Abstract
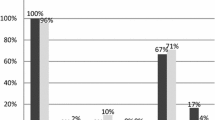
Epstein Barr virus (EBV) associated Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) has been defined as cases with clonal EBV infection, EBV genome and gene products in the Reed Sternberg cells. We evaluated the prevalence and clinico-pathological association of EBV in North Indian HL patients. Eighty-eight cases of histologically confirmed classic HL were evaluated for EBV by both IHC expression of LMP1 and real time PCR on formalin fixed lymph node tissue. The expression pattern was analyzed for any association with clinical and histomorphological parameters. Nodular sclerosis subtype was seen in 79.5% patients and mixed cellularity was seen in the remaining patients. Ninety percent of the cases were positive for EBV. The detection rate of EBV by IHC was higher. The EBV positive cases presented with higher disease stage (p < 0.05). The presence of histomorphological features like granuloma formation (5/5), atypical lymphocytes (8/8), histiocyte clusters (26/28), large area of necrosis (11/12), less prominent inflammatory response (25/27) was associated with EBV positivity (p > 0.05). In our study population a high proportion of HL cases showed positivity for EBV indicating a pathogenic role. The positivity was independent of age, gender and histological subtype. Further evaluation of EBV positivity in modulation of tumor immunity may provide insights into variable treatment outcome in EBV positive cases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gandhi MK, Lambley E, Burrows J, Dua U, EllioT S, Shaw PJ, Prince HM, Wolf M, Clarke K, Underhill C, Mills T, Mollee P, Gill D, Marlon P, Seymour JF, Khanna R (2006) Plasma Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) DNA is a biomarker for EBV-positive Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 12:460–464
Jarrett RF (2003) Risk factors for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma by EBV status and significance of detection of EBV genomes in serum of patients with EBV- associated Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 44(Suppl 3):S27–S32
Flavell KJ, Murray PG (2000) Hodgkin’s disease and the Epstein–Barr virus. Mol Pathol 53(5):262–269
Dinanad V, Dawar R, Arya S, Unni R, Mohanty B, Singh R (2007) Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Indian children: prevalence and significance of Epstein–Barr virus detection in Hodgkin’s and Reed-Sternberg cells. Eur J Cancer 43(1):161–168
Qi ZL, Han XQ, Hu J, Wang GH, Gao JW, Wang X, Liang DY (2013) Comparison of three methods for the detection of Epstein-Barr virus in Hodgkin’s lymphoma in paraffin-embedded tissues. Mol Med Rep 7:89–92
Eichenauer DA, Engert A, André M, Federico M, Illidge T, Hutchings M, Ladetto M (2014) Hodgkin’s lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu181
Wasielewski SV, Franklin J, Fischer R, Hubner K, Hansmann ML, Diehl V, Georgii A, Wasielewski RV (2002) Nodular sclerosing Hodgkin’s disease: new grading predicts prognosis in intermediate and advanced stages. Blood 05:1548
Rhodes A (2013) Fixation of tissues. Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques, 7th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 69–94
Herling M, Rassidakis GZ, Medeiros LJ, Vassilakopoulos TP, Kliche KO, Nadali G, Viviani S, Bonfante V, Giardini R, Chilosi M, Kittas C (2003) Expression of Epstein–Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in Hodgkin and Reed–Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: associations with presenting features, serum interleukin 10 levels, and clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res 9(6):2114–2120
Niesters HG, van Esser J, Fries E, Wolthers KC, Cornelissen J, Osterhaus AD (2000) Development of a real-time quantitative assay for detection of Epstein–Barr virus. J Clin Microbiol 38:712–715
Prakash S, Jain A, Jain B (2016) Development of novel triplex single-step real-time PCR assay for detection of Hepatitis Virus B and C simultaneously. Virology 31(492):101–107
Dinand V, Sachdeva A, Datta S, Bhalla S, Kalara M, Wattal C, Radhakrishnan N (2015) Plasma Epstein–Barr Virus(EBV) DNA as a biomarker for EBV-associated Hodgkin Lymphoma. Indian Paediatr 52:681–685
Naresh KN, Johnson J, Srinivas V, Soman CS, Saikia T, Advani SH, Badwe RA, Dinshaw KA, Muckaden M, Magrath I, Bhatia K (2001) Epstein-Barr virus association in classical Hodgkin’s disease provides survival advantage to patients and correlates with higher expression of proliferation markers in Reed-Sternberg cells. Ann Oncol 11(1):91–96
Karnik S, Srinivasan B, Nair S (2003) Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: immunohistochemical features and its association with EBV LMP-1. Experience from a South Indian hospital. Pathology 35:207–211
Gandhi MK, Tellam JT, Khanna R (2004) Epstein–Barr virus-associated Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Br J Haematol 125(3):267–281
Lingyun G, Xin W (2015) Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders: experimental and clinical developments. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(9):14656–14671
Skinnider BF, Mak TW (2002) The role of cytokines in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 99(12):4283–4297
Ramos-Vara JA (2011) Principles and methods of immunohistochemistry. Methods Mol Biol 691:83–96
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Mr. Shantanu Prakash for technical help in molecular detection of EBV in the formalin fixed tissue blocks from HL cases.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Approved by the institutional ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rani, P., Jain, M., Verma, N. et al. Epstein–Barr Virus Expression in Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma in an Indian Cohort and its Association with Clinical and Histomorphological Parameters. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 37, 372–378 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-020-01359-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-020-01359-9