Abstract
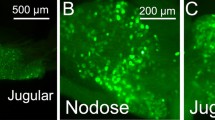
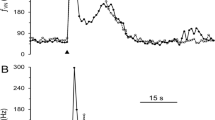
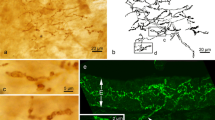
Intraganglionic laminar endings (IGLEs) represent the most prominent vagal afferent terminal structures throughout the gastrointestinal tract. They are most prominent in the esophagus and stomach, but can be found down to the distal colon. Their role as mechanosensors as proposed on anatomical grounds was recently substantiated in elegant functional experiments. There is evidence that vagal mechanosensors in the esophagus and stomach respond to ATP. Thus, the present study aimed at detecting purinergic receptors on IGLEs. IGLEs in the rat esophagus were identified by immunohistochemistry for calretinin and sections were co-incubated with antibodies directed against P2X2 or P2X3 receptors. Also, double label immunocytochemistry for purinergic receptors and calcitonin gene-related peptide as a marker for spinal afferents was performed. Terminal nerve fibers immunoreactive for P2X2 and P2X3, respectively, were observed between outer and inner layers of the tunica muscularis, covering myenteric ganglia totally or partly. Both P2X2 and P2X3 receptor immunoreactivities were highly co-localized with calretinin positive IGLEs as shown by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Numerous calcitonin gene-related peptide immunostained fibers were found to closely approach and intermingle with P2X immunopositive IGLEs. However, there was never co-staining for either of the purinergic receptors and calcitonin gene-related peptide within the same fibers. P2X3 but not P2X2 immunoreactivity was also observed within nerve fiber arborizations in the mucosa of the pharynx. In the nodose ganglion, 8.9±1.1% of P2X2 and 7.2±1.3% of P2X3 immunopositive neurons, respectively, co-stained for calretinin. On the other hand, 63.4±4.6% and 60.1±5.3% of calretinin positive cell bodies contained P2X2 and P2X3 receptor immunoreactivity, respectively. These results indicate that IGLEs are equipped with both P2X2 and P2X3 receptors. Thus, they may act as chemosensors or their mechanosensory properties may be modulated by ATP. It is also suggested that spinal afferents innervating the esophagus are equipped with neither P2X2 nor P2X3 purinergic receptors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G (1994) Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptor? Pharmacol Ther 64:445–475
Adriaensen D, Timmermans JP, Brouns I, Berthoud HR, Neuhuber WL, Scheuermann DW (1998) Pulmonary intraepithelial vagal nodose afferent nerve terminals are confined to neuroepithelial bodies: an anterograde tracing and confocal microscopy study in adult rats. Cell Tissue Res 293:395–405
Bardoni R, Goldstein PA, Lee CJ, Gu JG, MacDermott AB (1997) ATP P2X receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 17:5297–5304
Berthoud HR, Patterson LM, Neumann F, Neuhuber WL (1997A) Distribution and structure of vagal afferent intraganglionic laminar endings (IGLEs) in rat gastrointestinal tract. Anat Embryol (Berl) 195:183–191
Berthoud HR, Patterson LM, Willing AE, Müller K, Neuhuber WL (1997B) Capsaicin-resistant vagal afferent fibers in the rat gastrointestinal tract: Anatomical identification and functional integrity. Brain Res 746:195–206
Bradbury EJ, Burnstock G, McMahon SB (1998) The expression of P2X3 purinoreceptors in sensory neurons: effects of axotomy and glial-derived neurotrophic factor. Mol Cell Neurosci 12:256–268
Brierley SM, Nichols K, Grasby DJ, Waterman SA (2001) Neural mechanisms underlying migrating motor complex formation in mouse isolated colon. Br J Pharmacol 132:507–517
Brouns I, Adriaensen D, Burnstock G, Timmermans JP (2000) Intraepithelial vagal sensory nerve terminals in rat pulmonary neuroepithelial bodies express P2X(3) receptors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23:52–61
Burnstock G (1978) A basis for distinguishing two types of purinergic receptor. In: Straub RW, Bolis L (eds) Cell membrane receptors for drugs and hormones. A multidisciplinary approach. Raven Press, New York, pp 107–118
Burnstock G (1990) Local mechanisms of blood flow control by perivascular nerves and endothelium. J Hypertens Suppl 8:S95–106
Burnstock G (1996) Development and perspectives of the purinoceptor concept. J Auton Pharmacol 16:295–302
Burnstock G (1997) The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signalling molecules. Neuropharmacology 36:127–1139
Burnstock G, Kennedy C (1985) Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptors? Gen Pharmacol 16:433–440
Burnstock G, King BF (1996) Numbering of cloned P2 purinoceptors. Drug Dev Res 8:67–71
Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Poole DP, Furness JB (2002) Distribution of purine P2X2 receptors in the guinea-pig enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol 117:415–422
Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Furness JB (2003) P2X2 purine receptor immunoreactivity of intraganglionic laminar endings in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 312:167–174
Chen CC, Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Colquhoun D, Burnstock G, Wood JN (1995) A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature 377:428–431
Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Burnstock G (2001) P2X receptors in peripheral neurons. Progress in Neurobiology 65:107–134
Dütsch MS, Eichhorn U, Wörl J, Wank M, Berthoud HR, Neuhuber WL (1998) Vagal and spinal afferent innervation of the rat esophagus: A combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study with special emphasis on calcium-binding proteins. J Comp Neurol 398:289–307
Edwards FA, Gibb AJ, Colquhoun D (1992) ATP receptors mediate synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature 359:144–147
Evans RJ, Derkach V, Surprenant A (1992) ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature 359:503–505
Facer P, Knowles CH, Tam PK, Ford AP, Dyer N, Baecker PA, Anand P (2001) Novel capsaicin (VR1) and purinergic (P2X3) receptors in Hirschsprung’s intestine. J Pediatr Surg 36:1679–1684
Galligan JJ, Bertrand PP (1994) ATP mediates fast synaptic potentials in enteric neurons. J Neurosci 14:7563-7571
Galligan JJ, LePard KJ, Schneider DA, Zhou X (2000) Multiple mechanisms of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst 81:97–103
Green T, Dockray GJ (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in afferents to the upper gastrointestinal tract in the rat. Neurosci Lett 76:151–156
Hu HZ, Gao N, Lin Z, Gao C, Liu S, Ren J, Xia Y, Wood JD (2001) P2X(7) receptors in the enteric nervous system of guinea-pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol 440:299–310
Hubscher CH, Petruska JC, Rau KK, Johnson RD (2001) Co-expression of P2X receptor subunits on rat nodose neurons that bind the isolectin GS-I-B4. Neuroreport 12:2995–2997
Kirkup AJ, Booth CE, Chessell IP, Humphrey PP, Grundy D (1999) Excitatory effect of P2X receptor activation on mesenteric afferent nerves in the anaesthetised rat. J Physiol 520:551–563
Kressel M, Radespiel-Tröger M (1999) Anterograde tracing and immunohistochemical characterization of potentially mechanosensitive vagal afferents in the esophagus. J Comp Neurol 412:61–72
Kuramoto H, Kuwano R (1995) Location of sensory nerve cells that provide calbindin-containing laminar nerve endings in myenteric ganglia of the rat esophagus. J Auton Nerv Syst 54:126–136
Lewis C, Neidhart S, Holy C, North RA, Buell G, Surprenant A (1995) Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature 377:432–435
Lindh B, Aldskogius H, Hokfelt T (1989) Simultaneous immunohistochemical demonstration of intra-axonally transported markers and neuropeptides in the peripheral nervous system of the guinea pig. Histochemistry 92:367–376
McConalogue K, Todorov L, Furness JB, Westfall DP (1996) Direct measurement of the release of ATP and its major metabolites from the nerve fibres of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 23:807–812
Namasivayam S, Eardley I, Morrison JF (1999) Purinergic sensory neurotransmission in the urinary bladder: an in vitro study in the rat. BJU Int 84:854–860
Neuhuber WL (1987) Sensory vagal innervation of the rat esophagus and cardia: a light and electron microscopic anterograde tracing study. J Auton Nerv Syst 20:243–255
Neuhuber WL, Clerc N (1990) Afferent innervation of the esophagus in cat and rat. In: Zenker W, Neuhuber WL (eds) The primary afferent neuron. A survey of recent morpho-functional aspects. Plenum Press, New York, pp 93–107
Page AJ, Martin CM, Blackshaw LA (2002) Vagal mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors in mouse stomach and esophagus. J Neurophysiol 87:2095–2103
Petruska JC, Cooper BY, Gu JG, Rau KK, Johnson RD (2000) Distribution of P2X1, P2X2, and P2X3 receptor subunits in rat primary afferents: relation to population markers and specific cell types. J Chem Neuroanat 20:141–162
Poole DP, Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Chiocchetti R, Furness JB (2002) The distribution of P2X3 purine receptor subunits in the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Auton Neurosci 101:39–47
Prasad M, Fearon IM, Zhang M, Laing M, Vollmer C, Nurse CA (2001) Expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits in rat carotid body afferent neurones: role in chemosensory signalling. J Physiol 537:667–677
Rodrigo J, Hernandez CJ, Vidal MA, Pedrosa JA (1975) Vegetative innervation of the esophagus. II. Intraganglionic laminar endings. Acta Anat (Basel) 92:79–100
Rodrigo J, De Felipe J, Robles-Chillida EM, Perez Anton JA, Mayo I, Gomez A (1982) Sensory vagal nature and anatomical access paths to esophagus laminar endings in myenteric ganglia. Determination by surgical degeneration methods. Acta Anat (Basel) 112:47–57
Sternini C (1992) Enteric and visceral afferent CGRP neurons: targets of innervation and differential expression patterns. Ann N Y Acad Sci 657:170–186
Van Nassauw L, Brouns I, Adriaensen D, Timmermans JP (2002) Neurochemical identification of enteric neurons expressing P2X3 receptors in the guinea-pig ileum. Histochem Cell Biol 118:193–203
Vlaskovska M, Kasakov L, Rong W, Bodin P, Bardini M, Cockayne DA, Ford AP, Burnstock G (2001) P2X3 knock-out mice reveal a major sensory role for urothelially released ATP. J Neurosci 21:5670–5677
Vulchanova L, Arvidsson U, Riedl M, Wang J, Buell G, Surprenant A, North RA, Elde R (1996) Differential distribution of two ATP-gated channels (P2X receptors) determined by immunocytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8063–8067
Vulchanova L, Riedl MS, Shuster SJ, Buell G, Surprenant A, North RA, Elde R (1997) Immunohistochemical study of the P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits in rat and monkey sensory neurons and their central terminals. Neuropharmacology 36:1229–1242
Wang FB, Powley TL (2000) Topographic inventories of vagal afferents in gastrointestinal muscle. J Comp Neurol 421:302–324
Xiang Z, Bo X, Burnstock G (1998) Localization of ATP-gated P2X receptor immunoreactivity in rat sensory and sympathetic ganglia. Neurosci Lett 256:105–108
Yiangou Y, Facer P, Birch R, Sangameswaran L, Eglen R, Anand P (2000) P2X3 receptor in injured human sensory neurons. Neuroreport 11:993–996
Zagorodnyuk VP, Brookes SJ (2000) Transduction sites of vagal mechanoreceptors in the guinea pig esophagus. J Neurosci 20:6249–6255
Zagorodnyuk VP, Chen BN, Brookes SJ (2001) Intraganglionic laminar endings are mechano-transduction sites of vagal tension receptors in the guinea-pig stomach. J Physiol 534:255–268
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Karin Löschner for expert technical assistance, Dr. Marion Raab and Dr. Falk Schrödl for help with the illustrations. This study was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft SFB353/B15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ZJ., Neuhuber, W.L. Intraganglionic laminar endings in the rat esophagus contain purinergic P2X2 and P2X3 receptor immunoreactivity. Anat Embryol 207, 363–371 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-003-0351-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-003-0351-4