Abstract
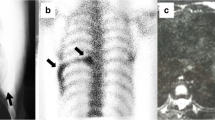
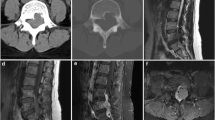
Although fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a benign fibro-osseous lesion, locally aggressive behaviour has rarely been described but is poorly characterised. In this study, we document clinical, radiological and pathological (including molecular genetics) findings in three cases of locally aggressive FD, two of which involved the ribs. Lesions in these cases, one of which was a recurrent lesion, were followed up for 2–7 years. All of the lesions showed typical histological features of FD but were characterised by extension through the bone cortex into the extra-osseous soft tissue. The lesions did not exhibit overexpression/amplification of CDK4 and MDM2; in two of the cases, a GNAS mutation was identified. Our findings confirm that FD can rarely exhibit locally aggressive behaviour with extension beyond the bone compartment into the surrounding soft tissue; these lesions can be distinguished from low-grade intramedullary osteosarcoma by lack of amplification/overexpression of CDK4 and MDM2 and the presence of a GNAS mutation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegal GP, Bianco P, Dal Cin P (2013) Fibrous dysplasia. In: Fletcher CD, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F (eds) Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bones. IARC, Lyon, pp 352–353
DiCaprio MR, Enneking WF (2005) Fibrous dysplasia. Pathophysiology, evaluation, and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 87:1848–1864
Weinstein LS, Shenker A, Gejman PV, Merino MJ, Friedman E, Spiegel AM (1991) Activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein in the McCune–Albright syndrome. N Engl J Med 325:1688–1695
Schwindinger WF, Francomano CA, Levine MA (1992) Identification of a mutation in the gene encoding a subunit of the stimulatory G protein of adenylyl cyclase in McCune–Albright syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5152–5156
Shenker A, Weinstein LS, Sweet DE, Spiegel AM (1994) An activating Gs alpha mutation is present in fibrous dysplasia of bone in the McCune–Albright syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 79:750–755
Henry A (1969) Monostotic fibrous dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 51:300–306
Schofield DF (1974) An aggressive fibrous dysplasia. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol 38:29–35
Gille P, Beugnet D, Carbillet JP, Giordan H (1987) Aggressive fibrous dysplasia of the mandible. Resection of the lower portion of the mandible. Chir Paediatr 28:262–265
Gambhir G, Batra R, Sethi N, Bansal A (2011) A rare case of fibrous dysplasia in an elderly patient, with brief review of literature of monostotic fibrous dysplasia of maxilla. Indian J Med Sciences 3:68–70
Gupta MK, Mhaske S (2011) Aggressive fibrous dysplasia of mandible—a case report. JIDA 5:503–505
Olasoji HO, Ugboko VI, Nggada HA (2006) Aggressive form of fibrous dysplasia of the mandible in childhood: case report. Otorhinolaryngology 1:89–92
Shapeero LG, Vanel D, Ackerman LV, Terrier-Lacombe MJ, Housin D, Schwaab G, Sigal R, Masselot J (1993) Aggressive fibrous dysplasia of the maxillary sinus. Skeletal Radiol 22:563–568
Vanel D, Couanet D, Micheau C, Piekarski JD, Schwaab G, Masselot J (1980) Pseudotumoural fibrous dysplasia of the maxilla: radiological studies and computed tomography contribution. Skeletal Radiol 5:99–103
Latham PD, Athanasou NA, Woods CG (1992) Fibrous dysplasia with locally aggressive malignant change. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 111:183–186
Yao L, Eckardt JJ, Seeger LL (1994) Fibrous dysplasia associated with cortical bony destruction: CT and MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomography 8:91–94
Yoshida A, Ushiku T, Motoi T, Shibata T, Beppu Y, Fukayama M, Tsuda H (2012) MDM2 and CDK4 immunohistochemical coexpression in high-grade osteosarcoma: correlation with a dedifferentiated subtype. Am J Surg Pathol 36:423–431
Wunder JS, Eppert K, Burrow SR, Gokgoz N, Bell RS, Andrulis IL (1999) Co-amplification and overexpression of CDK4, SAS and MDM2 occurs frequently in human parosteal osteosarcomas. Oncogene 21(18):783–788
Tarkkanen M, Bohling T, Gamberi G, Ragazzini P, Benassi MS, Kivioja A, Kailio P, Elomaa I, Picci P, Knuutila S (1998) Comparative genomic hybridization of low-grade central osteosarcoma. Mod Pathol 11:421–426
Idowu BD, Al-Adnani M, O’Donnell P, Yu L, Odell E, Diss T, Gale RE, Flanagan AM (2007) A sensitive mutation-specific screening technique for GNAS1 mutations in cases of fibrous dysplasia: the first report of a codon 227 mutation in bone. Histopathology 50:691–704
Kashima T, Halai D, Ye H, Hing SN, Delaney D, Pollock R, O’Donnell P, Tirabosco R, Flanagan AM (2012) Sensitivity of MDM2 amplification and unexpected multiple faint alphoid 12 (alpha 12 satellite sequences) signals in atypical lipomatous tumour. Mod Pathol 25:1384–1396
Dorfman HD, Ishida T, Tsuneyoshi M (1994) Exophytic variant of fibrous dysplasia (fibrous dysplasia protuberans). Hum Pathol 25:1234–1237
Franceschina MJ, Hankin RC, Irwin RB (1997) Low-grade central osteosarcoma resembling fibrous dysplasia. A report of two cases. Am J Orthop 26:432–440
Wenger DE, Sundaram M, Unni KK, Janney CG, Merkel K (2002) Microscopic correlation of radiographically disparate appearing well differentiated osteosarcoma. Skeletal Radiol 31:488–492
Pollard K, Engels C, Kaiser E, Werner M, Delling G (2001) Gsalpha gene mutations in monostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone and fibrous dysplasia-like low-grade central osteosarcoma. Virchows Arch 439:170–175
Ruggieri P, Sim FH, Bond JR, Unni KK (1994) Malignancies in fibrous dysplasia. Cancer 73:1411–1424
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Chris Lowe for typing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashima, T.G., Gamage, N.M., Ye, H. et al. Locally aggressive fibrous dysplasia. Virchows Arch 463, 79–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-013-1437-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-013-1437-x