Abstract
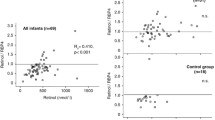
Despite high-dose vitamin A supplementation of very low birth weight infants (VLBW, <1500 g), their vitamin A status does not improve substantially. Unknown is the impact of urinary retinol excretion on the serum retinol concentration in these infants. Therefore, the effect of high-dose vitamin A supplementation on the urinary vitamin A excretion in VLBW infants was investigated. Sixty-three VLBW infants were treated with vitamin A (5000 IU intramuscular, 3 times/week for 4 weeks); 38 untreated infants were classified as control group. On days 3 and 28 of life, retinol, retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4), glomerular filtration rate, proteinuria, and Tamm–Horsfall protein were quantified in urine. On day 3 of life, substantial retinol and RBP4 losses were found in both groups, which significantly decreased until day 28. Notwithstanding, the retinol excretion was higher (P < 0.01) under vitamin A supplementation as compared to infants of the control group. On day 28 of life, the urinary retinol concentrations were predictive for serum retinol concentrations in the vitamin A treated (P < 0.01), but not in the control group (P = 0.570).
Conclusion: High urinary retinol excretion may limit the vitamin A supplementation efficacy in VLBW infants. Advanced age and thus postnatal kidney maturation seems to be an important contributor in the prevention of urinary retinol losses.
What is Known: |
• VLBW infants have low vitamin A status, even after 4-week high-dose vitamin A supplementation [Longardt AC, Eur J Clin Nutr 2014; Schmiedchen B, Longardt AC, Buehrer C, Raila J, Loui A, Schweigert FJ Neonatology 105:155-160, 2014] • VLBW infants excrete high amounts of retinol [Nagl B, Loui A, Raila J, Felderhoff-Mueser U, Obladen M, Schweigert FJ Pediatr Nephrol 24:61-66, 2009] |
What is New: |
• Urine retinol excretion reduces with increasing age of VLBW infants and is not suitable to assess vitamin A status in VLBW infants • High urinary retinol excretion may limit vitamin A supplementation efficacy in VLBW infants |


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GFR:
-
Glomerular filtration rate
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- i.m.:
-
Intramuscular
- RBP4:
-
Retinol-binding protein 4
- SGA:
-
Small for gestational age
- THP:
-
Tamm–Horsfall protein
- TTR:
-
Transthyretin
- UPC:
-
Urine protein-to-creatinine ratio
- VLBW:
-
Very low birth weight
References
Abitbol CL, Seeherunvong W, Galarza MG, Katsoufis C, Francoeur D, Defreitas M, Edwards-Richards A, Master Sankar Raj V, Chandar J, Duara S, Yasin S, Zilleruelo G (2014) Neonatal kidney size and function in preterm infants: what is a true estimate of glomerular filtration rate? J Pediatr 164(1026–1031), e1022
Awad H, el-Safty I, el-Barbary M, Imam S (2002) Evaluation of renal glomerular and tubular functional and structural integrity in neonates. Am J Med Sci 324:261–266
Bellovino D, Morimoto T, Tosetti F, Gaetani S (1996) Retinol binding protein and transthyretin are secreted as a complex formed in the endoplasmic reticulum in HepG2 human hepatocarcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res 222:77–83
Bhat PV, Manolescu DC (2008) Role of vitamin A in determining nephron mass and possible relationship to hypertension. J Nutr 138:1407–1410
Blomhoff R, Blomhoff HK (2006) Overview of retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol 66:606–630
Christensen EI, Moskaug JO, Vorum H, Jacobsen C, Gundersen TE, Nykjaer A, Blomhoff R, Willnow TE, Moestrup SK (1999) Evidence for an essential role of megalin in transepithelial transport of retinol. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:685–695
Christensen EI, Verroust PJ, Nielsen R (2009) Receptor-mediated endocytosis in renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch 458:1039–1048
Clagett-Dame M, DeLuca HF (2002) The role of vitamin A in mammalian reproduction and embryonic development. Annu Rev Nutr 22:347–381
Clark PM, Bryant TN, Hall MA, Lowes JA, Rowe DJ (1989) Neonatal renal function assessment. Arch Dis Child 64:1264–1269
Drukker A, Guignard JP (2002) Renal aspects of the term and preterm infant: a selective update. Curr Opin Pediatr 14:175–182
Fell JM, Thakkar H, Newman DJ, Price CP (1997) Measurement of albumin and low molecular weight proteins in the urine of newborn infants using a cotton wool ball collection method. Acta Paediatr 86:518–522
Gilbert T (2002) Vitamin A and kidney development. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17(Suppl 9):78–80
Guignard JP, Torrado A, Da Cunha O, Gautier E (1975) Glomerular filtration rate in the first three weeks of life. J Pediatr 87:268–272
Hinchliffe SA, Sargent PH, Howard CV, Chan YF, van Velzen D (1991) Human intrauterine renal growth expressed in absolute number of glomeruli assessed by the disector method and Cavalieri principle. Lab Invest 64:777–784
Jobe AH, Bancalari E (2001) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:1723–1729
Kato M, Kato K, Goodman DS (1984) Immunocytochemical studies on the localization of plasma and of cellular retinol-binding proteins and of transthyretin (prealbumin) in rat liver and kidney. J Cell Biol 98:1696–1704
Kokot F, Dulawa J (2000) Tamm-Horsfall protein updated. Nephron 85:97–102
Longardt AC, Schmiedchen B, Raila J, Schweigert FJ, Obladen M, Bührer C, Loui A (2014) Characterization of the vitamin A transport in preterm infants after repeated high-dose vitamin A injections. Eur J Clin Nutr
Mactier H, Weaver LT (2005) Vitamin A and preterm infants: what we know, what we don’t know, and what we need to know. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 90:F103–F108
Mactier H (2013) Vitamin A for preterm infants; where are we now? Semin Fetal Neonatal Med
Maden M (2000) The role of retinoic acid in embryonic and post-embryonic development. Proc Nutr Soc 59:65–73
Nagl B, Loui A, Raila J, Felderhoff-Mueser U, Obladen M, Schweigert FJ (2009) Urinary vitamin A excretion in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Nephrol 24:61–66
Raila J, Forterre S, Kohn B, Brunnberg L, Schweigert FJ (2003) Effects of chronic renal disease on the transport of vitamin A in plasma and urine of dogs. Am J Vet Res 64:874–879
Raila J, Willnow TE, Schweigert FJ (2005) Megalin-mediated reuptake of retinol in the kidneys of mice is essential for vitamin A homeostasis. J Nutr 135:2512–2516
Rodriguez MM, Gomez AH, Abitbol CL, Chandar JJ, Duara S, Zilleruelo GE (2004) Histomorphometric analysis of postnatal glomerulogenesis in extremely preterm infants. Pediatr Dev Pathol 7:17–25
Ross SA, McCaffery PJ, Drager UC, De Luca LM (2000) Retinoids in embryonal development. Physiol Rev 80:1021–1054
Schmiedchen B, Longardt AC, Buehrer C, Raila J, Loui A, Schweigert FJ (2014) The relative dose response test based on retinol-binding protein 4 is not suitable to assess vitamin A status in very low birth weight infants. Neonatology 105:155–160
Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ (1984) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr 104:849–854
Schweigert FJ, Steinhagen B, Raila J, Siemann A, Peet D, Buscher U (2003) Concentrations of carotenoids, retinol and alpha-tocopherol in plasma and follicular fluid of women undergoing IVF. Hum Reprod 18:1259–1264
Serafini-Cessi F, Malagolini N, Cavallone D (2003) Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein: biology and clinical relevance. Am J Kidney Dis 42:658–676
Sutherland MR, Gubhaju L, Yoder BA, Stahlman MT, Black MJ (2009) The effects of postnatal retinoic acid administration on nephron endowment in the preterm baboon kidney. Pediatr Res 65:397–402
Sutherland MR, Gubhaju L, Moore L, Kent AL, Dahlstrom JE, Horne RS, Hoy WE, Bertram JF, Black MJ (2011) Accelerated maturation and abnormal morphology in the preterm neonatal kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol: JASN 22:1365–1374
Tyson JE, Wright LL, Oh W, Kennedy KA, Mele L, Ehrenkranz RA, Stoll BJ, Lemons JA, Stevenson DK, Bauer CR, Korones SB, Fanaroff AA (1999) Vitamin A supplementation for extremely-low-birth-weight infants. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. N Engl J Med 340:1962–1968
Verroust PJ, Christensen EI (2002) Megalin and cubilin - the story of two multipurpose receptors unfolds. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17:1867–1871
Vieux R, Hascoet JM, Merdariu D, Fresson J, Guillemin F (2010) Glomerular filtration rate reference values in very preterm infants. Pediatrics 125:e1186–e1192
Vilar J, Gilbert T, Moreau E, Merlet-Benichou C (1996) Metanephros organogenesis is highly stimulated by vitamin A derivatives in organ culture. Kidney Int 49:1478–1487
Zimmerhackl LB, Rostasy K, Wiegele G, Rasenack A, Wilhelm C, Lohner M, Brandis M, Kinne RK (1996) Tamm-Horsfall protein as a marker of tubular maturation. Pediatr Nephrol 10:448–452
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to the infants and parents for taking part in this study and gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung; Subsidy Contract Number 2010_A151.
Authors’ contributions to manuscript
AL, ACL, JR, and FJS designed the research (project conception, development of overall research plan, and study oversight).
AL, ACL, and BS conducted the research (sample collection, data collection).
BS analyzed the data and performed statistical analysis.
BS wrote the paper.
AL, CB, and FJS had primary responsibility for final content.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung; Subsidy Contract Number 2010_A151.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
The study protocol was approved by the Charité’s institutional review board (No. EA2/053/07) and written parental consent was obtained for each infant.
Informed consent
Written parental consent was obtained for each infant included into the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Patrick Van Reempts
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmiedchen, B., Longardt, A.C., Loui, A. et al. Effect of vitamin A supplementation on the urinary retinol excretion in very low birth weight infants. Eur J Pediatr 175, 365–372 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-015-2647-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-015-2647-9