Abstract
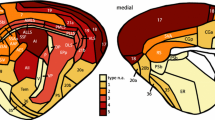
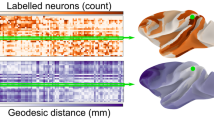
Structural connectivity among cortical areas provides the substrate for information exchange in the cerebral cortex and is characterized by systematic patterns of presence or absence of connections. What principles govern this cortical wiring diagram? Here, we investigate the relation of physical distance and cytoarchitecture with the connectional architecture of the mouse cortex. Moreover, we examine the relation between patterns of ipsilateral and contralateral connections. Our analysis reveals a mirrored and attenuated organization of contralateral connections when compared with ipsilateral connections. Both physical distance and cytoarchitectonic similarity of cortical areas are related to the presence or absence of connections. Notably, our analysis demonstrates that the combination of these factors relates better to cortico-cortical connectivity than each factor in isolation and that the two factors relate differently to ipsilateral and contralateral connectivity. Physical distance is more tightly related to the presence or absence of ipsilateral connections, but its relevance greatly diminishes for contralateral connections, while the contribution of cytoarchitectonic similarity remains relatively stable. Our results, together with similar findings in the cat and macaque cortex, suggest that a common set of principles underlies the macroscale wiring of the mammalian cerebral cortex.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbas H (1986) Pattern in the laminar origin of corticocortical connections. J Comp Neurol 252:415–422
Barbas H (2015) General cortical and special prefrontal connections: principles from structure to function. Ann Rev Neurosci 38:269–289
Barbas H, Hilgetag CC, Saha S, Dermon CR, Suski JL (2005) Parallel organization of contralateral and ipsilateral prefrontal cortical projections in the rhesus monkey. BMC Neurosci 6:32
Bastos AM, Vezoli J, Bosman CA, Schoffelen JM, Oostenveld R, Dowdall JR, De Weerd P, Kennedy H, Fries P (2015) Visual areas exert feedforward and feedback influences through distinct frequency channels. Neuron 85:390–401
Beul SF, Grant S, Hilgetag CC (2015a) A predictive model of the cat cortical connectome based on cytoarchitecture and distance. Brain Struct Funct 220:3167–3184
Beul SF, Barbas H, Hilgetag CC (2015b) A predictive structural model of the primate connectome. http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07222
Charvet CJ, Cahalane DJ, Finlay BL (2015) Systematic, cross-cortex variation in neuron numbers in rodents and primates. Cereb Cortex 25:147–160
Chen Y, Wang S, Hilgetag CC, Zhou C (2013) Trade-off between multiple constraints enables simultaneous formation of modules and hubs in neural systems. PLoS Comput Biol 9:e1002937
Chiang AS, Lin CY, Chuang CC, Chang HM, Hsieh CH, Yeh CW, Shih CT, Wu JJ, Wang GT, Chen YC et al (2011) Three-dimensional reconstruction of brain-wide wiring networks in Drosophila at single-cell resolution. Curr Biol 21:1–11
Costa LF, Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC (2007) Predicting the connectivity of primate cortical networks from topological and spatial node properties. BMC Syst Biol 1:16
Dombrowski SM, Hilgetag CC, Barbas H (2001) Quantitative architecture distinguishes prefrontal cortical systems in the rhesus monkey. Cereb Cortex 11:975–988
Ercsey-Ravasz M, Markov NT, Lamy C, Van Essen DC, Knoblauch K, Toroczkai Z, Kennedy H (2013) A predictive network model of cerebral cortical connectivity based on a distance rule. Neuron 80:184–197
French L, Pavlidis P (2011) Relationships between gene expression and brain wiring in the adult rodent brain. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1001049
Greilich H (1984) Quantitative Analyse der cortico-corticalen Fernverbindungen bei der Maus. Thesis, University of Tlibingen
Hilgetag CC, Grant S (2010) Cytoarchitectural differences are a key determinant of laminar projection origins in the visual cortex. NeuroImage 51:1006–1017
Ji S, Fakhry A, Deng W (2014) Integrative analysis of the connectivity and gene expression atlases of the mouse brain. NeuroImage 84:245–253
Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC (2006) Nonoptimal component placement, but short processing paths, due to long-distance projections in neural systems. PLoS Comput Biol 2:e95
Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC, van Ooyen A (2009) A simple rule for axon outgrowth and synaptic competition generates realistic connection lengths and filling fractions. Cereb Cortex 19:3001–3010
Ko H, Hofer SB, Pichler B, Buchanan K, Sjöström PJ, Mrsic-Flogel TD (2011) Functional specificity of local synaptic connections in neocortical networks. Nature 473:87–91
Lee CC, Winer J (2008a) Connections of cat auditory cortex: III. Corticocortical system. J Comp Neurol 507:1920–1943
Lee CC, Winer JA (2008b) Connections of cat auditory cortex: II. Commissural system. J Comp Neurol 507:1901–1919
Luppino G, Rozzi S, Calzavara R, Matelli M (2003) Prefrontal and agranular cingulate projections to the dorsal premotor areas F2 and F7 in the macaque monkey. Eur J Neurosci 17:559–578
Moretti P, Muñoz MA (2013) Griffiths phases and the stretching of criticality in brain networks. Nat Commun 4:2521
Müller-Linow M, Hilgetag CC, Hütt MT (2008) Organization of excitable dynamics in hierarchical biological networks. PLoS Comput Biol 4:e1000190
Oh SW et al (2014) A mesoscale connectome of the mouse brain. Nature 508:207–214
Pandya DN, Yeterian EH (1990) Prefrontal cortex in relation to other cortical areas in rhesus monkey: architecture and connections. In: Uylings HBM, van Eden CG, de Bruin JPC, Feenstra MGP, Pennartz CMA (eds) The prefrontal cortex: its structure, function and pathology. Progress in brain research, vol 85. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 6394
Paxinos G, Franklin K (2013) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic Press, London
Polleux F, Dehay C, Kennedy H (1997) The timetable of laminar neurogenesis contributes to the specification of corticla areas in mouse isocortex. J Comp Neurol 385:95–116
Rajkowska G, Kosmal A (1989) Contralateral connections of the dog’s frontal association cortex. Acta Neurobiol Exp 49:141–151
Rakic P (2002) Neurogenesis in adult primate neocortex: an evaluation of the evidence. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:65–71
Ramón y Cajal S (1899) Histology of the nervous system of man and the vertebrates, vol 1 (trans: N Swanson and LW Swanson), Ch 5. Oxford University Press, New York
Rao AR, Bandyopadhyay S (1996) A Markov chain Monte Carlo method for generating random (0,1)-matrices with given marginals. Sankhya A 58:225–242
Rubinov M, Ypma RJ, Watson C, Bullmore ET (2015) Wiring cost and topological participation of the mouse brain connectome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:10032–10037
Saito T, Rehmsmeier M (2015) The precision-recall plot is more informative than the ROC plot when evaluating binary classifiers on imbalanced datasets. PLoS One 10:e0118432
Scannell JW, Blakemore C, Young MP (1995) Analysis of connectivity in the cat cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 15:1463–1483
Smart IHM (1984) Histogenesis of the mesocortical area of the mouse telencephalon. J Anat 138:537–552
Sporns O, Tononi G, Edelman GM (2000) Theoretical neuroanatomy: Relating anatomical and functional connectivity in graphs and cortical connection matrices. Cereb Cortex 10:127–141
Sporns O, Tononi G, Kötter R (2005) The human connectome: a structural description of the human brain. PLoS Comput Biol 1:e42
Stark DE, Margulies DS, Shehzad ZE, Reiss P, Kelly AM, Uddin LQ, Gee DG, Roy AK, Banich MT, Castellanos FX, Milham MP (2008) Regional variation in interhemispheric coordination of intrinsic hemodynamic fluctuations. J Neurosci 28:13754–13764
Trusina A, Sneppen K, Dodd IB, Shearwin KE, Egan JB (2005) Functional alignment of regulatory networks: a study of temperate phages. PLoS Comput Biol 1:e74
Van De Werd HJJM, Uylings HBM (2014) Comparison of (stereotactic) parcellations in mouse prefrontal cortex. Brain Struct Funct 219:433–459
Van De Werd HJJM, Rajkowska G, Evers P, Uylings HBM (2010) Cytoarchitectonic and chemoarchitectonic characterization of the prefrontal cortical areas in the mouse. Brain Struct Funct 214:339–353
Vanduffel W, Payne BR, Lomber SG, Orban GA (1997) Functional impact of cerebral connections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:7617–7620
Varier S, Kaiser M (2011) Neural development features: spatio-temporal development of the Caenorhabditis elegans neuronal network. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1001044
Vidakovic B (2011) Statistics for bioengineering sciences, 1st edn. Springer, New York
Wang D, Buckner RL, Liu H (2014) Functional specialization in the human brain estimated by intrinsic hemispheric interaction. J Neurosci 34:12341–12352
Yeterian EH, Pandya DN, Tomaiuolo F, Petrides M (2012) The cortical connectivity of the prefrontal cortex in the monkey brain. Cortex 48:58–81
Young MP (1992) Objective analysis of the topological organization of the primate cortical visual system. Nature 358:152–155
Zingg B, Hintiryan H, Gou L, Song MY, Bay M, Bienkowski MS, Foster NN, Yamashita S, Bowman I, Toga AW, Dong HW (2014) Neural networks of the mouse neocortex. Cell 156:1096–1111
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Humboldt research fellowship from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation to AG and funding by the German Research Council DFG to CCH (SFB 936/A1,Z3; TRR169/A2). The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulas, A., Uylings, H.B.M. & Hilgetag, C.C. Principles of ipsilateral and contralateral cortico-cortical connectivity in the mouse. Brain Struct Funct 222, 1281–1295 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1277-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1277-y