Abstract
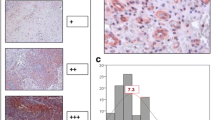
Endoglin (CD105) is a proliferation-associated protein abundantly expressed in angiogenic endothelial cells. Recent studies revealed that CD105 is intensively expressed in tumor vasculature, whereas intratumoral microvessel density (MVD) determined with the use of antibodies to CD105 has been found to be an important prognostic indicator for the outcome in a number of malignancies. In the current study, we investigated endoglin expression and evaluated MVD in 108 patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Endoglin was intensively expressed in intratumoral blood vessels, whilst lymphatics were rarely positive for CD105. High microvessel density was associated with a more aggressive tumor phenotype, including advanced clinical stage (p=0.008) and the presence of lymph node metastasis at the time of diagnosis (p=0.02). When microvessel counts were assessed for their prognostic values (high vs low MVD), there was a statistically significant difference in the overall survival among patients with tumors of the oral cavity and larynx (p<0.001) and in the disease-free survival among patients with tumors of the lower lip (p=0.01). The prognostic impact of microvessel density was not dependent on clinical stage or lymph node status. The results of the current study suggest that CD105 is a promising target for tumor imaging and prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebersold DM, Beer KT, Laissue J, Hug S, Kollar A, Greiner RH, Djonov V (2000) Intratumoral microvessel density predicts local treatment failure of radically irradiated squamous cell cancer of the oropharynx. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48:17–25
Altman DG, Lausen B, Sauerbrei W, Schumacher M (1994) Dangers of using “optimal” cutpoints in the evaluation of prognostic factors. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:829–835
Brattstrom D, Bergqvist M, Wester K, Hesselius P, Ren ZP, Scheibenpflug L, Wagenius G, Brodin O (2004) Endothelial markers and circulating angiogenic factors and p53 may be potential markers for recurrence in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer patients. Med Sci Monit 10:331–338
Brewer CA, Setterdahl JJ, Li MJ, Johnston JM, Mann JL, McAsey ME (2000) Endoglin expression as a measure of microvessel density in cervical cancer. Obstet Gynecol 96:224–228
Chien CY, Su CY, Hwang CF, Chuang HC, Hsiao YC, Wu SL, Huang CC (2005) Clinicopathologic significance of CD105 expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the hypopharynx. Head Neck 2005 (In press)
Costello B, Li C, Duff S, Butterworth D, Khan A, Perkins M, Owens S, Al-Mowallad AF, O’Dwyer S, Kumar S (2004) Perfusion of 99Tcm-labeled CD105 Mab into kidneys from patients with renal carcinoma suggests that CD105 is a promising vascular target. Int J Cancer 109:436–441
Dales JP, Garcia S, Carpentier S, Andrac L, Ramuz O, Lavaut MN, Allasia C, Bonnier P, Charpin C (2004) Long-term prognostic significance of neoangiogenesis in breast carcinomas: comparison of Tie-2/Tek, CD105, and CD31 immunocytochemical expression. Hum Pathol 35:176–183
Duff SE, Li C, Garland JM, Kumar S (2003) CD105 is important for angiogenesis: evidence and potential applications. FASEB J 17:984–992
Ellis LM, Liu W, Fan F, Reinmuth N, Shaheen RM, Jung YD, Ahmad S (2001) Role of angiogenesis inhibitors in cancer treatment. Oncology (Huntingt) 15:39–46
Evangelou E, Kyzas PA, Trikalinos TA (2005) Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of lymphatic endothelium markers: Bayesian approach. Mod Pathol 18:1490–1497
Folkman J (1990) What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82:4–6
Fonsatti E, Del Vecchio L, Altomonte M, Sigalotti L, Nicotra MR, Coral S, Natali PG, Maio M (2001) Endoglin: an accessory component of the TGF-beta-binding receptor-complex with diagnostic, prognostic, and bioimmunotherapeutic potential in human malignancies. J Cell Physiol 1888:1–7
Fonsatti E, Altomonte M, Nicotra MR, Natali PG, Maio M (2003) Endoglin (CD105): a powerful therapeutic target on tumor-associated angiogenetic blood vessels. Oncogene 22:6557–6563
Fonsatti E, Maio M (2004) Highlights on endoglin (CD105): from basic findings towards clinical applications in human cancer. J Transl Med 2:18–25
Gallo O, Masini E, Bianchi B, Bruschini L, Paglierani M, Franchi A (2002) Prognostic significance of cyclooxygenase-2 pathway and angiogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Hum Pathol 33:708–714
Hirakawa S, Hong YK, Harvey N, Schacht V, Matsuda K, Libermann T, Detmar M (2003) Identification of vascular lineage-specific genes by transcriptional profiling of isolated blood vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 162:575–586
Hong WK, Lippman SM, Itri LM, Karp DD, Lee JS, Byers RM, Schantz SP, Kramer AM, Lotan R, Peters LJ (1990) Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 323:795–801
Kumar S, Ghellal A, Li C, Byrne G, Haboubi N, Wang JM, Bundred N (1999) Breast carcinoma: vascular density determined using CD105 antibody correlates with tumor prognosis. Cancer Res 59:856–861
Kyzas PA, Stefanou D, Agnantis NJ (2004) Immunohistochemical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor correlates with positive surgical margins and recurrence in T1 and T2 squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lower lip. Oral Oncol 40:941–947
Kyzas PA, Geleff S, Batistatou A, Agnantis NJ, Stefanou D (2005) Evidence for lymphangiogenesis and its prognostic implications in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol 206:170–177
Kyzas PA, Loizou KT, Ioannidis JP (2005) Selective reporting biases in cancer prognostic factor studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1043–1055
Kyzas PA, Stefanou D, Agnantis NJ (2005) COX-2 expression correlates with VEGF-C and lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol 18:153–160
Kyzas PA, Stefanou D, Batistatou A, Agnantis NJ (2005) Prognostic significance of VEGF immunohistochemical expression and tumor angiogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131:624–630
Kyzas PA, Cunha IW, Ioannidis JP (2005) Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor immunohistochemical expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res 11:1434–1440
Kyzas PA, Stefanou D, Batistatou A, Agnantis NJ (2005) Hypoxia-induced tumor angiogenic pathway in head and neck cancer: an in vivo study. Cancer Lett 225:297–304
Li C, Gardy R, Seon BK, Duff SE, Abdalla S, Renehan A, O’Dwyer ST, Haboubi N, Kumar S (2003) Both high intratumoral microvessel density determined using CD105 antibody and elevated plasma levels of CD105 in colorectal cancer patients correlate with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer 88:1424–1431
Marioni G, Gaio E, Giacomelli L, Marchese-Ragona R, Staffieri C, Staffieri A, Marino F (2005) Endoglin (CD105) expression in head and neck basaloid squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Otolaryngol 125:307–311
Martone T, Rosso P, Albera R, Migliaretti G, Fraire F, Pignataro L, Pruneri G, Bellone G, Cortesina G (2005) Prognostic relevance of CD105+ microvessel density in HNSCC patient outcome. Oral Oncol 41:147–155
Massi D, Franchi A, Paglierani M, Ketabchi S, Borgognoni L, Reali UM, Santucci M (2004) Vasculogenic mimicry has no prognostic significance in pT3 and pT4 cutaneous melanoma. Hum Pathol 35:496–502
Mineo TC, Ambrogi V, Baldi A, Rabitti C, Bollero P, Vincenzi B, Tonini G (2004) Prognostic impact of VEGF, CD31, CD34, and CD105 expression and tumour vessel invasion after radical surgery for IB-IIA non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Pathol 57:5917
Nagatsuka H, Hibi K, Gunduz M, Tsujigiwa H, Tamamura R, Sugahara T, Sasaki A, Nagai N (2005) Various immunostaining patterns of CD31, CD34 and endoglin and their relationship with lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med 34:70–76
Pazouki S, Chisholm DM, Adi MM, Carmichael G, Farquharson M, Ogden GR, Schor SL, Schor AM (1997) The association between tumour progression and vascularity in the oral mucosa. J Pathol 183:39–43
Pfister DG, Ang K, Brockstein B, Colevas AD, Ellenhorn J, Goepfert H, Hicks WL Jr, Hong WK, Kies MS, Lydiatt W, McCaffrey T, Mittal BB, Ridge JA, Schuller DE, Shah JP, Spencer S, Trotti A 3rd, Urba S, Weymuller EA Jr, Wheeler RH 3rd, Wolf GT; National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2000) NCCN practice guidelines for head and neck cancers. Oncology (Huntingt) 14:163–194
Reinmuth N, Parikh AA, Ahmad SA, Liu W, Stoeltzing O, Fan F, Takeda A, Akagi M, Ellis LM (2003) Biology of angiogenesis in tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Microsc Res Tech 60:199–207
Saad RS, Jasnosz KM, Tung MY, Silverman JF (2003) Endoglin (CD105) expression in endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Pathol 22:248–253
Saad RS, Liu YL, Nathan G, Celebrezze J, Medich D, Silverman JF (2004) Endoglin (CD105) and vascular endothelial growth factor as prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Mod Pathol 17:197–203
Salven P, Heikkila P, Anttonen A, Kajanti M, Joesuu H (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor in squamous cell head and neck carcinoma: expression and prognostic significance. Mod Pathol 10:1128–1133
Salvesen HB, Gulluoglu MG, Stefansson I, Akslen LA (2003) Significance of CD 105 expression for tumour angiogenesis and prognosis in endometrial carcinomas. APMIS 111:1011–1018
Schimming R, Marme D (2002) Endoglin (CD105) expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Head Neck 24:151–156
Tanaka F, Otake Y, Yanagihara K, Kawano Y, Miyahara R, Li M, Yamada T, Hanaoka N, Inui K, Wada H (2001) Evaluation of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: comparison between anti-CD34 antibody and anti-CD105 antibody. Clin Cancer Res 7:3410–3415
Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB, Colpaert C, Marson LP, Gion M, Belien JA, de Waal RM, Van Marck E, Magnani E, Weidner N, Harris AL, Dirix LY (2002) Second international consensus on the methodology and criteria of evaluation of angiogenesis quantification in solid human tumours. Eur J Cancer 38:1564–1579
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J (1991) Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis–correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324:1–8
Wang JM, Kumar S, Pye D, Haboubi N, al-Nakib L (1994) Breast carcinoma: comparative study of tumor vasculature using two endothelial cell markers. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:386–388
Yagasaki H, Kawata N, Takimoto Y, Nemoto N (2003) Histopathological analysis of angiogenic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol 10:220–227
Yu JX, Zhang XT, Liao YQ, Zhang QY, Chen H, Lin M, Kumar S (2003) Relationship between expression of CD105 and growth factors in malignant tumors of gastrointestinal tract and its significance. World J Gastroenterol 9:2866–2869
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyzas, P.A., Agnantis, N.J. & Stefanou, D. Endoglin (CD105) as a prognostic factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch 448, 768–775 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-006-0195-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-006-0195-4