Abstract
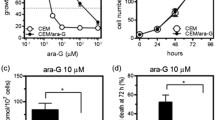
This report presents a quantitative analysis of the synergistic interaction of arabinosylcytosine (araC) and cladribine (CdA) in human H9-lymphoid cell lines sensitive and resistant to araC (H9-araC cells). H9-araC cells obtained by cultivation of H9 cells in the presence of 0.5 μM arabinosylcytosine (araC) had lower deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) than the parental cell line. The IC50 values of araC and CdA calculated by using median-effect analysis and CalcuSyn software were: 0.55 μM and 1.16 μM for CdA and 0.0058 μM and 3.5 μM for araC in H9 and H9-araC cells, respectively. These values were reduced to 0.10 μM and 0.38 μM for CdA and to 0.004 μM and to 0.77 μM for araC when the drugs were used in combination. Computerized simulation of dose reduction index (DRI) indicated that at 50–99% growth inhibition levels, the doses of araC could be reduced by 2.0 to 11.9-fold and 2.9 to 5.3-fold and the doses of CdA by 5.9 and 183.7-fold and 3.1 to 164.8-fold in H9 and H9-araC cells, respectively, when the drugs are used in combination. Assessment by combination index (CI) analysis showed that the combination exhibited moderate to strong synergistic lympho-cytotoxic effects. CdA metabolic studies (influx and activation) in the presence of deoxyadenosine, deoxycytidine, or araC suggested that CdA enters cells by a deoxyadenosine-inhibitable transport system, which is different than that of araC and deoxycytidine transport system. Thus, in addition to the known mechanisms, other mechanisms might be involved in the metabolism of CdA. The demonstration that araC and CdA combinations exert synergistic cytotoxicity even in the resistant cells raises hope that such a combination may be useful in tumors that were found resistant to these drugs.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- araC:
-
Arabinosylcytosine
- araCTP:
-
Arabinosylcytosine 5′-triphosphate
- CdA:
-
2-Chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine (Cladribine)
- CdAMP, CdADP, CdATP:
-
Mono-, di-, and tri-phosphates of CdA
- CI:
-
Combination index
- dA:
-
2′-Deoxyadenosine
- dC:
-
2′-Deoxycytidine
- dCK:
-
Deoxycytidine kinase
- DRI:
-
Dose reduction index
- dG:
-
Deoxyguanosine
- hENT1 and hENT2:
-
Human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 and 2
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
References
Agarwal RP, Wang W, Yo P, Han T, Fernandez M (1999) Cross resistance of dideoxycytidine resistant cell lines to azidothymidine. Biochem Pharmacol 58:1603–1608
Agarwal RP, Han T, Fernandez M (2001) Reduced cellular transport and activation of fluoropyrimidine nucleosides and resistance in human lymphocytic cell lines selected for arabinosyl-cytosine resistance. Biochem Pharmacol 61:39–47
Arnér ES (1996) On the phosphorylation of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine (CdA) and its correlation with clinical response in leukemia treatment. Leuk Lymphoma 21:225–231
Avery TL, Rehg JE, Lumm WC, Harwood FC, Santana VM, Blakley RL (1989) Biochemical pharmacology of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in malignant human hematopoietic cell lines and therapeutic effects of 2-bromodeoxyadenosine in drug combinations in mice. Cancer Res 49:4972–4978
Beutler E (1992) Cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine). Lancet 340:952–956
Bohman C, Eriksson S (1988) Deoxycytidine kinase from human leukemic spleen: preparations and characteristics of homogenous enzyme. Bichemistry 27:4258–4265
Carrera CJ, Piro LD, Saven A, Beutler E, Terai C, Carson DA (1991) 2-Chloro-deoxyadenosine chemotherapy triggers programmed cell death in normal and malignant lymphocytes. Adv Exp Med Biol 309(A):15–18
Carson DA, Wasson DB, Kaye J, Ullman B, Martin DW Jr, Robins RK, Montogomery JA (1980) Deoxycytidine kinase mediated toxicity of deoxyadenosine analogs toward malignant human lymphoblasts in vitro and toward murine L1210 leukemias in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:6865–6869
Carson DA, Wasson DB, Taetle R, Yu A (1983) Specific toxicity of 2-chloro-deoxyadenosine toward resting and proliferating human lymphocytes. Blood 62:737–743
Chou TC (1991) Quantitation of synergism and antagonism of two or more drugs by computerized analysis. In: Chou TC, Rideout DC (eds) Synergism and Antagonism in Chemotherapy. Academic, New York, pp 223–244
Chou TC (1998) Drug combinations: from laboratory to practice. J Lab Clin Med 131:6–8
Chou TC, Hayball M (1996) CalcuSyn for Windows, Multiple-Drug Dose-Effect Analyzer and Manual. Biosoft, Cambridge Place, Cambridge
Chou TC, Talalay P (1987) Applications of the median–effect principle for the assessment of low-dose risk of carcinogens and for the quantitation of synergism and antagonism of chemotherapeutic agents. In: Harrap KR, Connors TA (eds) New avenues of developmental cancer chemotherapy, Bristol-myers symposium series. Academic, New York, pp 37–64
Chou TC, Motzer RJ, Tong Y, Bosl GJ (1994) Computerized quantitation of synergism and antagonism of taxol, topotecan, and cisplatin against human teratocarcinoma cell growth: a rational approach to clinical protocol design. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:1517–1524
Chow KU, Boehrer S, Napieralski S, Nowak D, Knau A, Hoelzer D, Mitrou PS, Weidmann E (2003) In AML cell lines araC combined with purine analogues is able to exert synergistic as well as antagonistic effects on proliferation, apoptosis and disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential. Leuk Lymphoma 44:165–173
Chunduru SK, Appleman JR, Blakley RL (1993) Activity of human DNA polymerase alpha and beta with 2-chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine 5′-triphosphate and quantitative effect of incorporation on chain extension. Arch Biochem Biophys 302:19–30
Cole N, Gibson BE (1997) High-dose cytosine arabinoside in the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia. Blood Rev 11:39–45
Eriksson S, Kierdaszuk B, Munch-Petersen B, Oberg B, Johansson NG (1991) Comparison of the substrate specificities of human thymidine kinase 1 and 2 and deoxycytidine kinase toward antiviral and cytostatic nucleoside analogs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 176:586–592
Galmarini M, Mackey JR, Dumontet C (2001) Nucleoside analogues: mechanisms of drug resistance and reversal strategies. Leukemia 15:875–890
Gandhi V, Estey E, Keating MJ, Chucrallah A, Plunkett W (1996) Chlorodeoxyadenosine and arabinosylcytosine in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamic and molecular interactions. Blood 87:256–264
Griffig J, Koob R, Blakley RL (1989) Mechanism of inhibition of DNA synthesis by 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in human lymphoblastic cells. Cancer Res 49:6923–6928
Han T, Fernandez M, Sarkar M, Agarwal RP (2003) Arabinosylcytosine down-regulates thymidine kinase and induces cross-resistance to zidovudine in T-lymphoid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 307:564–568
Han T, Fernandez M, Chou TC, Agarwal RP (2004) 2-Chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine synergistically enhances azidothymidine cytotoxicity in azidothymidine resistant T-lymphoid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316:518–522
Hirota Y, Yoshioka A, Tanaka S, Watanabe K, Otani T, Minowada J, Matsuda A, Ueda T, Wataya Y (1989) Imbalance of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, DNA double-strand breaks, and cell death caused by 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in mouse FM3A cells. Cancer Res 49:915–919
Juliusson G, Elmhorn-Rosenborg A, Liliemark J (1992) Response to 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia resistant to fludarabine. N Engl J Med 327:1056–1061
Kawasaki H, Carrera CJ, Piro LD, Saven A, Kipps TJ, Carson DA (1993) Relationship of deoxycytidsine kinase and cytoplasmic 5’-nucleotidase to the chemotherapeutic efficacy of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine. Blood 81:597–601
Keating MJ, McCredie KB, Bodey GP, Smith TL, Gehan E, Freireich EJ (1982) Improved prospects for long-term survival in adults with acute myelogenous leukemia. JAMA 248:2481–2486
Kessel D, Hall TC, Wodinsky I (1967) Transport and phosphorylation as factors in the antitumor action of cytosine arabinoside. Science 156:1240–1241
Kornblau SM, Gandhi V, Andreeff HM, Beran M, Kantarjian HM, Koller CA, O’Brien S, Plunkett W, Estey E (1996) Clinical and laboratory studies of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine ± cytosine arabinoside for relapsed or refractory acute myelogenous leukemia in adults. Leukemia 10:1563–1569
Lassota P, Kazimierczuk Z, Darzynkiewicz Z (1994) Apoptotic death of lymphocytes upon treatment with 2-chloro-2’-deoxyadenosine (2-CdA). Arch Immulo Ther Exp Warsz 42:17–23
Lopez JA, Nassif E, Vennicola P, Krikorian JG, Agarwal RP (1985) Central nervous system pharmacokinetics of high-dose cytosine arabinoside. J Neuro Oncol 3:119–124
Mackey JR, Baldwin SA, Young JD, Cass CE (1998) The role of nucleoside transport in anticancer drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat 1:310–324
Momparler RL, Fisher GA (1968) Mammalian deoxynucleoside kinases. J Biol Chem 243:4298–4304
Nitisu N, Umeda M, Honma Y (2000) Myeloid and monocytoid leukemia cells have different sensitivity to differentiation-inducing activity of deoxyadenosine analogs. Leuk Res 24:1–9
Piro LD (1992) 2-Chlorodeoxyadenosine treatment of lymphoid malignancies. Blood 79:843–845
Piro LD, Carrera CJ, Carson DA, Beutler E (1990) Lasting remissions in hairy-cell leukemia induced by a single infusion of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine. N Engl J Med 322:1117–1121
Robak T (2001) Cladribine in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 40:551–564
Robak T (2003) Purine nucleoside analogs in the treatment of myeloid leukemias. Leuk Lymphoma 44:391–409
Robak T, Wrzesień-Kus A, Leh-Marańda E, Kowal M, Dmoszyńska A (2000) Combination regimen of Cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine), cytarabine and G-CSF (CLAG) as induction therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk lymphoma 39:121–129
Robertson LE, Chubb S, Meyn RE, Story M, Ford R, Hittelman WN, Plunkett W (1993) Induction of apoptotic cell death in chronic lymphoid leukemia by 2-chloro-2’-deoxyadenosine and 9-β-D-arabinosyl-2-fluoroadenine. Blood 81:143–150
Rustum YM, Preisler HD (1979) Correlation between leukemic cell retention of 1-β-D-arabinofuranosyl cytosine 5’-triphosphate and response to therapy. Cancer Res 39:42–49
Santana VM, Mirro Jr J, Harwood, FC, Cherrie J, Schell M, Kalwinsky D, Blakley RL (1991) A phase I clinical trial of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in pediatric patients with acute leukemia. J Clin Oncol 9:416–422
Sasvári-Székely M, Spasokoukotskaja T, Melinda S, Csapó Z, Turi A, Szántó I, Eriksson S, Staub M (1998) Activation of deoxycytidine kinase during inhibition of DNA synthesis by 2-chloro-2’-deoxyadenosine (cladribine) in human lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 56:1175–1179
Schirmer M, Stegmann AP, Konwalinka G (1998) Lack of cross-resistance with gemcitabine and cytarabine in cladribine-resistant HL-60 cells with elevated 5′-nucleotidase activity. Exp Hematol 26:1223–1228
Shewach DS, Reynolds KK, Hertel L (1992) Nucleotide specificity of human deoxycytidine kinase. Mol Pharmacol 42:518–524
Ullman B, Gudas LJ, Martin DW Jr (1979) Deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine cytotoxicity in cultured mouse T-lymphoma cells: a model for immunodeficiency disease. In: Pollara B, Pickering RJ, Meuwissen HJ, Porter IH (eds) Inborn Errors of Specific Immunity. Academic, New York, pp 237–259
Van Den Neste E, Martiat P, Mineur P, Delannoy A, Doyen C, Zenebergh A, Michaux JL, Ferrant A (1998) 2-Chlorodeoxyadenosine with or without daunorubicin in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol 76:19–23
Wang L, Karlsson A, Arner ES, Eriksson S (1993) Substrate specificity of mitochondrial 2′-deoxyguanosine kinase. Efficient phosphorylation of 2-chloro-deoxyadenosine. J Biol Chem 268:22847–22852
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Health and Human Services Grant NIAID AI 29155.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, T., Fernandez, M., Chou, TC. et al. Quantitation of synergism of arabinosylcytosine and cladribine against the growth of arabinosylcytosine-resistant human lymphoid cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131, 609–616 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0012-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0012-5