Abstract
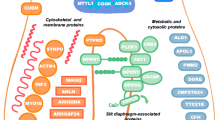
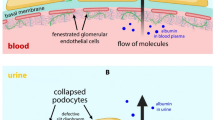
In the recent past, hereditary podocytopathies have increasingly been recognized to be involved in the development of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS). Mutations in podocyte genes substantially alter the development and structural architecture of the podocyte including its interdigitating foot processes. These constitute the basis of the slit diaphragm which is an essential part of the glomerular filtration barrier. Depending on the affected protein, the clinical course is variable with respect to onset and severity of the disease as well as treatment options. In general, hereditary podocytopathies are associated with a poorer renal outcome than the non-genetic variants. In addition, they require a different approach with respect to the applied therapeutic strategies as most patients do not respond to immunosuppressive agents. Therefore, genetic testing of podocyte genes should be considered as a routine diagnostic tool for patients with SRNS because the identification of a genetic origin has a direct implication on clinical course, renal outcome, and genetic counseling. In this educational paper, we will give an overview over the podocyte genes identified so far to be involved into the pathophysiology of hereditary podocytopathies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artero M, Biava C, Amend W, Tomlanovich S, Vincenti F (1992) Recurrent focal glomerulosclerosis: natural history and response to therapy. Am J Med 92(4):375–383
Artero ML, Sharma R, Savin VJ, Vincenti F (1994) Plasmapheresis reduces proteinuria and serum capacity to injure glomeruli in patients with recurrent focal glomerulosclerosis. Am J Kidney Dis 23:574–581
Barbaux S, Niaudet P, Gubler MC, Grünfeld JP, Jaubert F, Kuttenn F, Fékété CN, Souleyreau-Therville N, Thibaud E, Fellous M, McElreavey K (1997) Donor splice-site mutations in WT1 are responsible for Frasier syndrome. Nat Genet 17(4):467–470
Bertelli R, Ginevri F, Caridi G, Dagnino M, Sandrini S, Di Duca M, Emma F, Sanna-Cherchi S, Scolari F, Neri TM, Murer L, Massella L, Basile G, Rizzoni G, Perfumo F, Ghiggeri GM (2003) Recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after renal transplantation in patients with mutations of podocin. Am J Kidney Dis 41(6):1314–1321
Boute N, Gribouval O, Roselli S, Benessy F, Lee H, Fuchshuber A, Dahan K, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Antignac C (2000) NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet 24(4):349–354
Boyer O, Benoit G, Gribouval O, Nevo F, Tête MJ, Dantal J, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Touchard G, Karras A, Presne C, Grunfeld JP, Legendre C, Joly D, Rieu P, Mohsin N, Hannedouche T, Moal V, Gubler MC, Broutin I, Mollet G, Antignac C (2011) Mutations in INF2 are a major cause of autosomal dominant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(2):239–245
Brown EJ, Schlöndorff JS, Becker DJ, Tsukaguchi H, Tonna SJ, Uscinski AL, Higgs HN, Henderson JM, Pollak MR (2010) Mutations in the formin gene INF2 cause focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 42(1):72–76
Büscher AK, Kranz B, Büscher R, Hildebrandt F, Dworniczak B, Pennekamp P, Kuwertz-Bröking E, Wingen AM, John U, Kemper M, Monnens L, Hoyer PF, Weber S, Konrad M (2010) Immunosuppression and renal outcome in congenital and pediatric steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5(11):2075–2084
Caridi G, Bertelli R, Di Duca M, Dagnino M, Emma F, Onetti Muda A, Scolari F, Miglietti N, Mazzucco G, Murer L, Carrea A, Massella L, Rizzoni G, Perfumo F, Ghiggeri GM (2003) Broadening the spectrum of diseases related to podocin mutations. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(5):1278–1286
Caridi G, Bertelli R, Scolari F, Sanna-Cherchi S, Di Duca M, Ghiggeri GM (2003) Podocin mutations in sporadic focal-segmental glomerulosclerosis occurring in adulthood. Kidney Int 64(1):365
Cattran DC, Appel GB, Hebert LA, Hunsicker LG, Pohl MA, Hoy WE, Maxwell DR, Kunis CL (1999) A randomized trial of cyclosporine in patients with steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. North America Nephrotic Syndrome Study Group. Kidney Int 56(6):2220–2226
Chhabra ES, Ramabhadran V, Gerber SA, Higgs HN (2009) INF2 is an endoplasmic reticulum-associated formin protein. J Cell Sci 122(Pt 9):1430–1440
Coulthard MG (1989) Management of Finnish congenital nephrotic syndrome by unilateral nephrectomy. Pediatr Nephrol 3(4):451–453
Denamur E, Bocquet N, Baudouin V, Da Silva F, Veitia R, Peuchmaur M, Elion J, Gubler MC, Fellous M, Niaudet P, Loirat C (2000) WT1 splice-site mutations are rarely associated with primary steroid-resistant focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 57(5):1868–1872
Eckel J, Lavin PJ, Finch EA, Mukerji N, Burch J, Gbadegesin R, Wu G, Bowling B, Byrd A, Hall G, Sparks M, Zhang ZS, Homstad A, Barisoni L, Birbaumer L, Rosenberg P, Winn MP (2011) TRPC6 enhances angiotensin II-induced albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(3):526–535
Faul C, Donnelly M, Merscher-Gomez S, Chang YH, Franz S, Delfgaauw J, Chang JM, Choi HY, Campbell KN, Kim K, Reiser J, Mundel P (2008) The actin cytoskeleton of kidney podocytes is a direct target of the antiproteinuric effect of cyclosporine A. Nat Med 14:931–938
Franceschini N, North KE, Kopp JB, McKenzie L, Winkler C (2006) NPHS2 gene, nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a HuGE review. Genet Med 8(2):63–75
Frasier SD, Bashore RA, Mosier HD (1964) Gonadoblastoma associated with pure gonadal dysgenesis in monozygous twins. J Pediatr 64:740–745
Fuchshuber A, Jean G, Gribouval O, Gubler MC, Broyer M, Beckmann JS, Niaudet P, Antignac C (1995) Mapping a gene (SRN1) to chromosome 1q25-q31 in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome confirms a distinct entity of autosomal recessive nephrosis. Hum Mol Genet 4(11):2155–2158
Gao F, Maiti S, Sun G, Ordonez NG, Udtha M, Deng JM, Behringer RR, Huff V (2004) The Wt1+/R394W mouse displays glomerulosclerosis and early-onset renal failure characteristic of human Denys-Drash syndrome. Mol Cell Biol 24(22):9899–9910
Gellermann J, Stefanidis CJ, Mitsioni A, Querfeld U (2010) Successful treatment of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome associated with WT1 mutations. Pediatr Nephrol 25(7):1285–1289
Gessler M, Bruns GA (1988) Molecular mapping and cloning of the breakpoints of a chromosome 11p14.1-p13 deletion associated with the AGR syndrome. Genomics 3(2):117–122
Gigante M, Caridi G, Montemurno E, Soccio M, D'Apolito M, Cerullo G, Aucella F, Schirinzi A, Emma F, Massella L, Messina G, De Palo T, Ranieri E, Ghiggeri GM, Gesualdo L (2011) TRPC6 mutations in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome and atypical phenotype. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6(7):1626–1634
Gubler MC, Yang Y, Jeanpierre C, Barbaux S, Niaudet P (1999) WT1, renal development, and glomerulopathies. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp 29:299–315
Haber DA, Buckler AJ, Glaser T, Call KM, Pelletier J, Sohn RL, Douglass EC, Housman DE (1990) An internal deletion within an 11p13 zinc finger gene contributes to the development of Wilms' tumor. Cell 61(7):1257–1269
Habib R, Gubler MC, Antignac C, Gagnadoux MF (1993) Diffuse mesangial sclerosis: a congenital glomerulopathy with nephrotic syndrome. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp 22:43–57
Habib R, Hebert D, Gagnadoux MF, Broyer M (1982) Transplantation in idiopathic nephrosis. Transplant Proc 14(3):489–495
Habib R, Loirat C, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Bensman A, Levy M, Broyer M (1985) The nephropathy associated with male pseudohermaphroditism and Wilms' tumor (Drash syndrome): a distinctive glomerular lesion—report of 10 cases. Clin Nephrol 24(6):269–278
Higgs HN (2005) Formin proteins: a domain-based approach. Trends Biochem Sci 30(6):342–353
Hinkes B, Wiggins RC, Gbadegesin R, Vlangos CN, Seelow D, Nurnberg G, Garg P, Verma R, Chaib H, Hoskins BE, Ashraf S, Becker C, Hennies HC, Goyal M, Wharram BL, Schachter AD, Mudumana S, Drummond I, Kerjaschki D, Waldherr R, Dietrich A, Ozaltin F, Bakkaloglu A, Cleper R, Basel-Vanagaite L, Pohl M, Griebel M, Tsygin AN, Soylu A, Muller D, Sorli CS, Bunney TD, Katan M, Liu J, Attanasio M, O’Toole JF, Hasselbacher K, Mucha B, Otto EA, Airik R, Kispert A, Kelley GG, Smrcka AV, Gudermann T, Holzman LB, Nurnberg P, Hildebrandt F (2006) Positional cloning uncovers mutations in PLCE1 responsible for a nephrotic syndrome variant that may be reversible. Nat Genet 38:1397–1405
Höcker B, Knüppel T, Waldherr R, Schaefer F, Weber S, Tönshoff B (2006) Recurrence of proteinuria 10 years post-transplant in NPHS2-associated focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after conversion from cyclosporin A to sirolimus. Pediatr Nephrol 21(10):1476–1479
Holmberg C, Antikainen M, Rönnholm K, Ala Houhala M, Jalanko H (1995) Management of congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type. Pediatr Nephrol 9(1):87–93
Huber TB, Hartleben B, Kim J, Schmidts M, Schermer B, Keil A, Egger L, Lecha RL, Borner C, Pavenstädt H, Shaw AS, Walz G, Benzing T (2003) Nephrin and CD2AP associate with phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and stimulate AKT-dependent signaling. Mol Cell Biol 23(14):4917–4928
Huber TB, Kottgen M, Schilling B, Walz G, Benzing T (2001) Interaction with podocin facilitates nephrin signaling. J Biol Chem 276(45):41543–41546
International Study of Kidney Disease in Children (1981) The primary nephrotic syndrome in children. Identification of patients with minimal change nephrotic syndrome from initial response to prednisone. J Pediatr 98:561–564
Jeanpierre C, Denamur E, Henry I, Cabanis MO, Luce S, Cécille A, Elion J, Peuchmaur M, Loirat C, Niaudet P, Gubler MC, Junien C (1998) Identification of constitutional WT1 mutations, in patients with isolated diffuse mesangial sclerosis, and analysis of genotype/phenotype correlations by use of a computerized mutation database. Am J Hum Genet 62(4):824–833
Jungraithmayr TC, Hofer K, Cochat P, Chernin G, Cortina G, Fargue S, Grimm P, Knueppel T, Kowarsch A, Neuhaus T, Pagel P, Pfeiffer KP, Schäfer F, Schönermarck U, Seeman T, Toenshoff B, Weber S, Winn MP, Zschocke J, Zimmerhackl LB (2011) Screening for NPHS2 mutations may help predict FSGS recurrence after transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(3):579–585
Kaplan JM, Kim SH, North KN, Rennke H, Correia LA, Tong HQ, Mathis BJ, Rodríguez-Pérez JC, Allen PG, Beggs AH, Pollak MR (2000) Mutations in ACTN4, encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 24(3):251–256
Kaplinsky C, Ghahremani M, Frishberg Y, Rechavi G, Pelletier J (1996) Familial Wilms' tumor associated with a WT1 zinc finger mutation. Genomics 38(3):451–453
Kershaw DB, Sedman AB, Kelsch RC, Bunchman TE (1994) Recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in pediatric renal transplant recipients: successful treatment with oral cyclophosphamide. Clin Transplant 8:546–549
Kestilä M, Lenkkeri U, Männikkö M, Lamerdin J, McCready P, Putaala H, Ruotsalainen V, Morita T, Nissinen M, Herva R, Kashtan CE, Peltonen L, Holmberg C, Olsen A, Tryggvason K (1998) Positionally cloned gene for a novel glomerular protein–nephrin–is mutated in congenital nephrotic syndrome. Mol Cell 1(4):575–582
Kestilä M, Männikkö M, Holmberg C, Gyapay G, Weissenbach J, Savolainen ER, Peltonen L, Tryggvason K (1994) Congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type maps to the long arm of chromosome 19. Am J Hum Genet 54(5):757–764
Kovacevic L, Reid CJ, Rigden SP (2003) Management of congenital nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 18(5):426–430
Krall P, Canales CP, Kairath P, Carmona-Mora P, Molina J, Carpio JD, Ruiz P, Mezzano SA, Li J, Wei C, Reiser J, Young JI, Walz K (2010) Podocyte-specific overexpression of wild type or mutant trpc6 in mice is sufficient to cause glomerular disease. PLoS One 5(9):e12859
Lehtonen S, Ryan JJ, Kudlicka K, Iino N, Zhou H, Farquhar MG (2005) Cell junction-associated proteins IQGAP1, MAGI-2, CASK, spectrins, and alpha-actinin are components of the nephrin multiprotein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9814–9819
Little M, Wells C (1997) A clinical overview of WT1 gene mutations. Hum Mutat 9(3):209–225
Mathis BJ, Kim SH, Calabrese K, Haas M, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Pollak MR (1998) A locus for inherited focal segmental glomerulosclerosis maps to chromosome 19q13. Kidney Int 53(2):282–286
Michaud JL, Chaisson KM, Parks RJ, Kennedy CR (2006) FSGS-associated alpha-actinin-4 (K256E) impairs cytoskeletal dynamics in podocytes. Kidney Int 70(6):1054–1061
Niaudet P, Gubler MC (2006) WT1 and glomerular diseases. Pediatr Nephrol 21(11):1653–1660
Patrakka J, Ruotsalainen V, Reponen P, Qvist E, Laine J, Holmberg C, Tryggvason K, Jalanko H (2002) Recurrence of nephrotic syndrome in kidney grafts of patients with congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type: role of nephrin. Transplantation 73(3):394–403
Pelletier J, Bruening W, Kashtan CE, Mauer SM, Manivel JC, Striegel JE, Houghton DC, Junien C, Habib R, Fouser L et al (1991) Germline mutations in the Wilms' tumor suppressor gene are associated with abnormal urogenital development in Denys-Drash syndrome. Cell 67(2):437–447
Pereira AC, Pereira AB, Mota GF, Cunha RS, Herkenhoff FL, Pollak MR, Mill JG, Krieger JE (2004) NPHS2 R229Q functional variant is associated with microalbuminuria in the general population. Kidney Int 65(3):1026–1030
Philippe A, Nevo F, Esquivel EL, Reklaityte D, Gribouval O, Tête MJ, Loirat C, Dantal J, Fischbach M, Pouteil-Noble C, Decramer S, Hoehne M, Benzing T, Charbit M, Niaudet P, Antignac C (2008) Nephrin mutations can cause childhood-onset steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(10):1871–1878
Plank C, Kalb V, Hinkes B, Hildebrandt F, Gefeller O, Rascher W, Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Pädiatrische Nephrologie (2008) Cyclosporin A is superior to cyclophosphamide in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome-a randomized controlled multicentre trial by the Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Pädiatrische Nephrologie. Pediatr Nephrol 23(9):1483–1493
Pomeranz A, Wolach B, Bernheim J, Korzets Z, Bernheim J (1995) Successful treatment of Finnish congenital nephrotic syndrome with captopril and indomethacin. J Pediatr 126(1):140–142
Ponticelli C, Rizzoni G, Edefonti A, Altieri P, Rivolta E, Rinaldi S, Ghio L, Lusvarghi E, Gusmano R, Locatelli F et al (1993) A randomized trial of cyclosporine in steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 43(6):1377–1384
Primary nephrotic syndrome in children: clinical significance of histopathologic variants of minimal change and of diffuse mesangial hypercellularity (1981) A Report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Kidney Int 20:765-771
Rapola J (1987) Congenital nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 1(3):441–446
Reiser J, Polu KR, Möller CC, Kenlan P, Altintas MM, Wei C, Faul C, Herbert S, Villegas I, Avila-Casado C, McGee M, Sugimoto H, Brown D, Kalluri R, Mundel P, Smith PL, Clapham DE, Pollak MR (2005) TRPC6 is a glomerular slit diaphragm-associated channel required for normal renal function. Nat Genet 37(7):739–744
Rose EA, Glaser T, Jones C, Smith CL, Lewis WH, Call KM, Minden M, Champagne E, Bonetta L, Yeger H et al (1990) Complete physical map of the WAGR region of 11p13 localizes a candidate Wilms' tumor gene. Cell 60(3):495–508
Roselli S, Heidet L, Sich M, Henger A, Kretzler M, Gubler MC, Antignac C (2004) Early glomerular filtration defect and severe renal disease in podocin-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 24(2):550–560
Ruf RG, Lichtenberger A, Karle SM, Haas JP, Anacleto FE, Schultheiss M, Zalewski I, Imm A, Ruf EM, Mucha B, Bagga A, Neuhaus T, Fuchshuber A, Bakkaloglu A, Hildebrandt F; Arbeitsgemeinschaft Für Pädiatrische Nephrologie Study Group (2004) Patients with mutations in NPHS2 (podocin) do not respond to standard steroid treatment of nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(3):722–732
Ruotsalainen V, Ljungberg P, Wartiovaara J, Lenkkeri U, Kestilä M, Jalanko H, Holmberg C, Tryggvason K (1999) Nephrin is specifically located at the slit diaphragm of glomerular podocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(14):7962–7967
Santín S, García-Maset R, Ruíz P, Giménez I, Zamora I, Peña A, Madrid A, Camacho JA, Fraga G, Sánchez-Moreno A, Cobo MA, Bernis C, Ortiz A, de Pablos AL, Pintos G, Justa ML, Hidalgo-Barquero E, Fernández-Llama P, Ballarín J, Ars E, Torra R; FSGS Spanish Study Group (2009) Nephrin mutations cause childhood- and adult-onset focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 76(12):1268–1276
Savin VJ, Sharma R, Sharma M, McCarthy ET, Swan SK, Ellis E, Lovell H, Warady B, Gunwar S, Chonko AM, Artero M, Vincenti F (1996) Circulating factor associated with increased glomerular permeability to albumin in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med 334:878–883
Senggutuvan P, Cameron JS, Hartley RB, Rigden S, Chantler C, Haycock G, Williams DG, Ogg C, Koffman G (1990) Recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in transplanted kidneys: analysis of incidence and risk factors in 59 allografts. Pediatr Nephrol 4(1):21–28
Stefanidis CJ, Querfeld U (2011) The podocyte as a target: cyclosporin A in the management of the nephrotic syndrome caused by WT1 mutations. Eur J Pediatr (in press)
Tejani A, Ingulli E (1995) Cyclosporin in steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Contrib Nephrol 114:73–77
Tejani A, Stablein DH (1992) Recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis posttransplantation: a special report of the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2(12 Suppl):S258–S263
Tsukaguchi H, Sudhakar A, Le TC, Nguyen T, Yao J, Schwimmer JA, Schachter AD, Poch E, Abreu PF, Appel GB, Pereira AB, Kalluri R, Pollak MR (2002) NPHS2 mutations in late-onset focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: R229Q is a common disease-associated allele. J Clin Invest 110(11):1659–1666
Weber S, Gribouval O, Esquivel EL, Morinière V, Tête MJ, Legendre C, Niaudet P, Antignac C (2004) NPHS2 mutation analysis shows genetic heterogeneity of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome and low post-transplant recurrence. Kidney Int 66(2):571–579
Weins A, Kenlan P, Herbert S, Le TC, Villegas I, Kaplan BS, Appel GB, Pollak MR (2005) Mutational and biological analysis of alpha-actinin-4 in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(12):3694–3701
Winn MP, Conlon PJ, Lynn KL, Farrington MK, Creazzo T, Hawkins AF, Daskalakis N, Kwan SY, Ebersviller S, Burchette JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Howell DN, Vance JM, Rosenberg PB (2005) A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Science 308(5729):1801–1804
Winn MP, Conlon PJ, Lynn KL, Howell DN, Slotterbeck BD, Smith AH, Graham FL, Bembe M, Quarles LD, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM (1999) Linkage of a gene causing familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis to chromosome 11 and further evidence of genetic heterogeneity. Genomics 58(2):113–120
Yao J, Le TC, Kos CH, Henderson JM, Allen PG, Denker BM, Pollak MR (2004) Alpha-actinin-4-mediated FSGS: an inherited kidney disease caused by an aggregated and rapidly degraded cytoskeletal protein. PLoS Biol 2(6):e167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Büscher, A.K., Weber, S. Educational paper. Eur J Pediatr 171, 1151–1160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-011-1668-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-011-1668-2