Abstract
Cholinergic and non-cholinergic neurons in the brainstem pedunculopontine (PPT) and laterodorsal tegmental (LDT) nuclei innervate diverse forebrain structures. The cholinergic neurons within these regions send heavy projections to thalamic nuclei and provide modulatory input as well to midbrain dopamine cells in the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Cholinergic PPT/LDT neurons are known to send collateralized projections to thalamic and non-thalamic targets, and previous studies have shown that many of the afferents to the VTA arise from neurons that also project to midline and intralaminar thalamic nuclei. However, whether cholinergic projections to the VTA and anterior thalamus (AT) are similarly collateralized is unknown. Ultrastructural work from our laboratory has demonstrated that cholinergic axon varicosities in these regions differ both morphologically and with respect to the expression and localization of the high-affinity choline transporter. We therefore hypothesized that the cholinergic innervation to these regions is provided by separate sets of PPT/LDT neurons. Dual retrograde tract-tracing from the AT and VTA indicated that only a small percentage of the total afferent population to either region showed evidence of providing collateralized input to the other target. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic cells displayed a similarly low percentage of collateralization. These results are contrasted to a control case in which retrograde labeling from the midline paratenial thalamic nucleus and the VTA resulted in higher percentages of cholinergic and non-cholinergic dual-tracer labeled cells. Our results indicate that functionally distinct limbic target regions receive primarily segregated signaling from PPT/LDT neurons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton JP, O’Mara SM, Vann SD, Wright NF, Tsanov M, Erichsen JT (2010) Hippocampal-anterior thalamic pathways for memory: uncovering a network of direct and indirect actions. Eur J Neurosci 31:2292–2307
Angelucci A, Clascá F, Sur M (1996) Anterograde axonal tracing with the subunit B of cholera toxin: a highly sensitive immunohistochemical protocol for revealing fine axonal morphology in adult and neonatal brains. J Neurosci Methods 65:101–112
Barbas H, Henion TH, Dermon CR (1991) Diverse thalamic projections to the prefrontal cortex in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 313:65–94
Beckstead RM, Domesick VB, Nauta WJ (1979) Efferent connections of the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area in the rat. Brain Res 175:191–217
Beninato M, Spencer RF (1987) A cholinergic projection to the rat substantia nigra from the pedunculopontine nucleus. Brain Res 412:169–174
Berger B, Gaspar P, Verney C (1991) Dopaminergic innervation of the cerebral cortex: unexpected differences between rodents and primates. Trends Neurosci 14:21–27
Billet S, Cant NB, Hall WC (1999) Cholinergic projections to the visual thalamus and superior colliculus. Brain Res 847:121–123
Bolton RF, Cornwall J, Phillipson OT (1993) Collateral axons of cholinergic pontine neurones projecting to midline, mediodorsal and parafascicular thalamic nuclei in the rat. J Chem Neuroanat 6:101–114
Boucetta S, Jones BE (2009) Activity profiles of cholinergic and intermingled GABAergic and putative glutamatergic neurons in the pontomesencephalic tegmentum of urethane-anesthetized rats. J Neurosci 29:4664–4674
Chen S, Aston-Jones G (1995) Evidence that cholera toxin B subunit (CTb) can be avidly taken up and transported by fibers of passage. Brain Res 674:107–111
Cornwall J, Phillipson O (1988) Quantitative analysis of axonal branching using the retrograde transport of fluorescent latex microspheres. J Neurosci Methods 24:1–9
Cornwall J, Phillipson O (1989) Single neurones of the basal forebrain and laterodorsal tegmental nucleus project by collateral axons to the olfactory bulb and the mediodorsal nucleus in the rat. Brain Res 491:194–198
Cornwall J, Cooper JD, Phillipson OT (1990) Afferent and efferent connections of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus in the rat. Brain Res Bull 25:271–284
Crawley J, Olschowka J, Diz D, Jacobowitz D (1985) Behavioral significance of the coexistence of substance P, corticotropin releasing factor, and acetylcholinesterase in lateral dorsal tegmental neurons projecting to the medial frontal cortex of the rat. Peptides 6:891–901
Dado RJ, Burstein R, Cliffer KD, Giesler GJJ (1990) Evidence that Fluoro-Gold can be transported avidly through fibers of passage. Brain Res 533:329–333
Datta S, Siwek DF (2002) Single cell activity patterns of pedunculopontine tegmentum neurons across the sleep–wake cycle in the freely moving rats. J Neurosci Res 70:611–621
Del-Fava F, Hasue RH, Ferreira JG, Shammah-Lagnado SJ (2007) Efferent connections of the rostral linear nucleus of the ventral tegmental area in the rat. Neuroscience 145:1059–1076
Domesick VB (1969) Projections from the cingulate cortex in the rat. Brain Res 12:296–320
el Mansari M, Sakai K, Jouvet M (1989) Unitary characteristics of presumptive cholinergic tegmental neurons during the sleep–waking cycle in freely moving cats. Exp Brain Res 76:519–529
Emre M (2003) What causes mental dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease? Mov Disord 18:S63–S71
Erro E, Lanciego JL, Giménez-Amaya JM (1999) Relationships between thalamostriatal neurons and pedunculopontine projections to the thalamus: a neuroanatomical tract-tracing study in the rat. Exp Brain Res 127:162–170
Ferguson S, Savchenko V, Apparsundaram S, Zwick M, Wright J, Heilman C, Yi H, Levey A, Blakely R (2003) Vesicular localization and activity-dependent trafficking of presynaptic choline transporters. J Neurosci 23:9697–9709
Garcia-Cabezas MA, Martinez-Sanchez P, Sanchez-Gonzalez MA, Garzon M, Cavada C (2009) Dopamine innervation in the thalamus: monkey versus rat. Cereb Cortex 19:424–434
Geisler S, Zahm DS (2005) Afferents of the ventral tegmental area in the rat-anatomical substratum for integrative functions. J Comp Neurol 490:270–294
Giménez-Amaya J, McFarland N, de Las Heras S, Haber S (1995) Organization of thalamic projections to the ventral striatum in the primate. J Comp Neurol 354:127–149
Gonzalo-Ruiz A, Lieberman AR (1995) GABAergic projections from the reticular nucleus to the anteroventral and anterodorsal thalamic nuclei of the rat. J Chem Neuroanat 9:165–174
Gonzalo-Ruiz A, Sanz-Anquela MJ, Lieberman AR (1995) Cholinergic projections to the anterior thalamic nuclei in the rat: a combined retrograde tracing and choline acetyl transferase immunohistochemical study. Anat Embryol 192:335–349
Grant SJ, Highfield DA (1991) Extracellular characteristics of putative cholinergic neurons in the rat laterodorsal tegmental nucleus. Brain Res 559:64–74
Hallanger AE, Wainer BH (1988) Ascending projections from the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus and the adjacent mesopontine tegmentum in the rat. J Comp Neurol 274:483–515
Hallanger AE, Levey AI, Lee HJ, Rye DB, Wainer BH (1987) The origins of cholinergic and other subcortical afferents to the thalamus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 262:105–124
Halliday GM, Li YW, Blumbers PC, Joh TH, Cotton RG, Howe PR, Blessing WW, Geffen LB (1990) Neuropathology of immunohistochemically identified brainstem neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 27:373–385
Heckers S, Geula C, Mesulam MM (1992) Cholinergic innervation of the human thalamus: dual origin and differential nuclear distribution. J Comp Neurol 325:68–82
Hirsch EC, Graybiel AM, Duyckaerts C, Javoy-Agid F (1987) Neuronal loss in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in Parkinson disease and in progressive supranuclear palsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5976–5980
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl Å, Fuxe K, Johansson O (1974) Dopamine nerve terminals in the rat limbic cortex: aspects of the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Science 184:177–179
Holmstrand EC, Sesack SR (2004) Cholinergic neurons in the rat mesopontine tegmentum comprise about one quarter of the projection to the ventral tegmental area, Society for Neuroscience abstracts, vol 30, abstract 45.2
Holmstrand E, Asafu-Adjei J, Sampson A, Blakely R, Sesack S (2010) Ultrastructural localization of high-affinity choline transporter in the rat anteroventral thalamus and ventral tegmental area: differences in axon morphology and transporter distribution. J Comp Neurol 518:1908–1924
Ichikawa T, Ajiki K, Matsuura J, Misawa H (1997) Localization of two cholinergic markers, choline acetyltransferase and vesicular acetylcholine transporter in the central nervous system of the rat: in situ hybridization histochemistry and immunohistochemistry. J Chem Neuroanat 13:23–39
Inglis WI, Winn P (1995) The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus: where the striatum meets the reticular formation. Prog Neurobiol 47:1–29
Jellinger KA (1991) Pathology of Parkinson’s disease. Changes other than the nigrostriatal pathway. Mol Chem Neuropathol 14:153–197
Jones BE, Webster HH (1988) Neurotoxic lesions of the dorsolateral pontomesencephalic tegmentum-cholinergic cell area in the cat. I. Effects upon the cholinergic innervation of the brain. Brain Res 451:13–32
Jourdain A, Semba K, Fibiger HC (1989) Basal forebrain and mesopontine tegmental projections to the reticular thalamic nucleus: an axonal collateralization and immunohistochemical study in the rat. Brain Res 505:55–65
Karson CN, Garcia-Rill E, Biedermann J, Mrak RE, Husain MM, Skinner RD (1991) The brain stem reticular formation in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Res 40:31–48
Katz L, Burkhalter A, Dreyer W (1984) Fluorescent latex microspheres as a retrograde neuronal marker for in vivo and in vitro studies of visual cortex. Nature 310:498–500
Kobayashi Y, Isa T (2002) Sensory-motor gating and cognitive control by the brainstem cholinergic system. Neural Netw 15:731–741
Kolmac C, Mitrofanis J (1998) Patterns of brainstem projection to the thalamic reticular nucleus. J Comp Neurol 396:531–543
Koyama Y, Jodo E, Kayama Y (1994) Sensory responsiveness of “broad-spike” neurons in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus, locus coeruleus and dorsal raphe of awake rats: implication for cholinergic and monoaminergic neuron-specific responses. Neuroscience 63:1021–1031
Krauthamer GM, Grunwerg BS, Krein H (1995) Putative cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus projecting to the superior colliculus consist of sensory responsive and unresponsive populations which are functionally distinct from other mesopontine neurons. Neuroscience 69:507–517
Leonard CS, Llinas R (1994) Serotonergic and cholinergic inhibition of mesopontine cholinergic neurons controlling REM sleep: an in vitro electrophysiological study. Neuroscience 59:309–330
Leonard CS, Llinás RR (1990) Electrophysiology of mammalian pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental neurons in vitro: Implications for the control of REM sleep. In: Steriade M, Biesold D (eds) Brain cholinergic systems. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 205–223
Lindvall O, Björklund A, Moore R, Stenevi U (1974) Mesencephalic dopamine neurons projecting to neocortex. Brain Res 81:325–331
Liu Y, Edwards RH (1997) Differential localization of vesicular acetylcholine and monoamine transporters in PC12 cells but not CHO cells. J Cell Biol 139:907–916
Losier BJ, Semba K (1993) Dual projections of single cholinergic and aminergic brainstem neurons to the thalamus and basal forebrain in the rat. Brain Res 604:41–52
Loughlin S, Fallon J (1984) Substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area projections to cortex: topography and collateralization. Neuroscience 11:425–435
Luppi P-H, Fort P, Jouvet M (1990) Iontophoretic application of unconjugated cholera toxin B subunit (CTb) combined with immunohistochemistry of neurochemical substances: a method for transmitter identification of retrogradely labeled neurons. Brain Res 534:209–224
Mclean IW, Nakane PK (1974) Periodate–lysine–paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 22:1077–1083
McRitchie DA, Hardman CD, Halliday GM (1996) Cytoarchitectural distribution of calcium binding proteins in midbrain dopaminergic regions of rats and humans. J Comp Neurol 364:121–150
Melchitzky DS, Erickson SL, Lewis DA (2006) Dopamine innervation of the monkey mediodorsal thalamus: location of projection neurons and ultrastructural characteristics of axon terminals. Neuroscience 143:1021–1030
Mena-Segovia J, Winn P, Bolam JP (2008) Cholinergic modulation of midbrain dopaminergic systems. Brain Res. Rev 58:265–271
Mena-Segovia J, Micklem BR, Nair-Roberts RG, Ungless MA, Bolam JP (2009) GABAergic neuron distribution in the pedunculopontine nucleus defines functional subterritories. J Comp Neurol 515:397–408
Mesulam M-M (1995) Structure and function of cholinergic pathways in the cerebral cortex, limbic system, basal ganglia, and thalamus of the human brain. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven Press, New York. http://www.acnp.org/g4/GN401000012/Default.htm. Accessed 02/02/2011
Mesulam M, Mufson E, Wainer B, Levey A (1983) Central cholinergic pathways in the rat: an overview based on an alternative nomenclature (Ch1–Ch6). Neuroscience 10:1185–1201
Niimi K, Niimi M, Okada Y (1978) Thalamic afferents to the limbic cortex in the cat studied with the method of retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res 145:225–238
Oakman S, Faris P, Kerr P, Cozzari C, Hartman B (1995) Distribution of pontomesencephalic cholinergic neurons projecting to substantia nigra differs significantly from those projecting to ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 15:5859–5869
Omelchenko N, Sesack S (2006) Cholinergic axons in the rat ventral tegmental area synapse preferentially onto mesoaccumbens dopamine neurons. J Comp Neurol 494:863–875
Pakan J, Graham D, Iwaniuk A, Wylie D (2008) Differential projections from the vestibular nuclei to the flocculus and uvula-nodulus in pigeons (Columba livia). J Comp Neurol 508:402–417
Pan W, Hyland B (2005) Pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus controls conditioned responses of midbrain dopamine neurons in behaving rats. J Neurosci 25:4725–4732
Pascoe JP, Kapp BS (1993) Electrophysiology of the dorsolateral mesopontine reticular formation during pavlovian conditioning in the rabbit. Neuroscience 54:753–772
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic co-ordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA
Reep R (1984) Relationship between prefrontal and limbic cortex: a comparative anatomical review. Brain Behav Evol 25:5–80
Reese NB, Garcia-Rill E, Skinner RD (1995) The pedunculopontine nucleus—auditory input, arousal and pathophysiology. Prog Neurobiol 42:105–133
Sanders KH, Klein CE, Mayer TE, Heym CH, Handwerker HO (1980) Differential effects of noxious and non-noxious input on neurones according to location in ventral periaqueductal grey or dorsal raphe nucleus. Brain Res 186:83–97
Satoh K, Fibiger HC (1986) Cholinergic neurons of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus: efferent and afferent connections. J Comp Neurol 253:277–302
Schmeichel AM, Buchhalter LC, Low PA, Parisi JE, Boeve BW, Sandroni P, Benarroch EE (2008) Mesopontine cholinergic neuron involvement in Lewy body dementia and multiple system atrophy. Neurology 70:368–373
Schofield BR (2008) Retrograde axonal tracing with fluorescent markers. Curr Prot Neurosci 43:1–24
Sesack SR, Grace AA (2010) Cortico-basal ganglia reward network: microcircuitry. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:27–47
Shibata H (1992) Topographic organization of subcortical projections to the anterior thalamic nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol 323:117–127
Shibata H (1993) Efferent projections from the anterior thalamic nuclei to the cingulate cortex in the rat. J Comp Neurol 330:533–542
Shibata H, Kato A (1993) Topographic relationship between anteromedial thalamic nucleus neurons and their cortical terminal fields in the rat. Neurosci Res 17:63–69
Shibata H, Honda Y, Sasaki H, Naito J (2009) Organization of intrinsic connections of the retrosplenial cortex in the rat. Anat. Sci. Int 84:280–292
Smith Y, Raju D, Nanda B, Pare J, Galvan A, Wichmann T (2009) The thalamostriatal systems: anatomical and functional organization in normal and parkinsonian states. Brain Res Bull 78:60–68
Sofroniew M, Priestley J, Consolzaione A, Eckenstein F, Cuello A (1985) Cholinergic projections from the midbrain and pons to the thalamus in the rat, identified by combined retrograde tracing and choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry. Brain Res 329:213–223
Steriade M, Datta S, Paré D, Oakson G, Curró Dossi R (1990a) Neuronal activities in brain-stem cholinergic nuclei related to tonic activation processes in thalamocortical systems. J Neurosci 10:2541–2559
Steriade M, Paré D, Datta S, Oakson G, Curro Dossi R (1990b) Different cellular types in mesopontine cholinergic nuclei related to ponto-geniculo-occipital waves. J Neurosci 10:2560–2579
Swanson LW (1982) The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res Bull 9:321–353
Vertes R (2006) Interactions among the medial prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and midline thalamus in emotional and cognitive processing in the rat. Neuroscience 142:1–20
Vertes RP, Hoover WB (2008) Projections of the paraventricular and paratenial nuclei of the dorsal midline thalamus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 508:212–237
Wang HL, Morales M (2009) Pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei contain distinct populations of cholinergic, glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 29:340–358
Xu L, Ryugo D, Pongstaporn T, Johe K, Koliatsos V (2009) Human neural stem cell grafts in the spinal cord of SOD1 transgenic rats: differentiation and structural integration into the segmental motor circuitry. J Comp Neurol 514:297–309
Xuereb JH, Perry EK, Candy JM, Bonham JR, Perry RH, Marshall E (1990) Parameters of cholinergic neurotransmission in the thalamus in Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 99:185–197
Yeomans JS (1995) Role of tegmental cholinergic neurons in dopaminergic activation, antimuscarinic psychosis and schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 12:3–16
Zhang J-H, Sampogna S, Morales FR, Chase MH (2005) Age-related changes in cholinergic neurons in the laterodorsal and the pedunculo-pontine tegmental nuclei of cats: a combined light and electron microscopic study. Brain Res 1052:47–55
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by United States Public Health Service grant MH067937.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
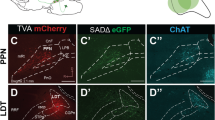
Montage of three-channel fluorescence images through the PPT of Case 37 demonstrates the intermingling of AT-projecting and VTA-projecting neurons within this nucleus. For each individual field, multiple focal planes were used to create a three dimensional projection in Image J that was subsequently flattened to display all the labeled neurons as if they lay within a single plane. These flattened images were then aligned to show the distribution of cells throughout the PPT at this particular rostrocaudal level. Similar to the schematic presented in Fig. 6, the lack of gross segregation of AT- and VTA-projecting neurons can be appreciated in this region. Additionally, by downloading the figure and manipulating the display of individual fluorescence channels, the specific combinations of labeling may be confirmed. Scale bar equals 100 μm. Abbreviations: scp, superior cerebellar peduncle. (TIFF 22113 kb)
Online Resource 2
Montage of three-channel fluorescence images through the dorsal LDT of Case 37 demonstrating the intermingling of AT-projecting and VTA-projecting neurons within this nucleus. Image creation was the same as for Online Resource 1. Scale bar equals 200 μm. Abbreviations: dtg, dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden; 4 V, fourth ventricle; mlf; medial longitudinal fasciculus. (TIFF 29549 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmstrand, E.C., Sesack, S.R. Projections from the rat pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei to the anterior thalamus and ventral tegmental area arise from largely separate populations of neurons. Brain Struct Funct 216, 331–345 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-011-0320-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-011-0320-2