohn J (2008) The molecular basis of cancer. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63
Richardson PG, Wolf J, Jakubowiak A, Zonder J, Lonial S, Irwin D, Densmore J, Krishnan A, Raje N, Bar M, Martin T, Schlossman R, Ghobrial IM, Munshi N, Laubach J, Allerton J, Hideshima T, Colson K, Poradosu E, Gardner L, Sportelli P, Anderson KC (2011) Perifosine plus bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma previously treated with bortezomib: results of a multicenter phase I/II trial. J Clin Oncol 29(32):4243–4249. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.33.9788
Richardson PG, Eng C, Kolesar J, Hideshima T, Anderson KC (2012) Perifosine, an oral, anti-cancer agent and inhibitor of the Akt pathway: mechanistic actions, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 8(5):623–633. doi:10.1517/17425255.2012.681376
Rudner J, Ruiner CE, Handrick R, Eibl HJ, Belka C, Jendrossek V (2010) The Akt-inhibitor Erufosine induces apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer cells and increases the short term effects of ionizing radiation. Radiat Oncol 5:108. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-5-108
Sobottka SB, Berger MR (1992) Assessment of antineoplastic agents by MTT assay: partial underestimation of antiproliferative properties. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 30(5):385–393
Sobottka SB, Berger MR, Eibl H (1993) Structure-activity relationships of four anti-cancer alkylphosphocholine derivatives in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer 53(3):418–425
Toker A, Yoeli-Lerner M (2006) Akt signaling and cancer: surviving but not moving on. Cancer Res 66(8):3963–3966. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0743
Wickenden JA, Watson CJ (2010) Key signalling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer. Signalling downstream of PI3 kinase in mammary epithelium: a play in 3 Akts. Breast Cancer Res 12(2):202. doi:10.1186/bcr2558
Wu R, Hu TC, Rehemtulla A, Fearon ER, Cho KR (2011) Preclinical testing of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling inhibitors in a mouse model of ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17(23):7359–7372. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1388
Yosifov DY, Dineva IK, Zaharieva MM, Konstantinov SM, Berger MR (2007) The expression level of the tumor suppressor retinoblastoma protein (Rb) influences the antileukemic efficacy of erucylphospho-N, N, N-trimethylpropylammonium (ErPC3). Cancer Biol Ther 6(6):930–935
Yosifov DY, Konstantinov SM, Berger MR (2009) Erucylphospho-N, N, N-trimethylpropylammonium shows substantial cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:350–358. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04694.x
Yosifov DY, Todorov PT, Zaharieva MM, Georgiev KD, Pilicheva BA, Konstantinov SM, Berger MR (2011) Erucylphospho-N, N, N-trimethylpropylammonium (erufosine) is a potential antimyeloma drug devoid of myelotoxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67(1):13–25. doi:10.1007/s00280-010-1273-5
Zaharieva MM, Konstantinov SM, Pilicheva B, Karaivanova M, Berger MR (2007) Erufosine: a membrane targeting antineoplastic agent with signal transduction modulating effects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1095:182–192. doi:10.1196/annals.1397.022
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the DAAD foundation for Ilina K. Dineva and the Alexander von Humboldt foundation for Maya M. Zaharieva.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dineva, I.K., Zaharieva, M.M., Konstantinov, S.M. et al. Erufosine suppresses breast cancer in vitro and in vivo for its activity on PI3K, c-Raf and Akt proteins. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 1909–1917 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1271-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1271-6