Abstract
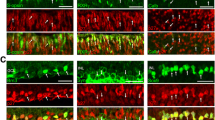
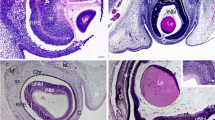
According to observations in various cell lines, elimination of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1) during the late G1 phase of the cell cycle is required for progression to the S phase. Eyes from C57BL/6 mice at embryonic days 13, 14, and 18, and at 4 weeks of age, were analyzed by a bromodeoxyuridine cell proliferation assay and by immunocytochemistry using anti-p27(KIP1) antibody. On embryonic days 14 and 18, p27(KIP1) was detected in the ciliary body. This protein also was detected in the nuclei of the many cells of the retinal pigment epithelium on embryonic day 18, and was present in all such cells at 4 weeks of age. When p27(KIP1)-/- knockout and control mice were injected with bromodeoxyuridine between postnatal days 7 and 10 and analyzed on day 11, positive cells were abundant in the retinal pigment epithelium and the ciliary body of p27(KIP1)-/- mice, whereas few cells were positive in control mice. By fluorescent nuclear staining in whole mounts of retinal pigment epithelium at 12 weeks of age, more nuclei were present in p27(KIP1)-/- than in the wild-type mice. These results suggest that p27(KIP1) was involved in regulation of proliferation in the RPE and the ciliary body.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bard JB, Ross AS (1982) The morphogenesis of the ciliary body of the avian eye. I. Lateral cell detachment facilitates epithelial folding. Dev Biol 92: 73–86
Blagosklonny MV, Wu GS, Omura S, el-Deiry WS (1996) Proteasome-dependent regulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 227:564–569
Bodenstein L, Sidman RL (1987) Growth and development of the mouse retinal pigment epithelium. I. Cell and tissue morphometrics and topography of mitotic activity. Dev Biol 121:192–204
Coats S, Flanagan WM, Nourse J, Roberts JM (1996) Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science 272:877–880
de Nooij JC, Letendre MA, Hariharan IK (1996) A cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, Dacapo, is necessary for timely exit from the cell cycle during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell 87:1237–1247
Dyer MA, Cepko CL (2000) Control of Muller glial cell proliferation and activation following retinal injury. Nat Neurosci 3:873–880
Harada T, Harada C, Watanabe M, Inoue Y, Sakagawa T, Nakayama N, Sasaki S, Okuyama S, Watase K, Wada K, Tanaka K (1998) Functions of the two glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT-1 in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4663–4666
Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1996) Cdk inhibitors in development and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6:56–64
Hirai A, Nakamura S, Noguchi Y, Yasuda T, Kitagawa M, Tatsuno I, Oeda T, Tahara K, Terano T, Narumiya S, Kohn LD, Saito Y (1997) Geranylgeranylated rho small GTPase(s) are essential for the degradation of p27Kip1 and facilitate the progression from G1 to S phase in growth-stimulated rat FRTL-5 cells. J Biol Chem 272:13–16
Hong Y, Roy R, Ambros V (1998) Developmental regulation of a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor controls postembryonic cell cycle progression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 125:3585–3597
Kato JY, Matsuoka M, Polyak K, Massague J, Sherr CJ (1994) Cyclic AMP-induced G1 phase arrest mediated by an inhibitor (p27Kip1) of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 activation. Cell 79:487–496
Kuwabara T, Weidman TA (1974) Development of the prenatal rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol 13:725–739
Lane ME, Sauer K, Wallace K, Jan YN, Lehner CF, Vaessin H (1996) Dacapo, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, stops cell proliferation during Drosophila development. Cell 87:1225–1235
Levine EM, Close J, Fero M, Ostrovsky A, Reh TA (2000) p27(Kip1) regulates cell cycle withdrawal of late multipotent progenitor cells in the mammalian retina. Dev Biol 219:299–314
Nakayama K, Ishida N, Shirane M, Inomata A, Inoue T, Shishido N, Horii I, Loh DY (1996) Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell 85:707–720
Nourse J, Firpo E, Flanagan WM, Coats S, Polyak K, Lee MH, Massague J, Crabtree GR, Roberts JM (1994) Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature 372:570–573
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V, Yew PR, Draetta GF, Rolfe M (1995) Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science 269:682–685
Polyak K, Lee MH, Erdjument-Bromage H, Koff A, Roberts JM, Tempst P, Massague J (1994) Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell 78:59–66
Reynisdottir I, Polyak K, Lavarone A, Massague J (1995) Kip/Cip and Ink4 Cdk inhibitors cooperate to induce cell cycle arrest in response to TGF-beta. Genes Dev 9:1831–1845
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1995) Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 9:1149–1163
Shirane M, Harumiya Y, Ishida N, Hirai A, Miyamoto C, Hatakeyama S, Nakayama K, Kitagawa M (1999) Down-regulation of p27(Kip1) by two mechanisms, ubiquitin-mediated degradation and proteolytic processing. J Biol Chem 274:13886–13893
Thanos D, Maniatis T (1995) NF-kappa B: a lesson in family values. Cell 80:529–532
Toyoshima H, Hunter T (1994) p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell 78:67–74
Yoshida K, Hu Y, Karin M (2000) IkappaB Kinase alpha Is essential for development of the mammalian cornea and conjunctiva. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3665–3669
Yoshida K, Behrens A, Le-Niculescu H, Wagner EF, Harada T, Imaki J, Ohno S, Karin M (2002a) Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates apoptosis in the retinal ganglion cells by optic nerve Ttransection. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1631–1635
Yoshida K, Nakayama K, Nagahama H, Harada T, Harada C, Imaki J, Matsuda A, Yamamoto K, Ito M, Ohno S, Nakayama KI (2002b) Involvement of p27(KIP1) degradation by Skp2 in the regulation of proliferation in response to wounding of corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:364–370
Zhang P, Wong C, DePinho RA, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1998) Cooperation between the Cdk inhibitors p27(KIP1) and p57(KIP2) in the control of tissue growth and development. Genes Dev 12:3162–3167
Zhang P, Wong C, Liu D, Finegold M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1999) p21(CIP1) and p57(KIP2) control muscle differentiation at the myogenin step. Genes Dev 13:213–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, K., Nakayama, K., Kase, S. et al. Involvement of p27(KIP1) in proliferation of the retinal pigment epithelium and ciliary body. Anat Embryol 208, 145–150 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-004-0382-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-004-0382-5