Abstract
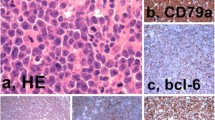
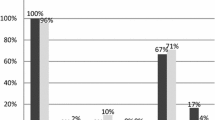
To analyze the clinicopathologic characteristics of childhood non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), EBER in situ hybridization was performed in 80 cases of NHLs. EBER-positive lymphomas account for 25% (20/80) and include NK/T-cell lymphoma (6/6), aggressive NK-cell leukemia (1/1), peripheral T cell lymphoma (5/11), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (5/14), hydroa-like T-cell lymphoma (1/1), marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (1/2), and post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder (1/1). Other types including 19 cases of Burkitt’s lymphoma were negative. For 9 EBER-positive cases, immunohistochemical staining for LMP-1, and EBNA-2 was performed to determine the EBV latency pattern. Two of nine EBER-positive cases expressed both LMP-1 and EBNA-2. Clinically, patients with EBV-positive B-cell lymphomas were cured with chemotherapy, whereas EBV-associated NK- and T cell lymphomas pursued fatal clinical course. In conclusion, EBVs infected in childhood NHLs are frequently associated not only with NK- and T- cell lymphomas but also large B-cell lymphomas.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JR, Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD(1998) Epidemiology of the non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: distributions of the major subtypes differ by geographic locations. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma classification project. Ann Oncol 9:717–720
Chabay PA, De Matteo EN, Aversa L, Maglio S, Grinstein S, Preciado MV (2002) Assessment of Epstein-Barr virus association with pediatric non-Hodgkin lymphoma in immunocompetent and in immunocompromised patients in Argentina. Arch Pathol Lab Med 126:331–335
Chao TY, Wang TY, Lee WH (1997) Association between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt’s lymphoma in Taiwan. Cancer 80:121–128
Kieff E, Rickinson AB (2001) Epstein-Barr virus and its replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE (ed) Fundamental virology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1185–1190
Stein H, Mann R, Delsol G, Poppema S, Pileri S, Jaffe ES, Said J, Swerdlow SH (2001) Classical Hodgkin lymphoma. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (ed) World Health Organization classification of tumours. Tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. IARC Press, Lyon, p 248
Joske D, Knecht H (1993) Epstein-Barr virus in lymphomas: a review. Blood Rev 7:215–222
Karajannis MA, Hummel M, Oschlies I, Anagnostopoulos I, Zimmermann M, Stein H, Parwaresch R, Reiter A (2003) Epstein-Barr virus infection in Western European pediatric non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 102:4244
Kuze T, Nakamura N, Hashimoto Y, Sasaki Y, Abe M (2000) The characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: comparison between EBV(+) and EBV(−) cases in Japanese population. Jpn J Cancer Res 91:1233–1240
Mansoor A, Stevenson MS, Li RZ, Frekko K, Weiss W, Ahmad M, Khan AH, Mushtaq S, Saleem M, Raffeld M, Kingma DW, Jaffe ES (1997) Prevalence of Epstein-Barr viral sequences and EBV LMP1 oncogene deletions in Burkitt’s lymphoma from Pakistan: epidemiological correlations. Hum Pathol 28:283–288
Okano M, Gross TG (2001) From Burkitt’s lymphoma to chronic active Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection: an expanding spectrum of EBV-associated diseases. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 18:427–442
Pallesen G, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Zhou X (1993) The association of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) with T cell lymphoproliferations and Hodgkin’s disease: two new developments in the EBV field. Adv Cancer Res 62:179–239
Peh SC, Nadarajah VS, Tai YC, Kim LH, Abdullah WA (2004) Pattern of Epstein-Barr virus association in childhood non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: experience of university of Malaya medical center. Pathol Int 54:151–157
Peylan-Ramu N, Diment J, Krichevsky S, Ben-Yehuda D, Bhatia K, Magrath IT (2001) Expression of EBV encoded nuclear small non-polyadenylated RNA (EBER) molecules in 32 cases of childhood Burkitt’s lymphoma from Israel. Leuk Lymphoma 40:405–411
Wilson JF, Jenkin RD, Anderson JR, Chilcote RR, Coccia P, Exelby PR, Kersey J, Kjeldsberg CR, Kushner J, Meadows A (1984) Studies on the pathology of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of childhood, I. The role of routine histopathology as a prognostic factor. A report from the children’s cancer study group. Cancer 53:1695–1704
Zhou XG, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Yan QG, Pallesen G (1994) High frequency of Epstein-Barr virus in Chinese peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Histopathology 24:115–122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Ko, Y., Suh, Y. et al. Characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus associated childhood non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in the Republic of Korea. Virchows Arch 447, 593–596 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-1277-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-1277-4