Abstract
Purpose
. The best way to deliver infusional 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and folinic acid (FA) has yet to be determined. The aim of this prospective phase II trial was to verify the tolerability, activity and efficacy of chronomodulated 5-FU-FA (FF5–16) every 3 weeks in 48 untreated patients (group A), and 28 pretreated and four non-measurable, advanced colorectal cancer (ACC) patients (group B).
Methods
The sinusoidal delivery of both drugs started at 10.00 p.m. and ended at 10.00 a.m., with peak flow at 4.00 a.m. for 5 consecutive days. The initial 5-FU dose was 900 mg/m2/day with intra-patient dose increase at 1,000 and 1,100 mg/m2/day, at the second and third course, respectively; FA was injected at a fixed dose of 150 mg/m2/day (Garufi et al.1997).
Results
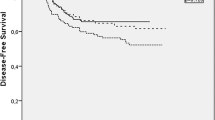
Neither death from toxicity nor hematological toxicities were encountered. Maximal toxicity consisted of Grade 3 oral mucositis in 41% of patients, in only 8% of 535 courses. It was possible to achieve objective responses in 31% of untreated patients, with a progression free survival (PFS) of 7 months, median survival of 14 months and a 2-year survival rate of 28%. Similar results for PFS and survival were obtained in pretreated patients as well. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis showed that response was related to the occurrence of mucositis and diarrhea (p=0.03 and p=0.0007) and to performance status (PS) (p=0.01). Quality of life, measured with the EORTC QLQ-C30+3 questionnaire, was unaffected by treatment and was better in patients with good PS and responsiveness.
Conclusions
In this chronomodulated FF5–16 phase II study, the probability of obtaining a relevant tumor reduction was significantly correlated with a patient variable such as PS, and toxicity variables such as mucositis and diarrhea. This observation and the validation of predictive factors for QoL deserve further investigation in ACC patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC (1993) The European Organization for the Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality of life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Nat Cancer Inst 85:365–376
Bressolle F, Joulia JM, Pinguet F, Ychou M, Astre C, Duffour J, Gomenni R (1999) Circadian rhythm of 5-fluorouracil population pharmacokinetics in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemoth and Pharmacol 44:295–302
Buchi KN, Moore JC, Hrushesky WJM, Sothern RB, Rubin NH (1991) Circadian rhythm of cellular proliferation in the human rectal mucosa. Gastroenterology 101:410–415
Burns B, Beland S (1984) Effects of biological time on the determination of the LD50 of 5-fluorouracilin mice. Pharmacology 28:296–300
Buyse M, Thirion P, Carlson RW, Burzykowski T, Molenberghs G, Piedbois P (2000) Relation between tumour response to first line chemotherapy and survival in advanced colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Lancet 356:373–378
Cohen AM, Minsky BD, Schilsky RL (1997) Cancer of the colon. In: De Vita V Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, (eds) Cancer: principles and practice of oncology, 5th edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 1144–1197
Cunningham D, Pyrhönen S, James RD et al (1998) Randomised trial of irinotecan plus supportive care versus supportive care alone after fluorouracil failure for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet 352:1413–1418
Curè H, Chevalier V, Pezet D et al (2000) Phase II trial of chronomodulated infusion of 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid in metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 20:4649–4654
Curé H, Chevalier V, Adenis A, Tubiana-Mathieu N, Niezgodzki G, Kwiatkowski F, Pezet D, Perpoint B, Coudert B, Focan C, Lévi F, Chipponi J, Chollet P (2002) Phase II trial of chronomodulated infusion of high dose 5-fluorouracil and l-folinic acid in previously untreated patients with metastatic colorectal cancer J Clin Oncol 20:1175–1181
De Gramont A, Bosset JF, Milan C, Rougier P, Bouche O, Etienne PL, Morvan F, Louvet C, Guillot T, Francois E, Bedenne L (1997) Randomized trial comparing monthly low-dose leucovorin and fluorouracil bolus with bimonthly high-dose leucovorin and fluorouracil bolus plus continuous infusion for advanced colorectal cancer: a French Intergroup Study. J Clin Oncol 15:808–815
De Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer G, Papamichel D, Le Bail N, Louvet C, Hendler D, de Braud F, Wilson C, Morvan F, Bonetti A (2000) Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:2938–2947
Earlam S, Glover C, Davies M, Fordy C, Allen-Mersh TG (1997) Effect of regional and systemic fluorinated pyrimidine chemotherapy on quality of life in colorectal liver metastasis patients. J Clin Oncol 5:2022–2029
Fleming RA, Milano G, Thyss A, Etienne MC, Renee N, Schneider M, Demard F (1992). Correlation between dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity in peripheral mononuclear cells and systemic clearance of fluorouracil in cancer patients. Cancer Res 52:2899–2902
Garufi C, Lévi F, Aschelter AM, Pace R, Giunta S, Nisticò C, Gallà DA, Silecchia GF, Franchi F, Narduzzi C, Terzoli E (1997) A phase I study of 5-day chronomodulated infusion of 5-fluorouracil and i-folinic acid in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer l33:1566–1572
Garufi C, Aschelter AM, Zappalà A (1999). Chronomodulated (chrono) infusion of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and 1-folinic acid (FA) in 91 patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer: the Regina Elena Cancer Institute experience. Eur J Cancer 35 [Suppl 4]:S71 (abstract 221)
Garufi C, Brienza S, Pugliese P, Aschelter AM, Bensmaine, Bertheault-Cvitkovic F, Nisticò C, Giunta S, Caterino M, Giannarelli D, Cosimelli M, Lévi F, Terzoli E (2000) Overcoming resistance to chronomodulated 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid by the addition of chronomodulated oxaliplatin in advanced colorectal cancer patients Anticancer Drugs 11:495–501
Giacchetti S, Perpoint B, Zidani R, Le Bail N, Faggiuolo R, Focan C, Chollet P, Llroy JF, Letorneau Y, Coudert B, Bertheault-Cvitkovic F, Larregain-Fournier D, Le Rol A, Walter S, Adam R, Misset JL (2000) Phase III multicenter randomized trial of oxaliplatin added to chronomodulated fluorouracil-leucovorin as first line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:136–147
Harris BE, Song R, Soong S, Diasio RB (1990) Relationship between dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity and plasma 5-fluorouracil levels: evidence for circadian variation of plasma drug levels in cancer patients receiving 5-fluorouracil by protracted continuous infusion. Cancer Res 50:197–201
Hryniuk WM (1988) The importance of dose-intensity in the outcome of chemotherapy. In: De Vita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA (eds) Important advances in oncology. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 121–125
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53:475–481
Köhne CH, Schöffski P, Wilke H, Kaufer C, Andreesen R, Klaasen U, Westerhausen M, Hiddemann W, Schott G, Harstick A, Bade J, Horster A, Schbert U, Hecker H, Dorken B, Schmoll HJ (1998) Effective biomodulation by leucovorin of high-dose infusion fluorouracil given as a weekly 24-hour infusion : Results of a randomized trial in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 16:418–426
Köhne CH, Cunningham D, Di CF, Glimelius B, Blijham G, Aranda E, Scheitauer W, Rougier P, Palmer M, Wils J, Baron B, Pignatti F, Schöffski P, Micheel S, Hecker H (2002) Clinical determinants of survival in patients with 5-fluorouracil-based treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: results of multivariate analysis of 3,852 patients. Ann Oncology 13:308–317
Lévi F (1997) Chronopharmacology of anticancer agents. In: Redfern PH, Lemmer B (eds) Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 229–331
Lévi F (2001) Circadian chronotherapy for human cancers. Lancet Oncol 2:307–315
Lévi F, Zidani R, Vannetzel JM, Perpoint B, Focan C, Faggiuolo R, Chollet P, Garufi C, Itzhaki M, Dogliotti L (1994) Chronomodulated versus fixed-infusion-rate delivery of ambulatory chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinic acid (leucovorin) in patients with colorectal cancer metastases: a randomized multi-institutional trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 186:1608–1616
Lévi F, Zidani R, Misset JL (1997) For the International Organization for Cancer Chronotherapy. Randomized multicenter trial of chronotherapy with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinic acid in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet 350:681–6
Lévi F, Zidani R, Brienza S, Dogliotti L, Perpoint B, Rotarski M, Letorneau Y, Llory JF, Chollet P, Le Rol A, Focan C (1999) For the International Organization for Cancer Chronotherapy. A multicenter evaluation of intensified ambulatory chronomodulated chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil and leucovorin as initial treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 85:2532–2540
Lokich JJ, Ahlgren JD, Gullo JJ, Philips JA, Fryer JG (1989) A prospective randomized comparison of continuous infusion fluorouracil with a conventional bolus schedule in metastatic colorectal carcinoma: a Mid-Atlantic oncology program study. J Clin Oncol 17:425–432
Maughan TS, James RD, Kerr DJ , Ledermann JA, McArdle C, Seymour MT, Cohen D, Hopwood P, Johnston C, Stephens RJ (2002) Comparison of survival, palliation, and quality of life with three chemotherapy regimens in metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 359:1555–1563
Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A (1981) Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 47:207–215
Meta-Analysis Group in Cancer (1998) Efficacy of intravenous continuous infusion of 5-fluorouracil compared with bolus administration in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 16:301–308
Petit E, Milano G, Lévi F, Thyss A, Bailleul F, Schneider M (1988) Circadian rhythm-varying plasma concentration of 5-fluorouracil during a five-day continuous infusion at constant rate in cancer patients. Cancer Res 48:1679–1685
Rougier P, Van Cutsem E, Bajetta E et al (1998) Randomised trial of irinotecan versus fluorouracil by continuous infusion after fluorouracil failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet 352:1407–1412
Smaaland R, Laerum O, Lote K, Sletvold O, Sothern RB, Bjerknes R (1991) DNA Synthesis in human bone marrow is circadian stage dependent. Blood 77:2603–2611
Warnakulasuriya KA, MacDonald DG (1993) Diurnal variation in labelling index in human buccal epithelium. Arch Oral Biol 12:1107–1111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terzoli, E., Garufi, C., Zappalà, A.R. et al. High-dose chronomodulated infusion of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and folinic acid (FA) (FF5–16) in advanced colorectal cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130, 445–452 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0560-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-004-0560-0