Abstract
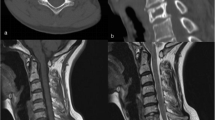
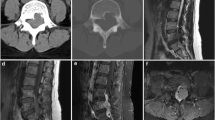
Fibrous dysplasia (FD) is a benign fibro-osseous disease of the bone that may be solitary or multicentric. It is important to distinguish this type of lesion from low-grade osteosarcomas (LGOS) and from secondary sarcomas, because malignant transformation has rarely been reported. It is classically described as having a ground-glass appearance, endosteal scalloping, and thinning of the cortex. Cortical disruption is considered evidence of malignancy, but it can also be present in benign FD with aggressive behavior. We present an unusual case of aggressive FD of the 7th left rib, already diagnosed more than 22 years ago, where cortical and costo-vertebral joint disruption and 7th thoracic vertebral body involvement were not evidence of malignant behavior. From a histological perspective, FD and LGOS are similar; even if histology is of fundamental importance, the diagnosis has to be made based on the clinical and radiological aspects as well, although at imaging, differentiation between FD and LGOS can be difficult. In the present case, even though the histological examination suggested a benign lesion, the radiological examination instead consistently suggests malignancy. It is for this reason that there should be a high index of suspicion during follow-up and a new biopsy should be scheduled in case any changes occur during follow-up.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campanacci M. Bone and soft tissue tumors: clinical features, imaging, pathology and treatment. 2nd ed. Austria: Vienna; 1999.
Zoccali C, Teori G, Prencipe U, Erba F. Mazabraud’s syndrome: a new case and review of the literature. Int Orthop. 2009;33(3):605–10.
Steiner GC, Forest M, Vacher-Lavenu MC. Ultrastructure of low-grade intraosseous osteosarcoma of bone: a comparative study with fibrous dysplasia and parosteal osteosarcoma. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2006;30(4):293–9.
Bertoni F, Bacchini P, Fabbri N, Mercuri M, Picci P, Ruggieri P, et al. Osteosarcoma. Low-grade intraosseous-type osteosarcoma, histologically resembling parosteal osteosarcoma, fibrous dysplasia, and desmoplastic fibroma. Cancer. 1993;71(2):338–45.
Dujardin F, Binh MB, Bouvier C, Gomez-Brouchet A, Larousserie F, Muret A, et al. MDM2 and CDK4 immunohistochemistry is a valuable tool in the differential diagnosis of low-grade osteosarcomas and other primary fibro-osseous lesions of the bone. Mod Pathol. 2011;24(5):624–37.
Chen CY, Zhang HZ, Jiang ZM, Zhou J, Chen J, Liu L. Value of MDM2, CDK4 and SATB2 immunohistochemistry in histologic diagnosis of low-grade osteosarcoma. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2016;45(6):387–92.
Carter JM, Inwards CY, Jin L, Evers B, Wenger DE, Oliveira AM, Fritchie KJ. Activating GNAS mutations in parosteal osteosarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014 Mar;38(3):402-9
Kuznetsov SA, Cherman N, Riminucci M, et al. Age-dependent demise of GNAS-mutated skeletal stem cells and “normalization” of fibrous dysplasia of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23:1731–40.
Salinas-Souza C, De Andrea C, Bihl M, Kovac M, Pillay N, Forshew T, et al. GNAS mutations are not detected in parosteal and low-grade central osteosarcomas. Mod Pathol. 2015 Oct;28(10):1336–42.
Franceschina MJ, Hankin RC, Irwin RB. Low-grade central osteosarcoma resembling fibrous dysplasia. A report of two cases. Am J Orthop. 1997;26(6):432–40.
Shah ZK, Peh WC, Koh WL, Shek TW. Magnetic resonance imaging appearances of fibrous dysplasia. Br J Radiol. 2005;78:1104–15.
Fitzpatrick KA, Taljanovic MS, Speer DP, Graham AR, Jacobson JA, Barnes GR, et al. Imaging findings of fibrous dysplasia with histopathologic and intraoperative correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;82(6):1389–98.
Latham PD, Athanasou NA, Woods CG. Fibrous dysplasia with locally aggressive malignant change. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1992;111(3):183–6.
Yao L, Eckardt JJ, Seeger LL. Fibrous dysplasia associated with cortical bony destruction: CT and MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1994;18:91–4.
Dorfman HD, Ishida T, Tsuneyoshi M. Exophytic variant of fibrous dysplasia (fibrous dysplasia protuberans). Hum Pathol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1234–7.
Hermann G, Garcia R. Exophytic fibrous dysplasia of the rib. Osteologiai Kozlemenyek. 2013;1-2:9–12.
Muthusamy S, Subhawong T, Conway SA, Temple HT. Locally aggressive fibrous dysplasia mimicking malignancy: a report of four cases and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(2):742–50.
Kashima TG, Gamage NM, Ye H, Amary MF, Flanagan AM, Ostlere SJ, et al. Locally aggressive fibrous dysplasia. Virchows Arch. 2013;463:79–84.
Vasiliadis HS, Arnaoutoglou C, Plakoutsis S, Doukas M, Batistatou A, Xenakis TA. Low-grade central osteosarcoma of distal femur, resembling fibrous dysplasia. World J Orthop. 2013;4(4):327–32.
Malhas AM, Sumathi VP, James SL, Menna C, Carter SR, Tillman RM, et al. Low-grade central osteosarcoma: a difficult condition to diagnose. Sarcoma. 2013;2012:764796.
Qu N, Yao W, Cui X, Zhang H. Malignant transformation in monostotic fibrous dysplasia: clinical features, imaging features, outcomes in 10 patients, and review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(3):e369.
Zídková H, Kolár J, Matĕjovsky Z. Aggressive features of pelvic fibrous dysplasia. Rofo. 1994;161(2):183–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zoccali, C., Attala, D., Rossi, B. et al. Fibrous dysplasia: an unusual case of a very aggressive form with costo-vertebral joint destruction and invasion of the contralateral D7 vertebral body. Skeletal Radiol 47, 1571–1576 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-2961-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-2961-1