Abstract
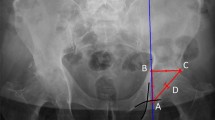
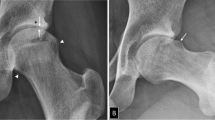
Guidelines for children with Down syndrome (DS) suggest to perform an annual hip screening to enable early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). How to perform this screening is not described. Delayed detection can result in disabling osteoarthritis of the hip. Therefore, we determined the association between clinical history, physical, and radiological examination in diagnosing DDH in children with DS. Referral centers for children with DS were interviewed to explore variety of hip examination throughout the Netherlands. Clinical features of 96 outclinic children were retrospectively collected. Clinical history was taken, physical examination was performed, and X-ray of the hip was analyzed. All the referral centers performed physical examination and clinical history; however, 20% performed X-ray. Following physical examination according to Galeazzi test 26.9% and to limited abduction 10.8% of the outclinic-studied children were at risk for DDH. Radiological examination showed moderate or severe abnormal deviating migration rate of 14.6% resp. 11.5% in the right and left hip. However, no association between clinical history, physical examination, and radiological examination was found.
Conclusion: Clinical history and physical examination are insufficient to timely detect DDH in children with Down syndrome. Thereby regular radiological examination of the hip is advised.
What is Known: • Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in people with Down syndrome (DS) develops during childhood. • Guidelines for medical support of children with DS suggest an annual hip screening to enable early detection of hip damaging. How to perform this annual screening is not described. | |
What is New: • This study shows no association between clinical history, physical and radiological examination of the hip. • We recommend regular radiological examination of the hip in children with DS in order to identify DDH early up to 16 years of age. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DDH:
-
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
- DS:
-
Down Syndrome
- L:
-
Left hip
- MMC:
-
Máxima Medical Center
- R:
-
Right hip
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Hindori-Mohangoo ADSY, van der Pal-de Bruin KM (2014) Aangeboren afwijkingen in Nederland 2001–2012. Gebaseerd op de landelijke perinale registratie. TNO Gezond Leven, Leiden
Pfitzer C, Helm PC, Rosenthal LM, Berger F, Bauer UMM, Schmitt KR (2018) Dynamics in prevalence of Down syndrome in children with congenital heart disease. Eur J Pediatr 177(1):107–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-017-3041-6
Abousamra O, Bayhan IA, Rogers KJ, Miller F (2016) Hip instability in down syndrome: a focus on acetabular retroversion. J Pediatr Orthop 36(5):499–504. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000484
Sankar WN, Millis MB, Kim YJ (2011) Instability of the hip in patients with Down syndrome: improved results with complete redirectional acetabular osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93(20):1924–1933. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.01806
Bittles AH, Bower C, Hussain R, Glasson EJ (2007) The four ages of Down syndrome. Eur J Pub Health 17(2):221–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckl103
Kelley SP, Wedge JH (2013) Management of hip instability in trisomy 21. J Pediatr Orthop 33(Suppl 1):S33–S38. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318281968e
Bennet GC, Rang M, Roye DP, Aprin H (1982) Dislocation of the hip in trisomy 21. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 64(3):289–294
Genetics Co (2001) Health supervision for children with Down syndrome. Pediatrics 107:442–449. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.107.2.442
Castelein RM (2002) Physical diagnosis--Ortolani's manoeuvre. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 146(23):1077–1080
Kioschos M, Shaw ED, Beals RK (1999) Total hip arthroplasty in patients with Down's syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 81(3):436–439
Remvig L, Engelbert RH, Berglund B, Bulbena A, Byers PH, Grahame R, Juul-Kristensen B, Lindgren KA, Uitto J, Wekre LL (2011) Need for a consensus on the methods by which to measure joint mobility and the definition of norms for hypermobility that reflect age, gender and ethnic-dependent variation: is revision of criteria for joint hypermobility syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome hypermobility type indicated? Rheumatology 50(6):1169–1171. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ker140
Broughton NS, Brougham DI, Cole WG, Menelaus MB (1989) Reliability of radiological measurements in the assessment of the child's hip. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 71(1):6–8
Tonnis D (1976) Normal values of the hip joint for the evaluation of X-rays in children and adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res 119:39–47
Delaunay S, Dussault RG, Kaplan PA, Alford BA (1997) Radiographic measurements of dysplastic adult hips. Skelet Radiol 26(2):75–81
Valkenburg AJ, Tibboel D, van Dijk M (2015) Pain sensitivity of children with Down syndrome and their siblings: quantitative sensory testing versus parental reports. Dev Med Child Neurol 57(11):1049–1055. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.12823
Knight DM, Alves C, Wedge JH (2011) Femoral varus derotation osteotomy for the treatment of habitual subluxation and dislocation of the pediatric hip in trisomy 21: a 10-year experience. J Pediatr Orthop 31(6):638–643. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182285fa5
Woolf SK, Gross RH (2003) Posterior acetabular wall deficiency in Down syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop 23(6):708–713
Schams M, Labruyere R, Zuse A, Walensi M (2017) Diagnosing developmental dysplasia of the hip using the Graf ultrasound method: risk and protective factor analysis in 11,820 universally screened newborns. Eur J Pediatr 176(9):1193–1200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-017-2959-z
Roberts GM, Starey N, Harper P, Nuki G (1980) Radiology of the pelvis and hips in adults with Down’s syndrome. Clin Radiol 31(4):475–478
Bulat E, Maranho DA, Kalish LA, Millis MB, Kim YJ, Novais EN (2017) Acetabular global insufficiency in patients with down syndrome and hip-related symptoms: a matched-cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 99(20):1760–1768. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.17.00341
Shaw ED, Beals RK (1992) The hip joint in Down’s syndrome. A study of its structure and associated disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res 278:101–107
Livingstone B, Hirst P (1986) Orthopedic disorders in school children with Down's syndrome with special reference to the incidence of joint laxity. Clin Orthop Relat Res 207:74–76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AFM van Gijzen has had a substantial contribution to the analysis and interpretation of the study. She added substantial data and results to the paper and rewrote the paper and processed the giving feedback. Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
As a student, EDM Rouers has collected all the data and the analysis and wrote the first draft of the paper. Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
QMP van Douveren has delivered a substantial contribution to the design of the study and acquisition of the data. Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
J Dieleman had a great part in the study design and the data analysis. Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
GE Hendriks has delivered a substantial contribution to the design and analysis of the study and acquisition of the data. Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
F Halbertsma has had a substantial contribution to the design of the study, analysis, and interpretation of the study. Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
LA Bok has had a substantial contribution to the design of the study, the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation. Agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Medical Ethical Commission. All procedures performed in studies were done according to regular yearly medical care for children with Down syndrome, studied in retrospect, and in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Mario Bianchetti
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Gijzen, A.F., Rouers, E.D., van Douveren, F.Q. et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in children with Down syndrome: comparison of clinical and radiological examinations in a local cohort. Eur J Pediatr 178, 559–564 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-019-03322-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-019-03322-x